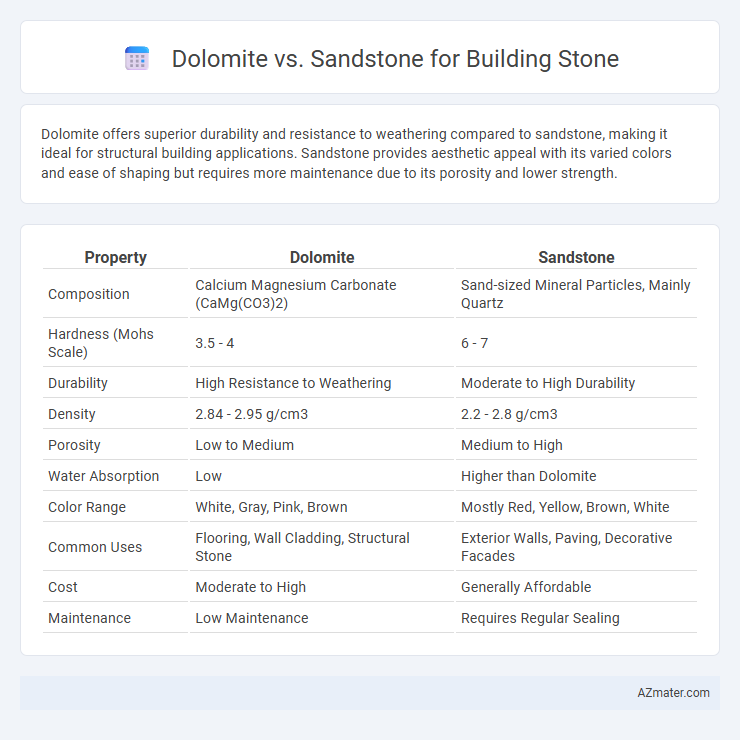
Dolomite offers superior durability and resistance to weathering compared to sandstone, making it ideal for structural building applications. Sandstone provides aesthetic appeal with its varied colors and ease of shaping but requires more maintenance due to its porosity and lower strength.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dolomite | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium Magnesium Carbonate (CaMg(CO3)2) | Sand-sized Mineral Particles, Mainly Quartz |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 3.5 - 4 | 6 - 7 |
| Durability | High Resistance to Weathering | Moderate to High Durability |
| Density | 2.84 - 2.95 g/cm3 | 2.2 - 2.8 g/cm3 |
| Porosity | Low to Medium | Medium to High |
| Water Absorption | Low | Higher than Dolomite |
| Color Range | White, Gray, Pink, Brown | Mostly Red, Yellow, Brown, White |
| Common Uses | Flooring, Wall Cladding, Structural Stone | Exterior Walls, Paving, Decorative Facades |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Generally Affordable |
| Maintenance | Low Maintenance | Requires Regular Sealing |
Introduction to Building Stones
Dolomite and sandstone are both popular building stones valued for their durability and aesthetic appeal in construction. Dolomite, a carbonate rock composed primarily of calcium magnesium carbonate, offers greater resistance to acid rain and weathering compared to sandstone, which is a sedimentary rock made mainly of quartz grains cemented by silica, calcium carbonate, or iron oxides. Sandstone's versatility and ease of carving make it ideal for decorative and structural elements, while dolomite's hardness and density provide superior strength for foundational and load-bearing applications.
Composition: Dolomite vs Sandstone
Dolomite is primarily composed of calcium magnesium carbonate (CaMg(CO3)2), whereas sandstone consists mainly of sand-sized mineral particles, predominantly quartz and feldspar. The crystalline structure of dolomite provides greater hardness and chemical resistance compared to the more porous and granular composition of sandstone. These compositional differences influence their durability, weathering properties, and suitability for various construction applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Dolomite has a higher hardness of 3.5-4 on the Mohs scale compared to sandstone's 6-7, making sandstone more resistant to scratching and abrasion. Sandstone typically exhibits higher porosity, ranging from 5% to 30%, while dolomite's porosity generally falls between 0.1% and 10%, affecting durability and water absorption. Dolomite's specific gravity ranges from 2.84 to 2.86, slightly higher than sandstone's 2.2 to 2.8, indicating denser material suited for structural applications.
Durability and Strength
Dolomite exhibits higher durability and compressive strength compared to sandstone, making it more resistant to weathering and wear in construction. Its crystalline structure provides superior load-bearing capacity, often exceeding 200 MPa, whereas typical sandstone strength ranges from 20 to 170 MPa depending on composition. Due to its robustness and low porosity, dolomite is preferred for high-stress structural applications, while sandstone is better suited for decorative or less demanding uses.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Dolomite offers a refined aesthetic appeal with its subtle grain texture and predominantly light gray to white color variations, making it ideal for elegant architectural designs. Sandstone provides a broader palette of warm hues, including reds, yellows, and browns, contributing to rustic and natural aesthetic qualities. Both stones vary in porosity and surface finish, influencing their suitability for different exterior or interior building applications.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Dolomite exhibits superior weather resistance compared to sandstone due to its dense crystalline structure and higher calcium magnesium carbonate content, making it less porous and more durable in harsh climatic conditions. Sandstone, while aesthetically appealing with its varied colors and textures, tends to absorb more moisture, leading to increased susceptibility to weathering and erosion over time. Consequently, dolomite offers enhanced longevity for building stone applications, especially in environments with frequent freeze-thaw cycles and acid rain exposure.
Workability and Ease of Shaping
Dolomite offers higher durability and resistance to weathering but requires more effort in cutting and shaping compared to sandstone, which is softer and easier to work with. Sandstone's granular texture allows for smoother carvings and faster processing, making it a preferred choice for intricate architectural details. The choice between dolomite and sandstone depends on balancing the need for structural strength against the ease of shaping and finishing in construction projects.
Maintenance Requirements
Dolomite requires less frequent maintenance than sandstone due to its higher hardness and resistance to weathering and chemical erosion, reducing cleaning and repair efforts over time. Sandstone, being softer and more porous, demands regular sealing to prevent moisture infiltration, staining, and surface deterioration, increasing upkeep costs. Choosing dolomite can lead to lower long-term maintenance expenses in building stone applications where durability and resistance to environmental factors are critical.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Dolomite typically incurs higher costs than sandstone due to its denser composition and the complex quarrying process required, impacting overall project budgets. Sandstone is generally more abundant and widely available, resulting in lower transportation expenses and greater accessibility for construction needs. Cost-effectiveness of sandstone versus dolomite largely depends on regional supply variations and specific structural requirements.
Best Applications for Dolomite and Sandstone
Dolomite, known for its strength and resistance to weathering, is best suited for construction projects requiring durable and load-bearing materials such as foundations, retaining walls, and road base layers. Sandstone, with its aesthetic appeal and workability, excels in decorative applications including facades, flooring, and interior cladding where texture and color variation are desirable. Both stones provide excellent thermal insulation properties, but dolomite's higher density makes it preferable for structural uses, while sandstone is favored in architectural finishes and landscaping elements.
Infographic: Dolomite vs Sandstone for Building Stone
 azmater.com
azmater.com