Porphyry offers superior durability and high resistance to wear and weathering, making it ideal for high-traffic roadstone applications. Basalt provides excellent strength and toughness but is generally more prone to surface abrasion compared to Porphyry.
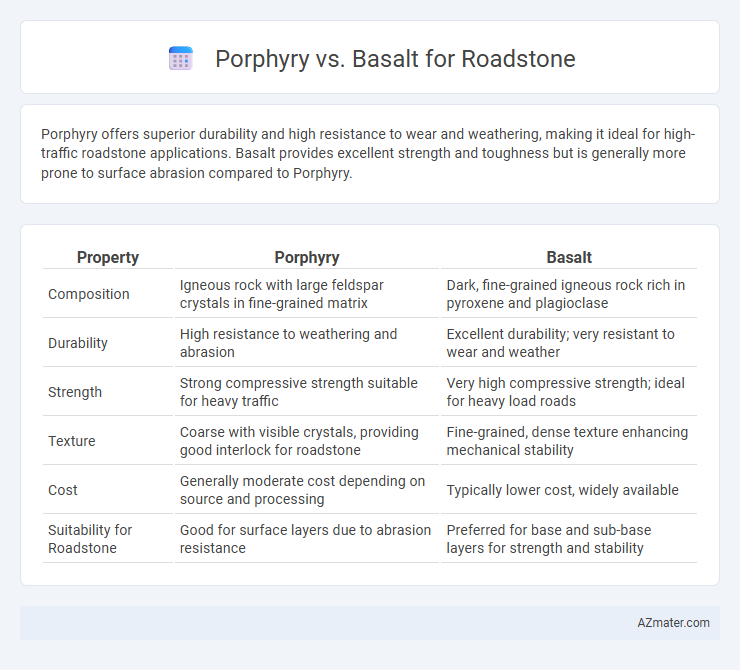
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porphyry | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Igneous rock with large feldspar crystals in fine-grained matrix | Dark, fine-grained igneous rock rich in pyroxene and plagioclase |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering and abrasion | Excellent durability; very resistant to wear and weather |
| Strength | Strong compressive strength suitable for heavy traffic | Very high compressive strength; ideal for heavy load roads |
| Texture | Coarse with visible crystals, providing good interlock for roadstone | Fine-grained, dense texture enhancing mechanical stability |
| Cost | Generally moderate cost depending on source and processing | Typically lower cost, widely available |
| Suitability for Roadstone | Good for surface layers due to abrasion resistance | Preferred for base and sub-base layers for strength and stability |
Introduction to Roadstone Materials
Porphyry and basalt are widely used roadstone materials distinguished by their durability and load-bearing capacity critical for pavement construction. Porphyry, an igneous rock with large crystal grains, offers excellent abrasion resistance and strength, making it suitable for high-traffic roads. Basalt, known for its fine-grained texture and high compressive strength, provides superior skid resistance and stability under heavy loads, enhancing road longevity.
What is Porphyry?
Porphyry is an igneous rock characterized by large-grained crystals such as feldspar or quartz embedded in a fine-grained matrix, making it highly durable and suitable for roadstone applications. Its hardness and resistance to abrasion ensure long-lasting road surfaces, outperforming softer materials like basalt in wear resistance. Porphyry's unique texture also provides excellent skid resistance, enhancing road safety in various climates.
What is Basalt?
Basalt is a dense, fine-grained volcanic igneous rock primarily composed of plagioclase and pyroxene minerals, known for its high compressive strength and durability. It is widely used as roadstone due to its excellent abrasion resistance, weathering durability, and ability to provide stable, long-lasting pavement surfaces. In comparison to Porphyry, Basalt offers superior resistance to wear and fracture, making it a preferred choice for heavy traffic road construction.
Geological Formation Differences
Porphyry is an igneous rock characterized by large, well-formed crystals embedded in a fine-grained matrix, formed from slow cooling magma deep within the Earth's crust. Basalt, by contrast, is a fine-grained volcanic rock created from rapid cooling of lava at or near the Earth's surface, resulting in a dense, homogeneous texture. These geological formation differences influence their durability and texture, making porphyry more variable in hardness and basalt consistently more dense for roadstone applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Porphyry exhibits higher compressive strength and superior abrasion resistance compared to basalt, making it more suitable for heavy traffic roadstone applications. Basalt features greater density and lower water absorption, enhancing its durability in freeze-thaw conditions and reducing weathering effects. Both stones possess excellent load-bearing capacity, but porphyry's mineral composition offers better resistance to deformation and surface wear under continuous vehicular stress.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Porphyry exhibits exceptional durability and superior weather resistance compared to basalt, making it ideal for roadstone in harsh climates. Its coarse-grained texture and mineral composition provide high abrasion resistance and better performance under freeze-thaw cycles. Basalt, while strong, tends to weather faster due to its finer grain and susceptibility to chemical breakdown, reducing its lifespan in road construction.
Performance in Road Construction
Porphyry offers high durability and excellent resistance to wear, making it ideal for heavy-traffic road surfaces, while basalt provides superior strength and excellent skid resistance essential for road safety. The dense, interlocking crystal structure of porphyry enhances load-bearing capacity, whereas basalt's fine-grained texture contributes to better compaction and reduced deformation under stress. Both aggregates deliver optimal performance, but basalt is often preferred in regions requiring enhanced skid resistance and porphyry in areas demanding extreme durability.
Cost and Availability Factors
Porphyry offers higher durability and strength compared to basalt, but it usually comes with a higher cost due to limited availability and more complex quarrying processes. Basalt is widely available and generally more affordable, making it a preferred choice for large-scale roadstone projects where budget constraints are significant. Cost efficiency of basalt combined with its abundance ensures faster project completion and reduced transportation expenses.
Environmental Impact Analysis
Porphyry roadstone offers lower carbon emissions during extraction and processing compared to basalt, largely due to its lower density and less intensive crushing requirements. Basalt, while durable, often requires more energy-intensive quarrying and processing, contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions and greater habitat disruption. Lifecycle assessments indicate porphyry's reduced environmental footprint makes it a preferable choice for sustainable infrastructure projects prioritizing ecological preservation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Roadstone
Porphyry offers superior durability and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for heavy traffic and long-lasting road surfaces, while basalt provides excellent compressive strength and cost-effectiveness suited for moderate traffic conditions. Evaluating project requirements such as load intensity, budget constraints, and longevity expectations will guide the optimal choice between porphyry and basalt roadstone. Selecting the right material ensures enhanced road performance, reduced maintenance costs, and sustainable infrastructure development.
Infographic: Porphyry vs Basalt for Roadstone
 azmater.com
azmater.com