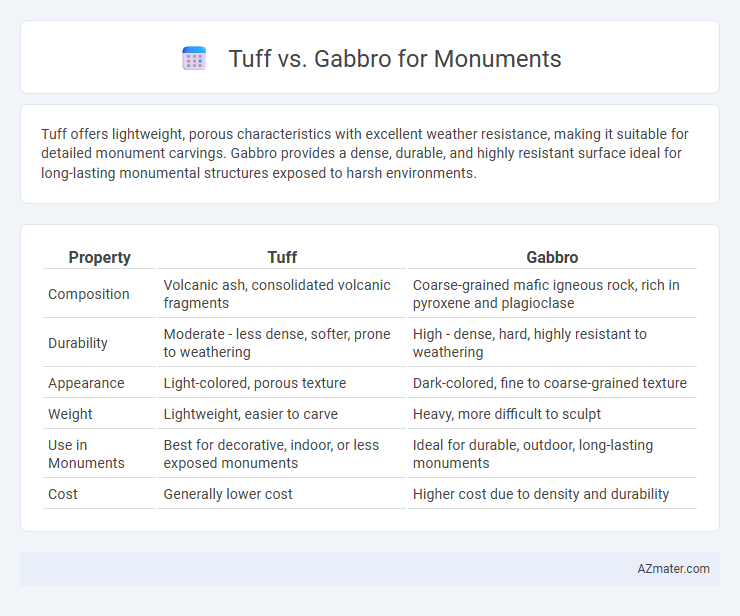
Tuff offers lightweight, porous characteristics with excellent weather resistance, making it suitable for detailed monument carvings. Gabbro provides a dense, durable, and highly resistant surface ideal for long-lasting monumental structures exposed to harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tuff | Gabbro |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Volcanic ash, consolidated volcanic fragments | Coarse-grained mafic igneous rock, rich in pyroxene and plagioclase |
| Durability | Moderate - less dense, softer, prone to weathering | High - dense, hard, highly resistant to weathering |
| Appearance | Light-colored, porous texture | Dark-colored, fine to coarse-grained texture |
| Weight | Lightweight, easier to carve | Heavy, more difficult to sculpt |
| Use in Monuments | Best for decorative, indoor, or less exposed monuments | Ideal for durable, outdoor, long-lasting monuments |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to density and durability |
Introduction to Tuff and Gabbro as Monument Stones
Tuff and Gabbro are widely used as monument stones due to their unique geological characteristics and durability. Tuff, a volcanic rock formed from consolidated volcanic ash, offers a lightweight and workable surface with a range of earthy colors ideal for detailed carving and weather-resistant monuments. Gabbro, an intrusive igneous rock with coarse grains composed mainly of plagioclase feldspar and pyroxene, provides a dense, hard surface known for its strength and resistance to erosion, making it suitable for enduring, polished monument structures.
Geological Formation and Composition of Tuff
Tuff is a volcaniclastic rock formed from consolidated volcanic ash and fragmented material, characterized by its porosity and lighter weight compared to gabbro, which is a dense, coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock composed mainly of plagioclase feldspar and pyroxene. The geological formation of tuff involves explosive volcanic eruptions that eject ash and debris, which then settle and lithify into a rock, making it more susceptible to weathering but easier to carve for monuments. Gabbro's intrusive origin and mineral composition provide superior durability and resistance to erosion, often preferred for long-lasting, monumental structures requiring high strength.
Geological Formation and Composition of Gabbro
Tuff, a volcanic rock formed from consolidated ash deposits during explosive eruptions, contrasts sharply with gabbro, an intrusive igneous rock crystallized slowly beneath the Earth's surface, resulting in coarse-grained textures. Gabbro's composition primarily consists of plagioclase feldspar, pyroxene, and minor olivine, contributing to its dense, durable nature ideal for monuments. The slow cooling process in gabbro's geological formation yields interlocking crystals that enhance its strength and weather resistance, making it a preferred choice over tuff in monumental architecture.
Physical Properties: Tuff vs Gabbro
Tuff is a lightweight, porous volcanic rock with low density and relatively low hardness, making it easier to carve but less durable for monuments exposed to weathering. Gabbro is a dense, coarse-grained igneous rock known for its high compressive strength and resistance to abrasion, providing superior longevity and structural stability for monumental applications. The physical durability and hardness of gabbro make it preferable for monuments requiring long-term preservation and resistance to environmental degradation compared to tuff.
Durability and Weather Resistance Comparison
Gabbro demonstrates superior durability and weather resistance compared to tuff, making it a preferred choice for monuments exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its coarse-grained, intrusive igneous composition provides exceptional strength and resistance to erosion, while tuff, being a softer, volcanic ash-based rock, tends to weather and degrade more quickly. For long-lasting monuments, gabbro's low porosity and high compressive strength ensure better performance against freeze-thaw cycles and acid rain exposure.
Aesthetic Features and Color Variations
Tuff offers a unique aesthetic characterized by its porous texture and soft, earthy tones ranging from light yellows to muted browns, which creates a warm, natural appearance ideal for rustic monuments. Gabbro, on the other hand, presents a dense, coarse-grained surface with deep, rich color variations including dark greens, blacks, and blues, delivering a sleek, polished finish suitable for modern or formal monuments. The choice between Tuff and Gabbro depends on desired monument style, with Tuff emphasizing organic irregularity and warmth, while Gabbro highlights durability and dramatic color depth.
Workability and Carving Ease
Tuff offers superior workability for monuments due to its softer, volcanic ash composition, enabling intricate carving with less effort and reduced tool wear. Gabbro, being a coarse-grained, dense igneous rock, presents challenges in carving, requiring more time and specialized tools to achieve detailed finishes. The ease of shaping tuff makes it a preferred choice for sculptors seeking fine detail and faster fabrication in monumental art.
Cost Analysis: Tuff vs Gabbro for Monuments
Tuff offers a more cost-effective option for monuments due to its lower extraction and processing expenses compared to gabbro, which is denser and requires more intensive quarrying techniques. While gabbro provides superior durability and a polished finish, its higher material and transportation costs can significantly increase overall monument expenses. Selecting tuff reduces initial investment without compromising aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for budget-conscious monument projects.
Historical and Contemporary Uses in Monuments
Tuff and gabbro have distinct historical and contemporary uses in monuments due to their geological properties; tuff, a volcanic rock, was favored in ancient Roman and Etruscan architecture for its lightweight and workable texture, enabling intricate carving and large-scale structures like the Colosseum. Gabbro, an intrusive igneous rock with a coarse-grained texture, has been extensively used in modern monuments and memorials for its durability, dark coloration, and polished finish, providing a strong aesthetic contrast in architectural design. Both stones continue to be selected based on their unique qualities, with tuff symbolizing historical craftsmanship and gabbro representing lasting strength and modern elegance in monument construction.
Choosing the Right Stone: Tuff or Gabbro for Your Monument
Tuff offers a unique volcanic texture and softer workability, ideal for intricate carvings on monuments, while gabbro provides superior durability and a polished finish suitable for long-lasting outdoor memorials. Selecting between tuff and gabbro depends on the monument's exposure to weather, desired aesthetic, and budget constraints. Gabbro's dense composition ensures resistance to erosion, making it a preferred choice for monuments requiring strength and low maintenance.
Infographic: Tuff vs Gabbro for Monument
 azmater.com
azmater.com