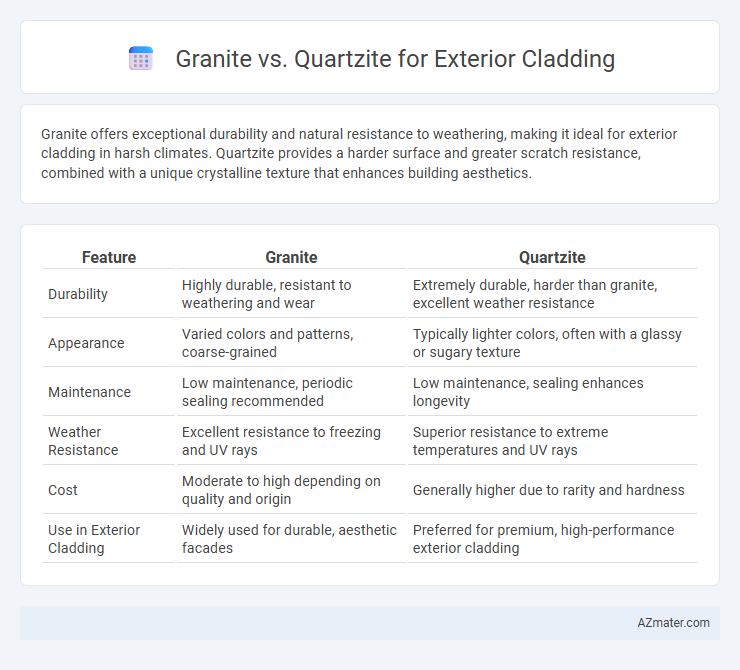
Granite offers exceptional durability and natural resistance to weathering, making it ideal for exterior cladding in harsh climates. Quartzite provides a harder surface and greater scratch resistance, combined with a unique crystalline texture that enhances building aesthetics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Granite | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to weathering and wear | Extremely durable, harder than granite, excellent weather resistance |
| Appearance | Varied colors and patterns, coarse-grained | Typically lighter colors, often with a glassy or sugary texture |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, periodic sealing recommended | Low maintenance, sealing enhances longevity |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent resistance to freezing and UV rays | Superior resistance to extreme temperatures and UV rays |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on quality and origin | Generally higher due to rarity and hardness |
| Use in Exterior Cladding | Widely used for durable, aesthetic facades | Preferred for premium, high-performance exterior cladding |
Introduction to Granite and Quartzite for Exterior Cladding
Granite and quartzite are popular natural stones used for exterior cladding due to their durability and aesthetic appeal. Granite, an igneous rock, is renowned for its hardness, resistance to weathering, and variety of color patterns, making it ideal for long-lasting facades. Quartzite, a metamorphic rock formed from sandstone, offers exceptional strength and resistance to abrasion and chemical damage, providing a sleek and modern exterior surface.
Geological Formation and Material Properties
Granite, an igneous rock formed from slowly cooled magma, consists mainly of quartz, feldspar, and mica, granting it high durability and resistance to weathering for exterior cladding. Quartzite originates from metamorphosed sandstone subjected to intense heat and pressure, resulting in a dense, non-porous material with superior hardness and resistance to abrasion. Both materials offer excellent structural integrity; however, quartzite's metamorphic formation often provides enhanced strength and a slightly higher resistance to acid rain compared to granite.
Aesthetic Comparison: Colors, Patterns, and Finishes
Granite offers a broad spectrum of colors ranging from deep blacks and rich browns to subtle pinks and grays, featuring granular patterns with natural flecks and speckles that create a timeless, rugged aesthetic for exterior cladding. Quartzite provides a more crystalline appearance with brighter, often white or light grey tones accented by bold veining and linear patterns, delivering a refined and elegant surface ideal for modern architectural designs. Both materials support various finishes including polished, honed, and flamed, enhancing durability while allowing customization of texture and reflectivity to suit diverse exterior applications.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Granite and quartzite are both highly durable materials ideal for exterior cladding, but granite exhibits superior weather resistance due to its lower porosity and natural ability to withstand freezing and thawing cycles. Quartzite, though harder than granite, can sometimes be more prone to surface etching and discoloration when exposed to prolonged moisture and harsh UV rays. For long-term durability in variable climates, granite's resistance to abrasion, chemical weathering, and environmental pollutants makes it a preferred choice for exterior applications.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Granite offers superior durability and low maintenance for exterior cladding, resisting weathering, stains, and scratches due to its dense composition and natural hardness. Quartzite, while slightly harder and more resistant to heat, requires periodic sealing to prevent moisture infiltration and potential surface degradation over time. Both materials provide excellent longevity, but granite's minimal upkeep makes it a preferred choice for long-lasting, weather-resistant exterior applications.
Installation Considerations and Techniques
Granite requires precise anchoring systems due to its density and weight, making mechanical fasteners or mortar adhesion crucial for exterior cladding stability. Quartzite, often more brittle, demands careful handling and specialized cutting tools to prevent fractures during installation, with emphasis on flexible adhesives to accommodate thermal expansion. Both materials benefit from ventilated rainscreen systems to enhance durability and moisture management in exterior applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Granite for exterior cladding offers durability and natural weather resistance, with moderate environmental impact due to quarrying and energy-intensive processing. Quartzite, composed mainly of natural quartz, provides high strength and resilience, often sourced more sustainably with less chemical processing involved. Both materials have long lifespans that reduce the need for frequent replacement, supporting sustainable building practices through durability and low maintenance requirements.
Cost Analysis and Budgeting Factors
Granite generally costs between $60 and $100 per square foot, making it a mid-range option for exterior cladding, whereas quartzite prices range from $70 to $120 per square foot due to its rarity and unique color variations. Budgeting for granite includes considering its durability and lower maintenance, which can reduce long-term expenses, while quartzite may require higher initial investment but offers superior resistance to weathering and fading. Labor costs, slab thickness, and installation complexity also impact the overall budget, with granite often easier to work with compared to the harder, more brittle quartzite.
Common Applications in Modern Architecture
Granite and quartzite are highly favored for exterior cladding in modern architecture due to their durability and aesthetic appeal. Granite's resistance to weathering and its wide range of colors and textures make it ideal for facades, retaining walls, and decorative elements in commercial and residential buildings. Quartzite offers superior hardness and a natural glassy finish, commonly used in high-traffic exterior surfaces and accent walls that require both elegance and long-term performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Stone for Your Project
Granite offers exceptional durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for exterior cladding in harsh climates. Quartzite provides a more uniform appearance and superior hardness, enhancing longevity and scratch resistance for exterior surfaces. Selecting between granite and quartzite depends on balancing aesthetic preferences, performance under environmental conditions, and maintenance requirements for your specific project.
Infographic: Granite vs Quartzite for Exterior Cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com