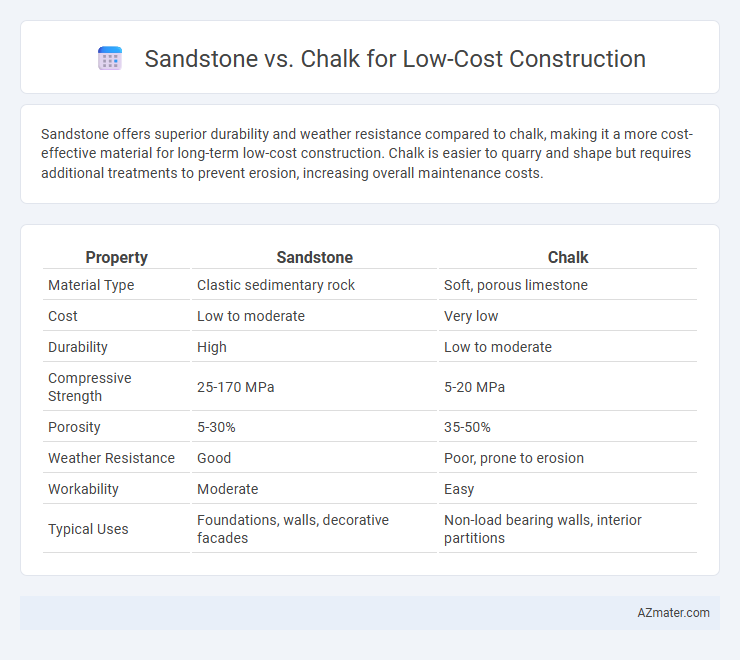
Sandstone offers superior durability and weather resistance compared to chalk, making it a more cost-effective material for long-term low-cost construction. Chalk is easier to quarry and shape but requires additional treatments to prevent erosion, increasing overall maintenance costs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sandstone | Chalk |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Clastic sedimentary rock | Soft, porous limestone |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Very low |
| Durability | High | Low to moderate |
| Compressive Strength | 25-170 MPa | 5-20 MPa |
| Porosity | 5-30% | 35-50% |
| Weather Resistance | Good | Poor, prone to erosion |
| Workability | Moderate | Easy |
| Typical Uses | Foundations, walls, decorative facades | Non-load bearing walls, interior partitions |
Introduction to Low-cost Construction Materials
Sandstone and chalk serve as popular low-cost construction materials due to their natural abundance and ease of extraction. Sandstone offers high durability and excellent load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for foundational structures in budget-sensitive projects. Chalk, while softer and less durable, provides insulation benefits and is cost-effective for non-structural elements, contributing to overall affordable building solutions.
Overview of Sandstone and Chalk
Sandstone is a durable sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized mineral particles, known for its high compressive strength and excellent weather resistance, making it suitable for load-bearing structures in low-cost construction. Chalk, a softer form of limestone primarily made up of calcite, is lightweight and easy to work with but has lower structural strength and higher porosity, which can affect durability and moisture resistance. Choosing between sandstone and chalk depends on project requirements such as load capacity, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
Geological Properties: Sandstone vs Chalk
Sandstone, composed primarily of compacted sand grains, exhibits higher compressive strength and durability compared to chalk, which is a soft, porous sedimentary rock made mostly of calcium carbonate. The dense, granular structure of sandstone provides better load-bearing capacity and weather resistance, making it more suitable for low-cost construction in structurally demanding environments. Chalk's lower density and higher porosity result in reduced strength and greater susceptibility to moisture damage, limiting its effectiveness in foundational or exterior applications.
Structural Strength and Durability Comparison
Sandstone offers higher structural strength and superior durability compared to chalk, making it more suitable for load-bearing low-cost construction projects. Chalk's porous composition results in lower compressive strength and increased susceptibility to weathering and erosion, limiting its long-term performance. Sandstone's denser grain structure provides enhanced resistance to environmental elements, ensuring greater building longevity and reduced maintenance costs.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Sandstone exhibits superior thermal insulation capabilities compared to chalk due to its denser mineral composition and lower porosity, which reduces heat transfer and maintains indoor comfort. Chalk's higher porosity results in increased thermal conductivity, making it less effective at insulating buildings and more prone to temperature fluctuations. Utilizing sandstone in low-cost construction enhances energy efficiency by stabilizing indoor temperatures and reducing heating and cooling demands.
Cost Analysis: Material and Labor
Sandstone offers a cost-effective option for low-cost construction due to its widespread availability and moderate quarrying expenses, while chalk generally incurs lower material costs but may require more extensive processing to enhance durability. Labor costs for sandstone construction can be higher owing to the stone's hardness and the need for skilled masons, whereas chalk's softness allows for easier handling and faster installation, reducing labor expenses. Overall, choosing between sandstone and chalk depends on balancing initial material costs with anticipated labor requirements and long-term maintenance in budget-sensitive projects.
Local Availability and Sourcing
Sandstone's widespread local availability in many regions makes it an economical choice for low-cost construction due to reduced transportation expenses and easier sourcing. Chalk, typically found in specific geological areas, may require longer supply chains, increasing overall costs despite its lower material price. Selecting sandstone or chalk largely depends on local geological deposits, directly impacting project budgets and material accessibility.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sandstone offers greater environmental benefits compared to chalk due to its durability and lower carbon footprint during extraction and processing, making it a more sustainable choice for low-cost construction. Chalk, being softer and more porous, often requires more frequent maintenance and replacement, increasing its long-term environmental impact and resource consumption. Utilizing locally sourced sandstone reduces transportation emissions and promotes sustainable building practices in budget-friendly construction projects.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Sandstone offers superior durability and weather resistance compared to chalk, making it a preferred choice for low-cost construction projects aiming for low maintenance and extended longevity. Chalk, being softer and more porous, tends to erode faster when exposed to moisture and requires more frequent repairs and protective coatings. Choosing sandstone reduces long-term upkeep costs and enhances structural stability in buildings subjected to varying environmental conditions.
Best Applications: Sandstone vs Chalk in Low-cost Projects
Sandstone excels in low-cost construction due to its durability, weather resistance, and ease of quarrying, making it ideal for structural walls, pavements, and foundations in budget-sensitive projects. Chalk, being softer and more porous, is better suited for interior non-load-bearing elements, temporary structures, or as a filler material where moisture resistance is less critical. Selecting sandstone or chalk depends on project requirements for strength, longevity, and environmental exposure, with sandstone offering superior long-term performance in exterior low-cost construction.
Infographic: Sandstone vs Chalk for Low-cost Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com