Thin stone veneer offers a lightweight, cost-effective alternative to traditional sandstone for paving, providing easy installation and a natural stone appearance. Sandstone, known for its durability and slip resistance, is ideal for outdoor paving in high-traffic areas but requires more maintenance and higher installation costs.
Table of Comparison
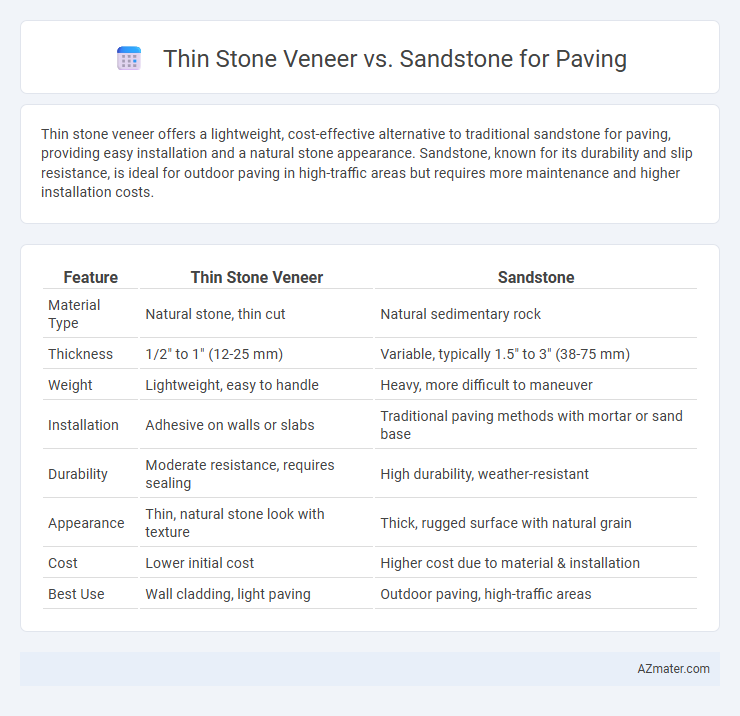
| Feature | Thin Stone Veneer | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural stone, thin cut | Natural sedimentary rock |
| Thickness | 1/2" to 1" (12-25 mm) | Variable, typically 1.5" to 3" (38-75 mm) |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavy, more difficult to maneuver |
| Installation | Adhesive on walls or slabs | Traditional paving methods with mortar or sand base |
| Durability | Moderate resistance, requires sealing | High durability, weather-resistant |
| Appearance | Thin, natural stone look with texture | Thick, rugged surface with natural grain |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost due to material & installation |
| Best Use | Wall cladding, light paving | Outdoor paving, high-traffic areas |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Paving Material
Thin stone veneer offers a lightweight, easy-to-install option ideal for decorative paving projects requiring flexibility and cost-efficiency. Sandstone provides durable, natural stone paving with rich textures and excellent resistance to weathering, making it suitable for high-traffic outdoor areas. Selecting between thin stone veneer and sandstone depends on project requirements such as budget, structural support, and aesthetic preferences.
Overview of Thin Stone Veneer
Thin stone veneer offers a lightweight, flexible alternative to traditional sandstone for paving, providing a natural stone appearance with significantly reduced thickness and weight. This material is engineered to be easy to install on various surfaces, making it ideal for both exterior and interior paving applications. Unlike solid sandstone, thin stone veneer enhances design versatility while maintaining durability and resistance to weathering.
Overview of Sandstone Paving
Sandstone paving is prized for its natural durability, wide range of warm earthy tones, and textured surface that provides excellent slip resistance. It weathers well over time, making it ideal for outdoor patios, pathways, and driveways, while its natural porous structure allows for good drainage. Compared to thin stone veneer, sandstone paving offers greater thickness and structural strength, supporting heavier loads and maintaining long-term performance in diverse climates.
Aesthetic Differences: Thin Stone Veneer vs. Sandstone
Thin stone veneer offers a sleek, uniform appearance with consistent thickness and color, creating a modern and polished aesthetic ideal for contemporary paving designs. Sandstone, on the other hand, provides natural variations in texture, color, and grain, resulting in a more rustic and earthy look that enhances outdoor spaces with organic warmth. The choice between the two influences the overall visual impact, with thin stone veneer emphasizing precision and refinement, while sandstone highlights natural beauty and rugged charm.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Thin stone veneer offers a durable and lightweight option for paving, with enhanced resistance to cracking and weathering due to its engineered backing and thin profile. Sandstone, a natural stone, provides excellent longevity with inherent hardness and resistance to abrasion but may require regular maintenance to prevent erosion and surface wear in high-traffic areas. Choosing between thin stone veneer and sandstone for paving depends on balancing the need for low-weight, versatile installation against the natural durability and classic aesthetic of authentic sandstone slabs.
Installation Process: Which is Easier?
Thin stone veneer offers a lighter and more flexible installation process compared to sandstone paving, as it can be applied directly onto surfaces with mortar or adhesive, reducing the need for heavy groundwork. Sandstone paving requires precise base preparation and careful placement to ensure stability and longevity, often involving more labor-intensive steps like leveling and securing each stone. Homeowners and contractors generally find thin stone veneer easier and faster to install due to its lightweight nature and adaptability to various substrates.
Maintenance Requirements
Thin stone veneer requires minimal maintenance, typically involving occasional cleaning with water and mild detergent to preserve its appearance. Sandstone paving demands more frequent upkeep due to its porous nature, necessitating regular sealing to prevent staining and water damage. Both materials benefit from periodic inspections to address potential cracks or chips, but sandstone generally incurs higher long-term maintenance costs.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment & Long-term Value
Thin stone veneer offers a lower initial investment compared to sandstone paving due to reduced material thickness and easier installation, cutting labor costs significantly. Sandstone paving demands higher upfront expenses but provides superior durability and weather resistance, resulting in lower maintenance and replacement costs over time. Evaluating long-term value, sandstone's resilience can justify higher initial costs, whereas thin stone veneer suits budget-conscious projects with shorter lifecycle expectations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Thin stone veneer offers a lower environmental impact compared to sandstone paving due to its reduced material extraction and transportation needs, resulting in less energy consumption and carbon emissions. Sandstone paving, while durable and natural, often involves extensive quarrying that can lead to habitat disruption and higher waste production. Choosing thin stone veneer supports sustainability by minimizing resource depletion and promoting efficient use of natural stone.
Conclusion: Making the Best Choice for Your Project
Thin stone veneer offers a lightweight, cost-effective solution ideal for decorative applications and easy installation, while sandstone provides unmatched durability and natural slip resistance suited for high-traffic paving projects. Assessing project requirements such as budget, aesthetic preference, and environmental exposure helps determine the most suitable material. For long-lasting outdoor paving with natural texture, sandstone is preferable; thin stone veneer fits best where visual appeal and quick application are priorities.
Infographic: Thin stone veneer vs Sandstone for Paving
 azmater.com
azmater.com