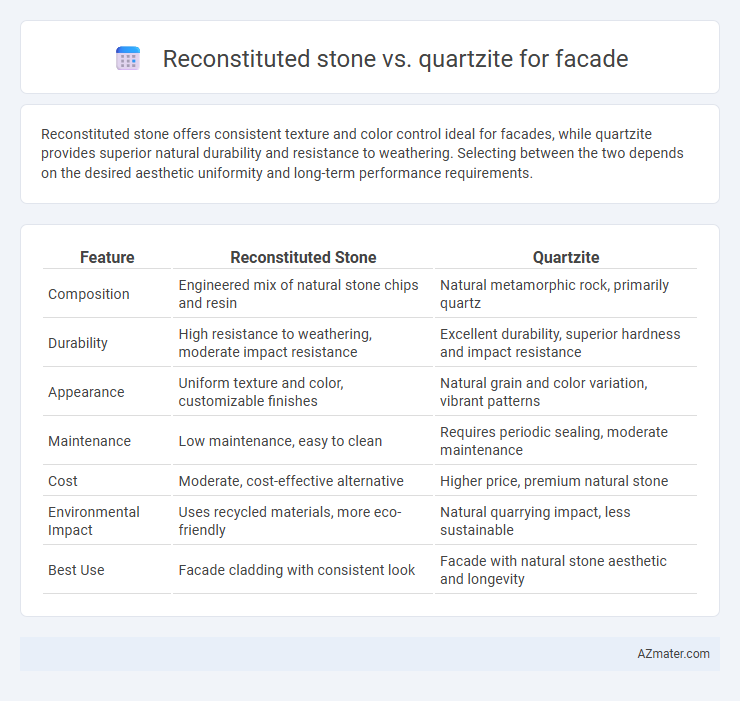
Reconstituted stone offers consistent texture and color control ideal for facades, while quartzite provides superior natural durability and resistance to weathering. Selecting between the two depends on the desired aesthetic uniformity and long-term performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reconstituted Stone | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Engineered mix of natural stone chips and resin | Natural metamorphic rock, primarily quartz |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering, moderate impact resistance | Excellent durability, superior hardness and impact resistance |
| Appearance | Uniform texture and color, customizable finishes | Natural grain and color variation, vibrant patterns |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Requires periodic sealing, moderate maintenance |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective alternative | Higher price, premium natural stone |
| Environmental Impact | Uses recycled materials, more eco-friendly | Natural quarrying impact, less sustainable |
| Best Use | Facade cladding with consistent look | Facade with natural stone aesthetic and longevity |
Introduction to Facade Materials
Reconstituted stone offers versatility and uniformity in facade applications due to its engineered composition of crushed natural stone and resin, providing consistent color and texture. Quartzite, a natural metamorphic rock, is prized for its exceptional hardness, durability, and unique veining patterns that enhance architectural aesthetics. Both materials deliver robust performance for building facades, but quartzite's natural origin and weather resistance make it ideal for long-term exterior use, while reconstituted stone allows for customizable design options.
What is Reconstituted Stone?
Reconstituted stone is an engineered material made from crushed natural stone, cement, and pigments, designed to mimic the appearance and texture of natural stone while offering enhanced durability and uniformity. It provides greater design flexibility and consistent quality compared to quartzite, which is a natural metamorphic rock known for its hardness and unique veining. Reconstituted stone is often chosen for facades due to its cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and resistance to weathering.
Understanding Quartzite as a Facade Choice
Quartzite is a natural metamorphic rock renowned for its exceptional hardness and durability, making it a superior choice for facades subject to harsh weather conditions. Unlike reconstituted stone, which is engineered from crushed natural stone and resin, quartzite offers a unique, non-repetitive pattern and higher resistance to scratching and staining. Its natural composition ensures long-lasting aesthetic appeal and structural integrity, providing a premium, low-maintenance facade solution.
Aesthetic Differences: Reconstituted Stone vs Quartzite
Reconstituted stone offers a uniform appearance with customizable colors and textures, providing a consistent aesthetic ideal for modern facade designs. Quartzite features natural veining and color variations, creating a unique, organic look valued for its timeless elegance. The choice between reconstituted stone and quartzite hinges on whether a controlled, predictable finish or a naturally dynamic visual appeal is preferred for the facade.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Reconstituted stone offers consistent durability and excellent weather resistance due to its engineered composition, making it less prone to cracking and fading when exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Quartzite, a natural metamorphic rock, is highly durable with exceptional hardness and resistance to abrasion, but it may be more susceptible to weathering effects like staining and surface erosion over time. For facade applications, reconstituted stone provides enhanced stability and uniform performance in varied climates, while quartzite delivers natural aesthetics with robust long-term resilience.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Reconstituted stone offers easier installation due to its uniform size and lighter weight compared to quartzite, which often requires specialized cutting tools and skilled labor because of its natural hardness. Maintenance for reconstituted stone is generally minimal, involving periodic cleaning and sealing to prevent staining, while quartzite demands more frequent sealing and careful cleaning to preserve its natural durability and resistance to weathering. Both materials require proper installation techniques to ensure facade longevity, but quartzite's inherent strength provides greater resistance to chipping and abrasion over time.
Cost Comparison: Reconstituted Stone vs Quartzite
Reconstituted stone typically offers a more cost-effective option for facades, with prices averaging 30-50% lower than natural quartzite due to lower material and installation expenses. Quartzite, prized for its durability and natural aesthetic, commands higher costs driven by quarrying, processing, and transport fees. Budget-sensitive projects often favor reconstituted stone for its balance of affordability and visual appeal, while premium applications may justify quartzite's premium investment.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Reconstituted stone offers a sustainable alternative for facades by utilizing crushed natural stone combined with resin, significantly reducing quarrying waste and energy consumption compared to quarried quartzite. Quartzite, a natural stone, involves extensive mining and transportation, leading to a higher carbon footprint and potential ecosystem disruption. Choosing reconstituted stone supports eco-friendly construction by promoting material efficiency and lowering environmental impact without sacrificing aesthetic durability.
Suitability for Modern Architectural Designs
Reconstituted stone offers consistent texture and customizable colors that align well with the sleek aesthetics of modern architectural designs, providing enhanced durability and resistance to weathering. Quartzite presents a natural, high-strength surface with unique veining patterns, ideal for creating visually striking facades that emphasize natural stone beauty. Both materials provide excellent structural integrity for exterior applications, but reconstituted stone allows for greater versatility in design precision and installation ease.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Facade
Reconstituted stone offers greater design flexibility and uniformity, ideal for facades requiring precise shapes and consistent color, while quartzite provides unmatched natural durability and a unique, organic appearance that resists weathering. For long-term facade performance, quartzite's high hardness and natural resistance to heat and moisture make it suitable for harsh climates, whereas reconstituted stone is often more cost-effective and easier to install. Evaluating factors such as budget, aesthetic preferences, climate exposure, and maintenance requirements will help determine whether reconstituted stone or quartzite best meets the specific needs of your facade project.
Infographic: Reconstituted stone vs Quartzite for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com