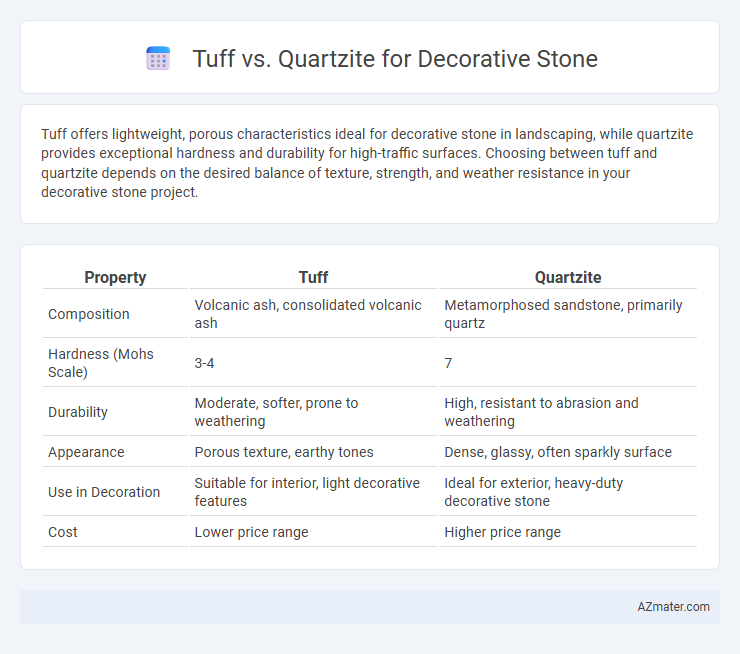
Tuff offers lightweight, porous characteristics ideal for decorative stone in landscaping, while quartzite provides exceptional hardness and durability for high-traffic surfaces. Choosing between tuff and quartzite depends on the desired balance of texture, strength, and weather resistance in your decorative stone project.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tuff | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Volcanic ash, consolidated volcanic ash | Metamorphosed sandstone, primarily quartz |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 3-4 | 7 |
| Durability | Moderate, softer, prone to weathering | High, resistant to abrasion and weathering |
| Appearance | Porous texture, earthy tones | Dense, glassy, often sparkly surface |
| Use in Decoration | Suitable for interior, light decorative features | Ideal for exterior, heavy-duty decorative stone |
| Cost | Lower price range | Higher price range |
Introduction to Tuff and Quartzite
Tuff is a lightweight, porous volcanic rock formed from consolidated volcanic ash, prized for its ease of carving and unique textures which enhance decorative stone applications. Quartzite is a hard, metamorphic rock originating from sandstone, characterized by its durability, high silica content, and natural gloss that offers exceptional resistance to weathering. Both stones are favored for decorative purposes, but quartzite's strength contrasts with tuff's softness, influencing their suitability based on design requirements.
Geological Origins and Formation
Tuff, a volcanic rock formed from consolidated volcanic ash, originates from explosive volcanic eruptions that rapidly deposit fine ash layers, resulting in a porous and lightweight stone ideal for decorative use. Quartzite, a metamorphic rock, forms from the intense heat and pressure metamorphosing sandstone, leading to a dense, durable stone with high quartz content prized for its hardness and resistance. The geological origins differentiate tuff's igneous volcanic processes from quartzite's regional metamorphism, influencing their textures and suitability for decorative applications.
Physical Appearance and Color Variations
Tuff offers a distinctive, porous texture with earthy hues ranging from soft browns and reds to greys, creating a rustic and natural aesthetic ideal for decorative stone applications. Quartzite is known for its hard, crystalline structure and a broader color palette including whites, blues, greens, and subtle pinks, providing a sleek and durable surface with high visual appeal. The contrasting physical appearances make tuff suitable for more organic, weathered designs, while quartzite fits modern, polished environments requiring vibrant color variations.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Quartzite demonstrates superior durability and hardness compared to tuff, making it an ideal choice for decorative stone applications requiring long-lasting performance. With a Mohs hardness rating of 7, quartzite is significantly harder than tuff, which typically ranges around 3 to 4, resulting in better resistance to scratching and weathering. This inherent strength allows quartzite to maintain its aesthetic appeal and structural integrity in high-traffic or outdoor environments where tuff may deteriorate more quickly.
Water Absorption and Weather Resistance
Tuff exhibits higher water absorption rates compared to quartzite, making it more susceptible to moisture-related damage and weathering over time. Quartzite's dense, crystalline structure provides superior weather resistance and low permeability, ensuring enhanced durability in outdoor decorative applications. Selecting quartzite for decorative stone projects results in a longer-lasting finish with minimal water absorption and excellent resistance to harsh environmental conditions.
Ease of Cutting and Installation
Tuff offers superior ease of cutting and installation due to its softer, more porous nature compared to quartzite, which is significantly harder and denser, requiring specialized tools and more effort to shape. This softness reduces labor time and costs, making tuff a preferred choice for intricate decorative stone applications where precision and speed are critical. Quartzite's durability provides long-term resilience but increases installation complexity, often necessitating skilled professionals for cutting and fitting.
Maintenance Requirements
Tuff exhibits lower maintenance requirements compared to quartzite due to its softer composition, making it easier to clean but more susceptible to weathering and surface erosion over time. Quartzite's hardness and density provide superior durability and resistance to scratches, stains, and erosion, reducing the frequency of sealing and repairs needed for decorative stone applications. Regular sealing is recommended for both materials to enhance longevity, with quartzite generally requiring less frequent maintenance interventions in high-traffic or exposed environments.
Cost and Availability
Tuff is generally more cost-effective than quartzite due to its abundant availability and ease of quarrying, making it a popular choice for decorative stone applications. Quartzite, being a harder and more durable metamorphic rock, tends to be more expensive and less readily available, especially in specific colors or finishes. The price difference often reflects quartzite's superior strength and resistance to weathering, influencing project budgets and sourcing considerations.
Popular Applications in Decorative Stonework
Tuff's lightweight and porous nature makes it ideal for interior wall cladding, garden sculptures, and decorative facades, providing a rustic and natural texture that enhances aesthetic appeal. Quartzite, known for its hardness and durability, is popular in high-traffic areas such as countertops, flooring, and exterior paving, offering a polished and elegant finish resistant to wear and weathering. Both stones are favored in landscaping and architectural projects, with tuff preferred for softer, textured designs and quartzite chosen for sleek, long-lasting surfaces.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tuff, a volcanic rock, generally has a lower environmental impact due to its easier quarrying process and reduced energy consumption compared to the harder, denser quartzite. Quartzite requires intensive mining and processing, which increases carbon emissions and depletes natural resources at a higher rate. Choosing tuff for decorative stone enhances sustainability by minimizing habitat disruption and promoting energy efficiency in extraction and fabrication.
Infographic: Tuff vs Quartzite for Decorative Stone
 azmater.com
azmater.com