Tuff offers lightweight, easy-to-cut properties with good insulation, while limestone provides superior durability and weather resistance for building stone applications. Choosing between tuff and limestone depends on structural requirements and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
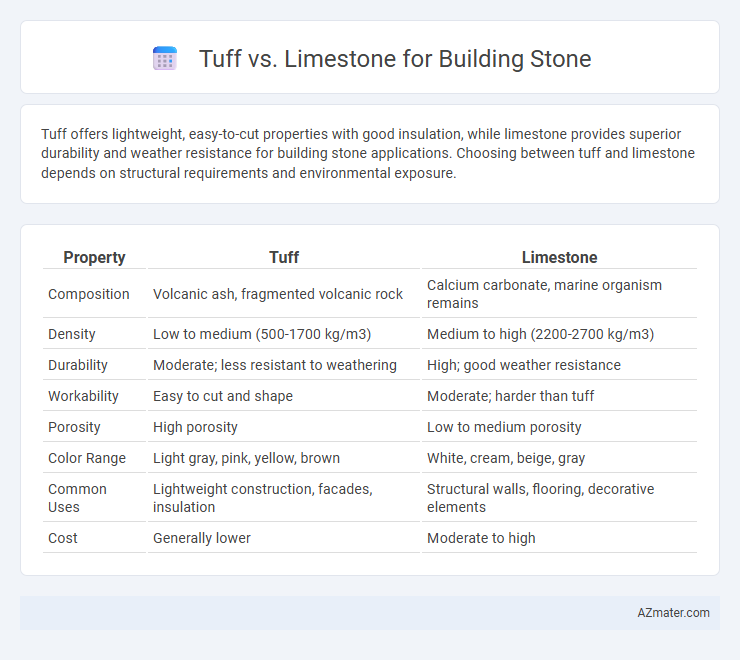
| Property | Tuff | Limestone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Volcanic ash, fragmented volcanic rock | Calcium carbonate, marine organism remains |
| Density | Low to medium (500-1700 kg/m3) | Medium to high (2200-2700 kg/m3) |
| Durability | Moderate; less resistant to weathering | High; good weather resistance |
| Workability | Easy to cut and shape | Moderate; harder than tuff |
| Porosity | High porosity | Low to medium porosity |
| Color Range | Light gray, pink, yellow, brown | White, cream, beige, gray |
| Common Uses | Lightweight construction, facades, insulation | Structural walls, flooring, decorative elements |
| Cost | Generally lower | Moderate to high |
Introduction to Tuff and Limestone as Building Stones
Tuff is a volcanic rock composed of compressed volcanic ash, prized for its lightweight yet durable properties, making it ideal for insulation and decorative building elements. Limestone, a sedimentary rock primarily composed of calcium carbonate, is widely used in construction for its strength, ease of carving, and resistance to weathering. Both stones offer distinct advantages: tuff's porosity provides thermal insulation, while limestone's density ensures structural stability in building applications.
Geological Formation and Composition
Tuff is a volcanic rock formed from consolidated volcanic ash ejected during explosive eruptions, characterized by its lightweight, porous texture and high silica content. Limestone originates from sedimentary processes, primarily composed of calcium carbonate derived from marine organisms' skeletal fragments, exhibiting a dense and compact structure. The distinct geological formations and mineral compositions influence their durability, workability, and suitability for various building applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Tuff exhibits lower density and compressive strength compared to limestone, making it lighter yet less durable for structural applications. Limestone offers higher hardness and better resistance to weathering due to its calcite composition, resulting in superior longevity in building construction. Porosity in tuff increases its water absorption rate, whereas limestone's lower porosity enhances its performance in moisture-prone environments.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Tuff exhibits moderate durability but is more porous and susceptible to weathering compared to limestone, which offers higher density and superior resistance to erosion and moisture. Limestone's calcium carbonate composition enhances its ability to withstand freeze-thaw cycles and acidic rain, making it ideal for exterior building applications. For long-term structural integrity, limestone is preferred over tuff due to its robust weather resistance and lower maintenance requirements.
Workability and Ease of Shaping
Tuff, a volcanic rock characterized by its softness and porosity, offers superior workability and ease of shaping compared to limestone, making it ideal for intricate carvings and detailed architectural features. Limestone, while denser and harder, provides greater durability but requires more effort and specialized tools to shape, potentially increasing labor time and costs. Builders often select tuff when precision and reduced cutting effort are priorities, whereas limestone is preferred for structural strength and longevity.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Varieties
Tuff offers a distinctive aesthetic appeal with its porous texture and warm earth-tone hues ranging from soft yellows to reddish-browns, making it ideal for rustic or Mediterranean-style architecture. Limestone provides a classic and elegant appearance characterized by smooth surfaces and a broad palette including creamy whites, beiges, grays, and occasionally blues, allowing versatile applications in both traditional and contemporary designs. The choice between tuff and limestone hinges on desired visual impact and color diversity, with limestone generally offering a wider spectrum and refined look compared to tuff's natural, rugged charm.
Cost and Availability
Tuff generally offers a lower cost compared to limestone due to its widespread availability in volcanic regions and easier quarrying process. Limestone availability depends heavily on regional geology, often leading to higher transportation costs in non-limestone areas, which increases its overall expense. Both stones vary in price based on local market demand and extraction complexity, but tuff's lighter weight and softness typically reduce costs in building applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tuff exhibits lower embodied energy compared to limestone due to its volcanic origin and softer composition, resulting in less energy-intensive extraction and processing. Limestone mining often leads to significant habitat disruption and carbon dioxide emissions from calcination during cement production, raising environmental concerns. Tuff's natural insulation properties contribute to energy efficiency in buildings, enhancing sustainability through reduced heating and cooling demands.
Common Architectural Applications
Tuff is widely used in wall cladding, facades, and decorative elements due to its lightweight and easy workability, ideal for intricate carvings and historic restoration projects. Limestone is favored for structural components, paving, and columns because of its durability, natural aesthetic, and resistance to weathering. Both stones serve prominent roles in architectural design, with tuff offering versatility in detail work and limestone providing strength and longevity.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Project
Tuff and limestone differ primarily in composition and durability, impacting their suitability for building projects. Tuff, a lightweight volcanic rock, offers excellent insulation and ease of carving but may lack the long-term strength and weather resistance of dense limestone. Limestone provides superior structural integrity and a classic aesthetic, making it ideal for load-bearing applications and historic-style architecture in construction.
Infographic: Tuff vs Limestone for Building Stone
 azmater.com
azmater.com