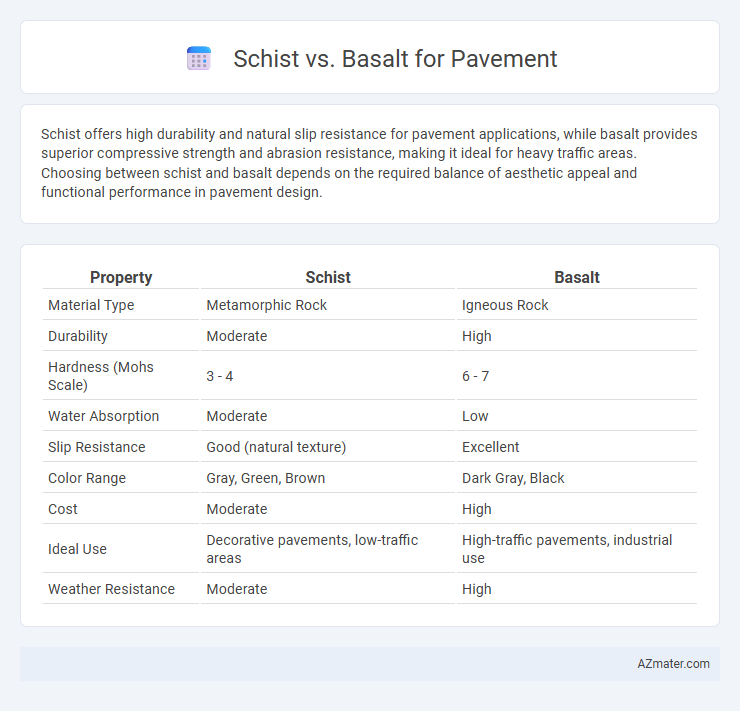
Schist offers high durability and natural slip resistance for pavement applications, while basalt provides superior compressive strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for heavy traffic areas. Choosing between schist and basalt depends on the required balance of aesthetic appeal and functional performance in pavement design.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Schist | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Metamorphic Rock | Igneous Rock |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 3 - 4 | 6 - 7 |
| Water Absorption | Moderate | Low |
| Slip Resistance | Good (natural texture) | Excellent |
| Color Range | Gray, Green, Brown | Dark Gray, Black |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Ideal Use | Decorative pavements, low-traffic areas | High-traffic pavements, industrial use |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Schist and Basalt as Pavement Materials
Schist is a metamorphic rock characterized by its foliated texture and ease of splitting, making it suitable for decorative and low-traffic pavement applications. Basalt, an igneous rock with a fine-grained, dense composition, offers exceptional durability, strength, and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for high-traffic road surfaces and heavy-load pavement. The choice between schist and basalt depends on factors such as mechanical strength requirements, aesthetic preferences, and environmental exposure conditions.
Geological Formation and Composition
Schist and basalt differ significantly in geological formation and composition, impacting their suitability for pavement. Schist is a metamorphic rock formed under intense heat and pressure, characterized by its foliated texture and abundant mica minerals, which impart a layered structure but can reduce durability. Basalt is an extrusive igneous rock formed from rapidly cooled lava, composed primarily of plagioclase and pyroxene minerals, offering a dense, hard, and fine-grained texture ideal for high-strength, wear-resistant pavement applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Schist exhibits a foliated texture with pronounced mineral alignment, resulting in lower compressive strength and higher susceptibility to weathering compared to basalt, which is an igneous rock characterized by a fine-grained, dense, and homogeneous matrix with superior durability. Basalt's high compressive strength, abrasion resistance, and low porosity make it ideal for heavy traffic pavement applications, whereas schist's cleavage planes reduce its load-bearing capacity and increase the risk of fracturing under stress. The mechanical stability of basalt outperforms schist in pavement scenarios where long-term resilience and minimal maintenance are critical.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Schist, known for its foliated structure, offers moderate durability but can be prone to splitting and erosion under heavy traffic and freeze-thaw cycles. Basalt, a dense volcanic rock, provides superior durability and exceptional weather resistance, making it ideal for pavements exposed to harsh climates and heavy loads. Basalt's low porosity and high compressive strength ensure longer lifespan and minimal maintenance compared to schist in pavement applications.
Load-Bearing Capacity
Basalt exhibits higher load-bearing capacity compared to schist, making it more suitable for pavement applications requiring heavy traffic support. The dense, fine-grained structure of basalt provides greater compressive strength and durability under repetitive loads. In contrast, schist's foliated texture can lead to weakness along cleavage planes, reducing its effectiveness in high-stress pavement environments.
Cost and Availability
Schist is generally more expensive for pavement due to its limited availability and the complexity of quarrying and cutting its foliated structure. Basalt, being abundant and widely distributed, offers lower material and transportation costs, making it more cost-effective for large-scale projects. The durability and compressive strength of basalt also reduce long-term maintenance expenses compared to schist pavement.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Schist offers easier installation due to its natural cleft surface, allowing for better interlocking and reduced slipping hazards, while basalt's denser, harder texture requires more specialized cutting tools and longer installation times. Maintenance of schist pavements involves routine sealing to prevent moisture infiltration and flaking, whereas basalt surfaces demand less frequent sealing but more attention to potential surface cracks caused by freeze-thaw cycles. Choosing between schist and basalt for pavement depends on the desired balance of installation efficiency against long-term durability and maintenance frequency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Schist offers lower embodied carbon compared to basalt due to less intensive quarrying and processing requirements, leading to reduced greenhouse gas emissions in pavement applications. Basalt, while harder and more durable, often involves energy-intensive extraction and transportation, increasing its environmental footprint. Choosing schist for pavement enhances sustainability by minimizing ecological disturbance and promoting resource efficiency in construction projects.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Schist's natural foliation and shimmer create a visually striking pavement surface, offering unique textures and earthy tones that complement rustic and traditional designs. Basalt provides a sleek, uniform appearance with deep gray to black hues, ideal for modern, minimalist aesthetics and precise geometric layouts. The design flexibility of basalt allows for smooth finishes and sharp edges, while schist's variability supports organic, irregular patterns enhancing visual interest.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Schist and Basalt for Pavement
Schist provides a unique aesthetic with its foliated texture and natural variation, ideal for decorative pavement where visual appeal is prioritized. Basalt offers superior durability and strength, making it a more practical choice for high-traffic or heavy-load pavement applications. Selecting between schist and basalt depends on balancing design preferences with performance requirements and budget constraints.
Infographic: Schist vs Basalt for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com