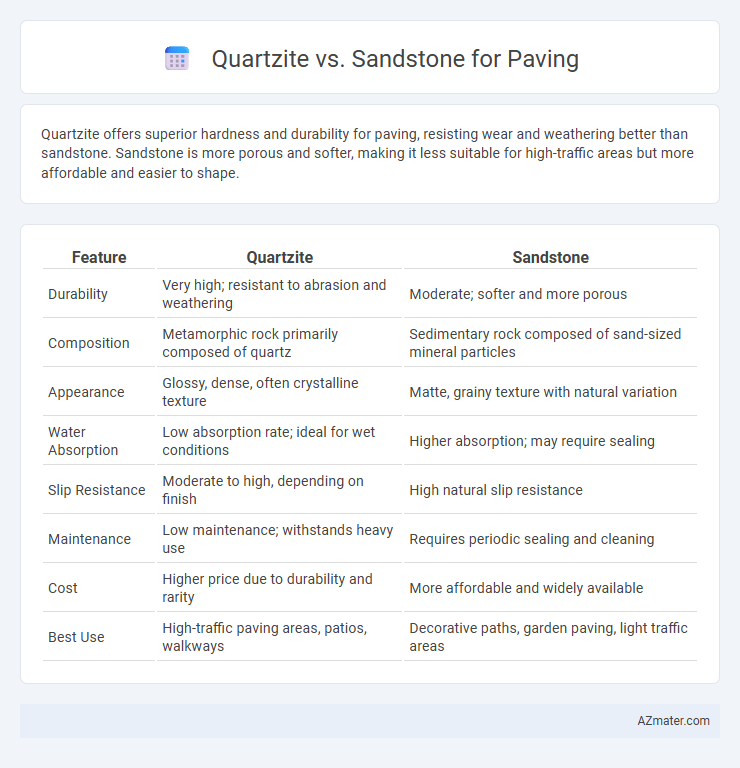
Quartzite offers superior hardness and durability for paving, resisting wear and weathering better than sandstone. Sandstone is more porous and softer, making it less suitable for high-traffic areas but more affordable and easier to shape.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Quartzite | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Very high; resistant to abrasion and weathering | Moderate; softer and more porous |
| Composition | Metamorphic rock primarily composed of quartz | Sedimentary rock composed of sand-sized mineral particles |
| Appearance | Glossy, dense, often crystalline texture | Matte, grainy texture with natural variation |
| Water Absorption | Low absorption rate; ideal for wet conditions | Higher absorption; may require sealing |
| Slip Resistance | Moderate to high, depending on finish | High natural slip resistance |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; withstands heavy use | Requires periodic sealing and cleaning |
| Cost | Higher price due to durability and rarity | More affordable and widely available |
| Best Use | High-traffic paving areas, patios, walkways | Decorative paths, garden paving, light traffic areas |
Introduction to Quartzite and Sandstone
Quartzite is a natural metamorphic rock formed from sandstone under intense heat and pressure, known for its exceptional hardness and durability, making it ideal for high-traffic paving applications. Sandstone, a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized mineral particles or rock fragments, offers a softer, more porous surface with varied textures and colors suitable for aesthetic outdoor paving. Both materials provide unique advantages, with quartzite excelling in strength and weather resistance, while sandstone offers versatility in design and cost-effectiveness.
Composition and Formation
Quartzite, a metamorphic rock, forms when sandstone undergoes intense heat and pressure, resulting in a dense, hard material composed predominantly of interlocking quartz crystals. Sandstone, a sedimentary rock, consists mainly of sand-sized mineral particles, primarily quartz, cemented together by silica, calcium carbonate, or iron oxide. The transformation process gives quartzite superior durability and resistance to weathering compared to the relatively softer and more porous sandstone, making it more suitable for high-traffic paving applications.
Appearance and Color Variations
Quartzite offers a natural, glassy texture with vibrant color variations ranging from white and gray to pink and red, providing a striking aesthetic for paving projects. Sandstone features a more earthy, matte finish with subtle hues including tan, brown, yellow, and reddish tones, adding warmth and rustic charm to outdoor spaces. Both stones' unique mineral compositions influence their color depth and pattern diversity, making them popular choices for decorative paving.
Durability and Hardness
Quartzite offers superior durability and hardness compared to sandstone, making it highly resistant to scratches, abrasion, and weathering, ideal for high-traffic paving. Sandstone, while softer and more porous, tends to wear down faster under heavy use and requires more maintenance to prevent erosion and staining. The high quartz content in quartzite contributes to its exceptional strength, whereas sandstone's sedimentary composition compromises its long-term resilience.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Quartzite is significantly more weather-resistant than sandstone due to its dense, non-porous structure, making it ideal for paving in harsh climates with frequent freeze-thaw cycles. The high silica content in quartzite enhances its durability and longevity, often lasting several decades without significant wear. Sandstone, while aesthetically pleasing, is softer and more porous, which leads to faster erosion and reduced lifespan when exposed to prolonged moisture and temperature fluctuations.
Slip Resistance and Surface Texture
Quartzite offers superior slip resistance compared to sandstone due to its harder, denser mineral composition and naturally rough surface texture, making it ideal for high-traffic paving areas. Sandstone's softer, more porous surface tends to wear down faster and become slippery when wet, requiring additional treatments to enhance traction. The interlocking, granular texture of quartzite provides consistent grip underfoot, while sandstone's smoother grains can compromise safety in wet or icy conditions.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Quartzite offers superior durability and requires less maintenance during paving installation due to its natural resistance to weathering and abrasion. Sandstone, while easier to cut and install because of its softer texture, demands more frequent sealing and cleaning to prevent staining and erosion. The choice between quartzite and sandstone for paving hinges on balancing installation simplicity with long-term upkeep commitments.
Cost Comparison: Quartzite vs Sandstone
Quartzite generally costs more than sandstone due to its greater durability and resistance to weathering, making it a long-lasting option for paving. Sandstone is more affordable upfront but may require more maintenance and replacement over time, increasing the total cost of ownership. Choosing between quartzite and sandstone involves weighing the initial investment against long-term durability and maintenance expenses.
Best Uses and Applications for Paving
Quartzite offers superior hardness and durability, making it ideal for high-traffic paving areas such as driveways, walkways, and patios that require resistance to abrasion and weathering. Sandstone provides a softer, more porous surface with excellent slip resistance, suitable for decorative garden paths, pool surrounds, and patios in moderate climates. Both materials excel in different paving applications, with quartzite preferred for longevity and strength, while sandstone is chosen for aesthetic appeal and natural texture.
Which Stone is Right for Your Project?
Quartzite offers superior durability and hardness, making it ideal for high-traffic paving projects requiring long-lasting performance. Sandstone provides a softer, more porous surface with natural, earthy tones that suit decorative or less demanding outdoor applications. Consider quartzite for strength and weather resistance, while sandstone fits well with aesthetic appeal and budget-friendly paving solutions.
Infographic: Quartzite vs Sandstone for Paving
 azmater.com
azmater.com