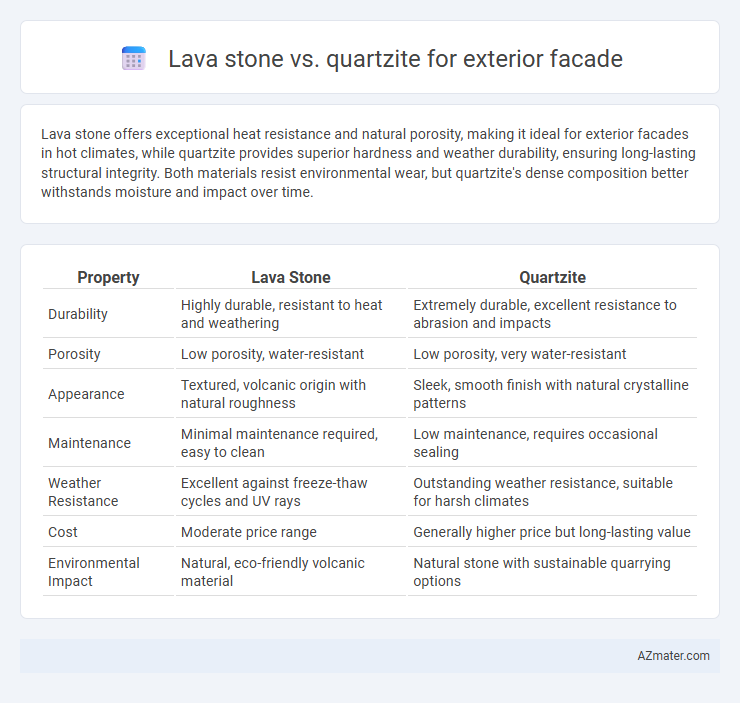
Lava stone offers exceptional heat resistance and natural porosity, making it ideal for exterior facades in hot climates, while quartzite provides superior hardness and weather durability, ensuring long-lasting structural integrity. Both materials resist environmental wear, but quartzite's dense composition better withstands moisture and impact over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lava Stone | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to heat and weathering | Extremely durable, excellent resistance to abrasion and impacts |
| Porosity | Low porosity, water-resistant | Low porosity, very water-resistant |
| Appearance | Textured, volcanic origin with natural roughness | Sleek, smooth finish with natural crystalline patterns |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance required, easy to clean | Low maintenance, requires occasional sealing |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent against freeze-thaw cycles and UV rays | Outstanding weather resistance, suitable for harsh climates |
| Cost | Moderate price range | Generally higher price but long-lasting value |
| Environmental Impact | Natural, eco-friendly volcanic material | Natural stone with sustainable quarrying options |
Introduction to Lava Stone and Quartzite
Lava stone, a natural volcanic rock known for its durability and thermal resistance, offers a rugged, textured surface ideal for exterior facades exposed to harsh weather conditions. Quartzite, a metamorphic rock formed from sandstone, is prized for its hardness, aesthetic appeal, and resistance to abrasion, making it a popular choice for facade cladding with a sleek, natural stone finish. Both materials provide unique structural and visual benefits, with lava stone excelling in heat insulation and quartzite offering exceptional strength and elegance.
Key Differences Between Lava Stone and Quartzite
Lava stone offers superior heat resistance and natural porosity, making it ideal for exterior facades in hot climates, while quartzite boasts exceptional hardness and durability, resisting scratches and weathering more effectively. Lava stone's volcanic origin provides a unique porous texture and lightweight properties, whereas quartzite, a metamorphic rock, is denser and less absorbent, contributing to its longevity under harsh environmental conditions. The color palette also differs, with lava stone featuring predominantly dark, earthy tones, and quartzite available in a wider range of hues including whites, grays, and blues, influencing aesthetic choices for facade design.
Durability Comparison for Exterior Facades
Lava stone exhibits exceptional durability against weathering, thermal shock, and abrasion, making it highly resistant to cracks and fading on exterior facades. Quartzite offers superior hardness and resistance to acidic rainfall, UV exposure, and freeze-thaw cycles, ensuring long-lasting structural integrity and minimal maintenance. Both materials provide robust exterior facade solutions, but quartzite typically outperforms in hardness, while lava stone excels in thermal resilience.
Weather Resistance: Lava Stone vs Quartzite
Lava stone offers exceptional weather resistance for exterior facades due to its volcanic origin, which provides natural durability against extreme temperatures, moisture, and UV radiation. Quartzite, a metamorphic rock, also exhibits superior weather resistance with its dense composition, enabling it to withstand harsh weather conditions and resist erosion and fading over time. Both materials are ideal for exterior applications, but lava stone's lightweight and porous structure may offer better thermal insulation and moisture drainage compared to the denser, less porous quartzite.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Versatility
Lava stone offers a unique, porous texture with deep natural hues that enhance the rugged, volcanic aesthetic of exterior facades, making it ideal for rustic and contemporary designs. Quartzite features a smooth, crystalline surface with vibrant color variations and high durability, allowing for sleek modern facades and intricate architectural detailing. Both materials provide exceptional weather resistance, but quartzite's polished finish is preferred for refined, minimalist designs while lava stone emphasizes organic, earthy appeal.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Lava stone offers exceptional durability with low maintenance needs, being highly resistant to weathering, staining, and erosion, making it ideal for exterior facades in harsh climates. Quartzite, known for its natural hardness and resistance to abrasion, requires periodic sealing to maintain its appearance and protect against moisture infiltration, which impacts its maintenance frequency. Both materials provide long-lasting facades, but lava stone generally demands less upkeep over time, enhancing its cost-effectiveness for exterior applications.
Cost Analysis: Lava Stone vs Quartzite
Lava stone for exterior facades typically offers a more budget-friendly option due to its abundant availability and lower quarrying costs compared to quartzite. Quartzite, being a harder and more durable natural stone, commands higher pricing driven by more intensive extraction and finishing processes. Maintenance expenses for both materials are relatively low, but initial cost differences make lava stone preferable for large-scale projects seeking cost savings without sacrificing aesthetic appeal.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lava stone offers superior environmental benefits over quartzite for exterior facades due to its natural formation through volcanic activity, requiring minimal processing and generating lower carbon emissions. Quartzite extraction and processing involve significant energy consumption and habitat disruption, increasing its environmental footprint. Utilizing lava stone supports sustainable construction by leveraging abundant, durable materials with low embodied energy and enhanced thermal properties, contributing to energy efficiency in building design.
Installation Process and Practical Considerations
Lava stone features a porous texture that requires specialized adhesives and skilled labor for secure exterior facade installation, while quartzite's dense, non-porous nature allows for standard mechanical anchoring or mortar application, simplifying the process. Lava stone demands careful sealing to prevent weather-induced deterioration, increasing maintenance frequency, whereas quartzite offers exceptional durability and low porosity, making it highly resistant to staining and weathering in outdoor environments. Cost implications vary as lava stone installation involves higher labor due to its fragility and custom cutting needs, whereas quartzite's hardness may require specialized cutting tools but overall offers longer-term practicality with minimal upkeep.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Exterior Facade
Lava stone offers exceptional durability and natural heat resistance, making it ideal for exterior facades exposed to extreme weather conditions. Quartzite provides a harder surface with a brilliant natural gloss, ensuring longevity and a sleek appearance while resisting erosion and staining. Choosing between lava stone and quartzite depends on your climate, desired aesthetic, and maintenance preferences for a resilient and visually appealing exterior.
Infographic: Lava stone vs Quartzite for Exterior facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com