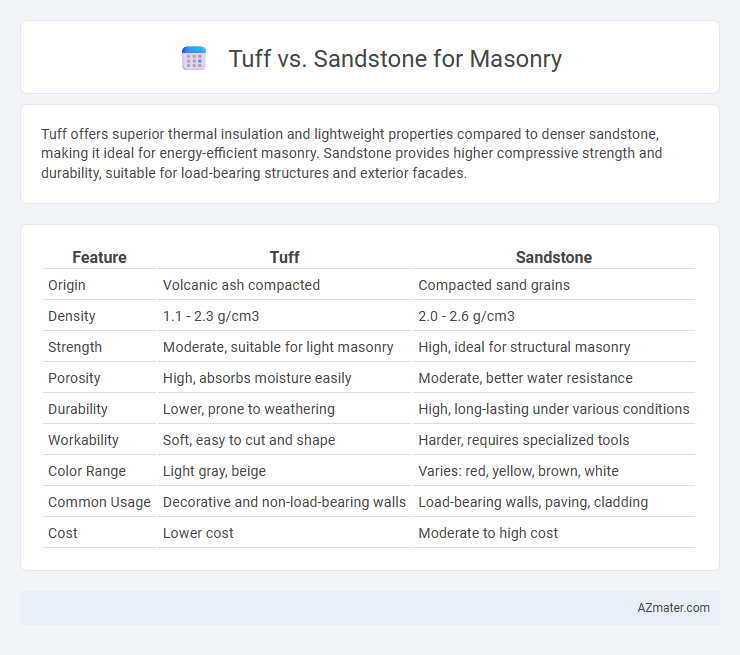
Tuff offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties compared to denser sandstone, making it ideal for energy-efficient masonry. Sandstone provides higher compressive strength and durability, suitable for load-bearing structures and exterior facades.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tuff | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Volcanic ash compacted | Compacted sand grains |
| Density | 1.1 - 2.3 g/cm3 | 2.0 - 2.6 g/cm3 |
| Strength | Moderate, suitable for light masonry | High, ideal for structural masonry |
| Porosity | High, absorbs moisture easily | Moderate, better water resistance |
| Durability | Lower, prone to weathering | High, long-lasting under various conditions |
| Workability | Soft, easy to cut and shape | Harder, requires specialized tools |
| Color Range | Light gray, beige | Varies: red, yellow, brown, white |
| Common Usage | Decorative and non-load-bearing walls | Load-bearing walls, paving, cladding |
| Cost | Lower cost | Moderate to high cost |
Understanding Tuff and Sandstone: Geological Overview
Tuff is a volcanic rock formed from compacted volcanic ash, characterized by its relatively soft texture and excellent workability in masonry. Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of sand-sized mineral particles, known for its durability and natural grainy texture that enhances structural strength. Understanding their geological origins helps builders select appropriate materials based on factors like porosity, compressive strength, and weather resistance.
Key Physical Properties: Tuff vs Sandstone
Tuff exhibits low density and high porosity, resulting in excellent thermal insulation but reduced compressive strength compared to sandstone, which is denser and more durable with higher load-bearing capacity. Sandstone's fine to medium grain structure provides better abrasion resistance and weathering durability, making it ideal for high-traffic masonry applications. Moisture absorption rates are significantly higher in tuff, which can affect its long-term structural integrity, whereas sandstone offers moderate water resistance, enhancing its suitability for exterior masonry.
Durability and Weather Resistance Comparison
Tuff offers moderate durability with good resistance to weathering due to its volcanic ash composition, making it suitable for regions with mild climates. Sandstone demonstrates higher durability and superior weather resistance, especially in harsh environments, as its dense grain structure resists erosion and moisture penetration effectively. The choice between tuff and sandstone depends on the specific environmental conditions and long-term structural requirements of the masonry project.
Workability and Construction Ease
Tuff offers superior workability compared to sandstone due to its softer texture, allowing easier cutting and shaping during masonry. This characteristic reduces labor time and minimizes tool wear, enhancing construction efficiency on-site. Sandstone's hardness, while durable, requires more effort and precision, often increasing construction complexity and costs.
Aesthetic Differences in Masonry Applications
Tuff offers a porous texture and earthy tones ranging from pale yellow to brown, creating a rustic and natural appearance in masonry applications. Sandstone features a finer grain with uniform color variations such as red, pink, and cream, lending a more polished and elegant finish. The choice between tuff and sandstone significantly influences the visual character and tactile experience of built surfaces in architectural projects.
Cost Factors: Tuff vs Sandstone
Tuff offers a cost-effective option for masonry due to its abundance and ease of extraction, leading to lower material and transportation expenses compared to sandstone. Sandstone typically commands higher prices because of its greater density, durability, and more intensive quarrying processes, which increase labor and equipment costs. When considering long-term economic impact, tuff's lower initial cost may be offset by sandstone's superior longevity and reduced maintenance requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tuff, a volcanic rock, offers a lower environmental impact due to its natural abundance and minimal processing requirements compared to sandstone, which often requires extensive quarrying and energy-intensive cutting. Tuff's porous structure provides natural insulation, reducing energy consumption in buildings and enhancing sustainability. Sandstone, while durable, typically causes more habitat disruption and carbon emissions during extraction, making tuff a more eco-friendly choice for masonry projects focused on sustainability.
Historical and Regional Usage Patterns
Tuff, a volcanic rock widely used in Mediterranean and Central Italian masonry, exhibits ease of carving and weather resistance favored since Roman times, particularly visible in structures like the Roman Colosseum. Sandstone, abundant in regions such as the UK and India, has been a preferred material for centuries due to its durability and availability, prominently featured in medieval castles and temples. Regional geology heavily influenced masonry choices, with tuff predominating in volcanic landscapes and sandstone in sedimentary basins, shaping architectural heritage accordingly.
Maintenance and Longevity in Masonry Structures
Tuff offers moderate maintenance requirements due to its porous nature, which can absorb moisture and require sealing to prevent deterioration, while sandstone generally demands more frequent upkeep to address weathering and erosion concerns. Longevity in masonry structures is influenced by tuff's lightweight composition, making it less prone to cracking under stress, whereas sandstone's higher density contributes to greater durability but can suffer from surface flaking over time. Proper maintenance protocols, such as regular inspections and protective treatments, are critical for maximizing the lifespan of both tuff and sandstone masonry installations.
Choosing the Right Stone: Factors to Consider
When choosing between tuff and sandstone for masonry, factors such as durability, porosity, and aesthetic appeal play crucial roles. Tuff, a volcanic rock, offers excellent insulation properties and weather resistance, making it suitable for exterior walls in harsh climates. Sandstone provides a softer texture and warmth in color variations but requires more maintenance due to its higher porosity and susceptibility to erosion.
Infographic: Tuff vs Sandstone for Masonry
 azmater.com
azmater.com