Quartzite offers superior hardness and weather resistance compared to sandstone, making it ideal for durable and long-lasting wall cladding. Sandstone provides a softer, more porous texture with natural variations, enhancing aesthetic appeal but requiring more maintenance in exterior applications.
Table of Comparison
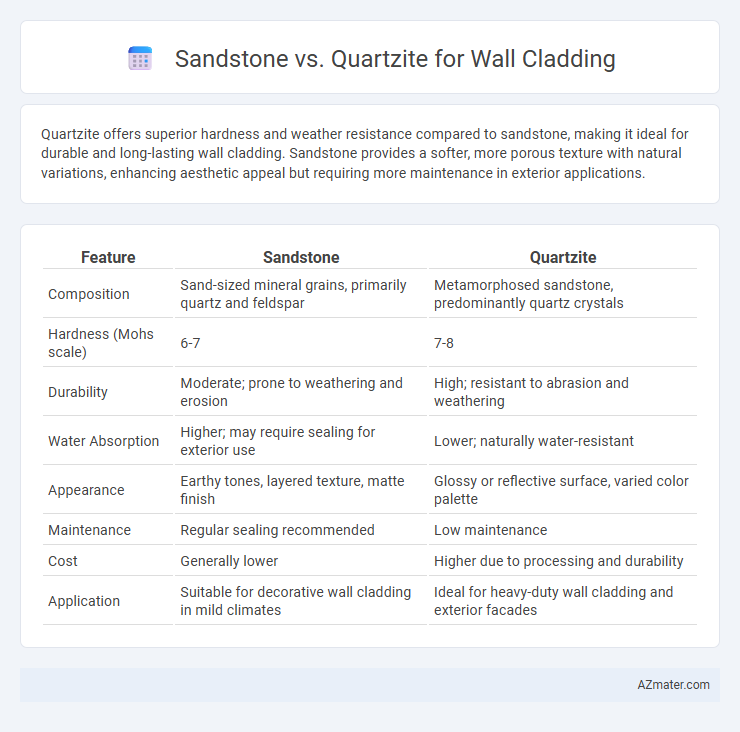
| Feature | Sandstone | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sand-sized mineral grains, primarily quartz and feldspar | Metamorphosed sandstone, predominantly quartz crystals |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 6-7 | 7-8 |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to weathering and erosion | High; resistant to abrasion and weathering |
| Water Absorption | Higher; may require sealing for exterior use | Lower; naturally water-resistant |
| Appearance | Earthy tones, layered texture, matte finish | Glossy or reflective surface, varied color palette |
| Maintenance | Regular sealing recommended | Low maintenance |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to processing and durability |
| Application | Suitable for decorative wall cladding in mild climates | Ideal for heavy-duty wall cladding and exterior facades |
Introduction to Wall Cladding Materials
Wall cladding materials like sandstone and quartzite offer distinct advantages for both aesthetic appeal and durability in architectural design. Sandstone is valued for its natural texture and warm tones, making it a popular choice for traditional and rustic applications, while quartzite provides superior hardness and resistance to weathering, ideal for modern and high-traffic environments. Understanding the mineral composition, porosity, and maintenance requirements of these stones helps in selecting the best cladding material to enhance building facades effectively.
What is Sandstone? Key Characteristics
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of sand-sized mineral particles or rock fragments, predominantly quartz and feldspar, known for its natural, earthy tones and granular texture. Its key characteristics include durability, porosity, and varied color ranges from tan, yellow, red, brown, to gray, making it suitable for wall cladding that requires both aesthetic appeal and moderate weather resistance. Sandstone's ease of cutting and carving allows for versatile design applications in exterior and interior wall cladding projects.
Understanding Quartzite: Features and Properties
Quartzite is a highly durable metamorphic rock formed from sandstone under intense heat and pressure, resulting in a dense, hard surface ideal for wall cladding. It features excellent resistance to scratching, weathering, and chemical erosion, making it suitable for both interior and exterior applications. Its natural glossy finish and range of colors enhance aesthetic appeal while providing long-lasting structural integrity.
Aesthetic Appeal: Sandstone vs Quartzite
Sandstone offers a warm, earthy aesthetic with natural grain patterns and a variety of color tones ranging from beige to deep red, making it ideal for rustic or traditional wall cladding. Quartzite presents a sleek, polished look with high gloss and subtle veining, enhancing modern and contemporary designs with its vibrant whites, grays, and occasional blues. Both materials provide unique visual textures, but sandstone emphasizes natural ruggedness whereas quartzite highlights elegance and durability in wall cladding applications.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Quartzite exhibits superior durability and strength compared to sandstone, making it more resistant to scratches, chips, and weathering in wall cladding applications. With a Mohs hardness rating of 7, quartzite outperforms sandstone, which typically ranges from 6 to 7, ensuring longer-lasting structural integrity. Its dense, interlocking quartz grains provide enhanced resistance to impact and compression, ideal for exterior and high-traffic wall surfaces.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Quartzite demonstrates superior weather resistance and longevity compared to sandstone due to its natural hardness and low porosity, which makes it less susceptible to erosion, moisture damage, and freeze-thaw cycles. Sandstone is more prone to wear and requires sealing to prevent water infiltration, leading to potential discoloration and degradation over time. For wall cladding in harsh climates, quartzite stands out as a durable and long-lasting material, minimizing maintenance and preserving aesthetic appeal.
Maintenance Requirements: Effort and Cost
Sandstone wall cladding requires regular sealing and more frequent maintenance to prevent erosion and staining, resulting in moderate effort and ongoing costs. Quartzite offers superior durability and resistance to weathering, reducing maintenance frequency and long-term expenses despite a higher initial investment. Choosing quartzite minimizes upkeep effort and cost, making it preferable for low-maintenance wall cladding.
Installation Process and Practical Considerations
Sandstone is easier to cut and shape during the installation process, making it suitable for intricate wall cladding designs, while quartzite's hardness requires specialized tools and skilled labor, increasing installation time and cost. Practical considerations include sandstone's porosity, which necessitates sealing to prevent moisture absorption and staining, whereas quartzite offers superior durability and resistance to weathering with minimal maintenance. Both materials require proper substrate preparation, but quartzite's higher density demands stronger anchoring systems for secure wall cladding applications.
Cost Analysis: Sandstone vs Quartzite
Sandstone generally offers a lower cost for wall cladding compared to quartzite due to its abundance and easier extraction process. Quartzite's higher price reflects its superior hardness, durability, and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for long-term exterior applications. Maintenance expenses for sandstone may increase over time because of its porosity, whereas quartzite often requires less upkeep, balancing initial costs with lifecycle value.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Project
Sandstone offers natural warmth and texture with ease of carving, ideal for traditional or rustic wall cladding, while quartzite provides superior hardness, durability, and resistance to weathering, making it perfect for modern, high-traffic, or exterior applications. Consider project-specific factors like exposure to elements, desired aesthetics, maintenance requirements, and budget to select between the porous, softer sandstone and the dense, non-porous quartzite. For long-term investment and low upkeep, quartzite emerges as the best choice, whereas sandstone suits projects prioritizing natural variation and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Sandstone vs Quartzite for Wall Cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com