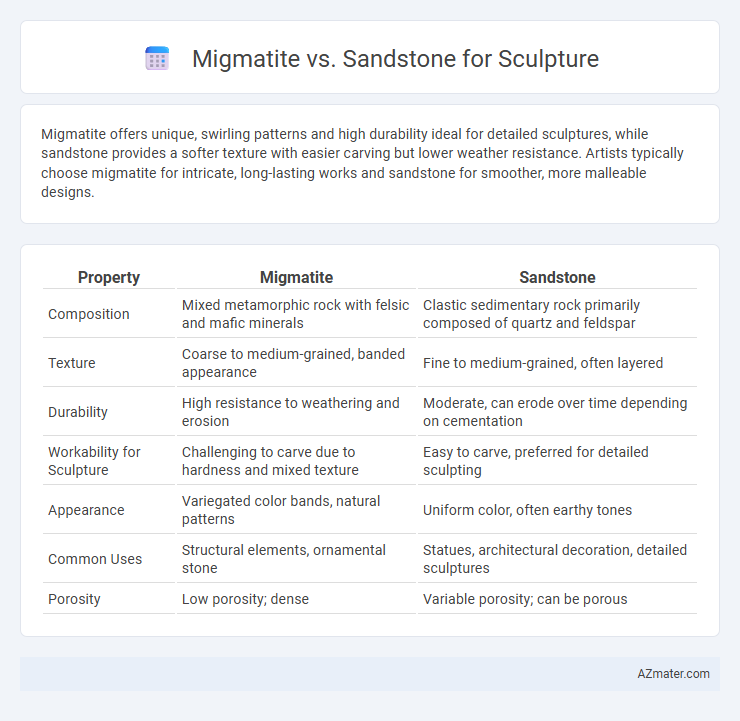
Migmatite offers unique, swirling patterns and high durability ideal for detailed sculptures, while sandstone provides a softer texture with easier carving but lower weather resistance. Artists typically choose migmatite for intricate, long-lasting works and sandstone for smoother, more malleable designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Migmatite | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Mixed metamorphic rock with felsic and mafic minerals | Clastic sedimentary rock primarily composed of quartz and feldspar |
| Texture | Coarse to medium-grained, banded appearance | Fine to medium-grained, often layered |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering and erosion | Moderate, can erode over time depending on cementation |
| Workability for Sculpture | Challenging to carve due to hardness and mixed texture | Easy to carve, preferred for detailed sculpting |
| Appearance | Variegated color bands, natural patterns | Uniform color, often earthy tones |
| Common Uses | Structural elements, ornamental stone | Statues, architectural decoration, detailed sculptures |
| Porosity | Low porosity; dense | Variable porosity; can be porous |
Introduction to Migmatite and Sandstone
Migmatite is a composite rock formed under high-temperature conditions, exhibiting a blend of metamorphic and igneous features that provide unique textures ideal for detailed sculpture work. Sandstone, a clastic sedimentary rock primarily composed of quartz and feldspar, offers versatility with its fine to coarse grains and ease of carving, favored by sculptors for its natural color variations and durability. Both materials present distinct characteristics: migmatite's complex patterns enhance aesthetic appeal, while sandstone's workable softness enables intricate designs.
Geological Origins of Migmatite and Sandstone
Migmatite forms through high-grade regional metamorphism involving partial melting of pre-existing rocks, resulting in a composite of igneous and metamorphic textures. Sandstone originates from the lithification of sand-sized mineral particles, primarily quartz, deposited in sedimentary environments such as rivers, beaches, and deserts. The contrasting geological origins affect their suitability for sculpture, with migmatite offering intricate mineral patterns and durability, while sandstone provides relative softness and ease of carving.
Physical Properties Comparison
Migmatite, a metamorphic rock with a mixed composition of igneous and sedimentary layers, offers superior hardness and durability compared to sandstone, which is a softer sedimentary rock composed mainly of quartz or feldspar grains. The high density and resistance to weathering of migmatite make it ideal for detailed and long-lasting sculptures, while sandstone's porosity and lower compressive strength often lead to faster erosion and surface wear. Sculptors favor migmatite when strength and fine detail retention are critical, whereas sandstone is chosen for ease of carving and more affordable material costs.
Workability and Sculpting Techniques
Migmatite offers a unique blend of metamorphic and igneous properties, making it moderately hard and durable but challenging to carve with fine detail compared to sandstone. Sandstone, with its granular texture and softer composition, provides excellent workability allowing for intricate sculpting techniques such as chiseling and sanding. Sculptors often prefer sandstone for its ease of shaping and ability to hold fine textures, while migmatite requires more robust tools and techniques to achieve precise forms.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Migmatite offers superior durability and weather resistance compared to sandstone due to its mixed metamorphic and igneous origins, which provide enhanced strength and resistance to erosion. Sandstone, being a sedimentary rock, is more porous and susceptible to weathering processes like frost damage and acid rain, making it less ideal for outdoor sculptures exposed to harsh environments. Sculptors seeking long-lasting works for exterior display often prefer migmatite for its toughness and ability to withstand environmental stressors over extended periods.
Aesthetic Qualities and Visual Appeal
Migmatite offers a unique aesthetic with its intricate blend of igneous and metamorphic textures, creating a visually striking swirled pattern that enhances sculptural depth and complexity. Sandstone provides a warm, natural appeal with its granular texture and range of earthy tones, allowing for smooth, matte finishes that highlight organic forms. Sculptors prefer migmatite for dramatic visual impact while sandstone is favored for its subtle elegance and textural versatility.
Historical Uses in Sculpture
Migmatite, a metamorphic rock with intricate mixed textures, has been historically favored for sculptures requiring durability and unique visual patterns, often seen in ancient and modern monumental works. Sandstone, softer and easier to carve, has been widely used in classical sculptures and architectural decorations due to its accessibility and weathering properties, especially in regions like Egypt and India. The choice between migmatite and sandstone in sculpture largely depended on the desired longevity and detail, with migmatite offering resistance to erosion and sandstone allowing finer detailing.
Cost and Availability
Migmatite typically costs more than sandstone due to its complex formation and rarity, making it less readily available for sculpture projects. Sandstone is widely accessible and generally more affordable, favored by artists for its ease of carving and consistent supply. Sculptors often select sandstone when budget constraints and material availability are primary considerations.
Environmental Impact of Quarrying
Migmatite quarrying significantly disrupts local ecosystems due to its extraction from deep, metamorphic rock formations, often leading to extensive landscape alteration and habitat loss. Sandstone quarrying, while generally less invasive, can cause soil erosion and sediment runoff affecting nearby waterways. Both materials require energy-intensive mining processes, but sandstone's sedimentary nature often allows for more sustainable, surface-level extraction compared to the deeper, more destructive mining of migmatite.
Choosing the Right Stone for Sculpture
Migmatite offers a unique blend of metamorphic durability and intricate veining, making it ideal for sculptures requiring both strength and detailed texture, while sandstone is softer and easier to carve, preferred for intricate designs but less resistant to weathering. Sculptors should select migmatite for outdoor or large-scale projects demanding longevity and structural integrity, whereas sandstone suits indoor sculptures or pieces emphasizing fine detail and smooth finishes. Evaluating factors such as hardness, grain structure, and environmental exposure ensures the chosen stone enhances both the artistic vision and durability of the sculpture.
Infographic: Migmatite vs Sandstone for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com