Quartzite offers superior durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for long-lasting monuments. Basalt provides high compressive strength and a dark, uniform appearance but is more prone to surface erosion in harsh climates.
Table of Comparison
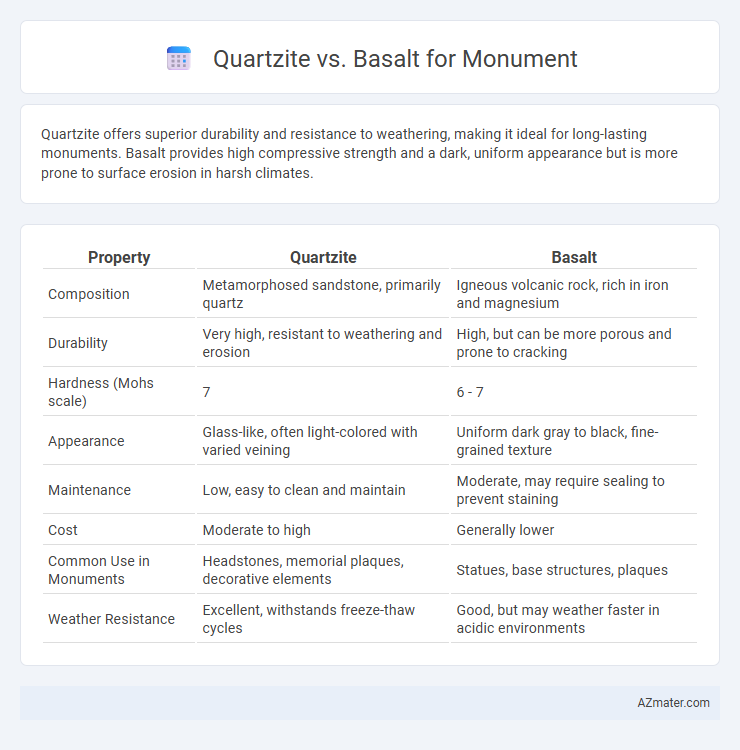
| Property | Quartzite | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Metamorphosed sandstone, primarily quartz | Igneous volcanic rock, rich in iron and magnesium |
| Durability | Very high, resistant to weathering and erosion | High, but can be more porous and prone to cracking |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 7 | 6 - 7 |
| Appearance | Glass-like, often light-colored with varied veining | Uniform dark gray to black, fine-grained texture |
| Maintenance | Low, easy to clean and maintain | Moderate, may require sealing to prevent staining |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower |
| Common Use in Monuments | Headstones, memorial plaques, decorative elements | Statues, base structures, plaques |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent, withstands freeze-thaw cycles | Good, but may weather faster in acidic environments |
Introduction to Quartzite and Basalt as Monument Materials
Quartzite, a metamorphic rock formed from sandstone, is highly valued for its exceptional hardness and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for monuments requiring long-lasting durability. Basalt, an igneous rock formed from rapid cooling of lava, offers a dense, fine-grained texture and remarkable compressive strength, lending itself well to monumental structures exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Both quartzite and basalt provide distinct aesthetic and structural benefits, with quartzite showcasing vibrant, crystalline patterns and basalt offering a sleek, uniform appearance.
Geological Formation and Properties
Quartzite forms through the metamorphism of quartz-rich sandstone under intense heat and pressure, resulting in a highly durable, hard, and dense rock with excellent resistance to weathering. Basalt originates from the rapid cooling of basaltic lava at the Earth's surface, characterized by its fine-grained texture, high density, and significant compressive strength. Quartzite's crystalline structure provides superior scratch and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting monuments, while basalt's uniform texture and dark color offer aesthetic appeal and resilience against environmental factors.
Physical Appearance and Color Variations
Quartzite exhibits a striking appearance with a glassy luster and a wide range of color variations from white and gray to pink and red, making it ideal for monuments that require both durability and aesthetic appeal. Basalt features a dense, fine-grained texture with a predominantly dark color palette, including deep black, gray, and occasionally greenish hues, lending a solemn and powerful presence to memorials. The distinct color diversity in quartzite contrasts with the consistent, muted tones of basalt, influencing the visual impact and design flexibility of monuments.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Quartzite exhibits superior durability and exceptional weather resistance, making it an ideal choice for monuments exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its high quartz content and interlocking crystal structure provide excellent resistance to abrasion, chemical weathering, and temperature fluctuations compared to basalt. Basalt, while dense and strong, is more susceptible to chemical weathering and erosion over time due to its volcanic origin and finer grain texture.
Workability and Sculpting Ease
Quartzite offers excellent durability and a smooth surface, making it highly suitable for detailed sculpting and intricate monument work. Basalt, while extremely hard and dense, can be more challenging to work with due to its toughness and tendency to fracture unpredictably during shaping. Sculptors often prefer quartzite for ease of carving as it balances hardness with workability, ensuring fine details remain intact without excessive tool wear.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Quartzite offers superior durability and low maintenance requirements due to its dense, non-porous structure that resists weathering and staining, making it ideal for long-lasting monuments. Basalt is also durable but tends to be more porous and susceptible to erosion and moss growth, necessitating more frequent cleaning and sealing to preserve its appearance. Both stones provide excellent longevity, but quartzite's resistance to environmental wear ensures a longer lifespan with minimal upkeep.
Cost Comparison: Quartzite vs Basalt
Quartzite generally commands a higher price than basalt due to its durability, hardness, and aesthetic appeal, making it a premium choice for monuments. Basalt offers a more cost-effective option with good weather resistance and strength, often preferred for budget-conscious projects. Cost variations depend on quarry location, processing methods, and installation complexity, but quartzite's superior longevity can translate to lower long-term maintenance expenses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Quartzite, a natural metamorphic rock composed primarily of quartz, offers high durability with minimal environmental degradation due to its abundant availability and low chemical reactivity. Basalt, a volcanic igneous rock, provides excellent sustainability attributes through its carbon sequestration abilities and longevity in harsh outdoor conditions. The environmental impact of using quartzite or basalt in monuments largely depends on quarrying methods, with basalt often favored for its lower carbon footprint and enhanced resistance to weathering.
Popular Uses of Quartzite and Basalt in Monuments
Quartzite is favored for monuments due to its high durability, resistance to weathering, and appealing crystalline texture, making it ideal for statues, memorials, and architectural cladding. Basalt is commonly used in monuments for its dense, fine-grained structure and dark color, providing a strong and visually striking base or foundation stone. Both materials offer longevity, but quartzite's aesthetic appeal and basalt's strength make each suitable for different monument design needs.
Choosing the Right Stone for Lasting Monuments
Quartzite offers exceptional durability and resistance to weathering, making it an ideal choice for lasting monuments exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its natural hardness and fine-grained texture provide a polished, elegant appearance that maintains longevity over time. Basalt, while strong and dense, often suits monumental structures requiring heavy mass and strength, but it can be more prone to surface erosion compared to quartzite in certain climates.
Infographic: Quartzite vs Basalt for Monument
 azmater.com
azmater.com