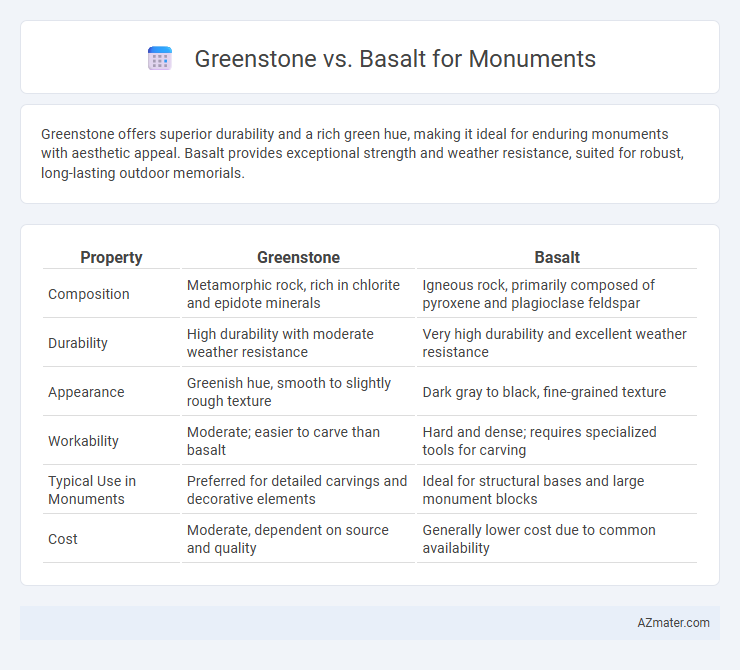
Greenstone offers superior durability and a rich green hue, making it ideal for enduring monuments with aesthetic appeal. Basalt provides exceptional strength and weather resistance, suited for robust, long-lasting outdoor memorials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Greenstone | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Metamorphic rock, rich in chlorite and epidote minerals | Igneous rock, primarily composed of pyroxene and plagioclase feldspar |
| Durability | High durability with moderate weather resistance | Very high durability and excellent weather resistance |
| Appearance | Greenish hue, smooth to slightly rough texture | Dark gray to black, fine-grained texture |
| Workability | Moderate; easier to carve than basalt | Hard and dense; requires specialized tools for carving |
| Typical Use in Monuments | Preferred for detailed carvings and decorative elements | Ideal for structural bases and large monument blocks |
| Cost | Moderate, dependent on source and quality | Generally lower cost due to common availability |
Introduction: Greenstone vs Basalt for Monuments
Greenstone and basalt are both durable igneous rocks commonly used in monument construction, valued for their strength and weather resistance. Greenstone, typically metamorphosed volcanic rock, exhibits a fine grain and rich greenish hue, enhancing the aesthetic appeal and symbolic significance of memorials. Basalt, a dense, dark volcanic rock, offers exceptional longevity and a smooth, polished finish, making it a preferred choice for enduring monuments exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Geological Origins and Composition
Greenstone originates from metamorphosed volcanic and sedimentary rocks rich in chlorite, epidote, and actinolite minerals, commonly formed in ancient volcanic arcs. Basalt is an extrusive igneous rock primarily composed of plagioclase feldspar and pyroxene, originating from rapid cooling of lava at the Earth's surface. The distinct mineral compositions and formation processes influence their durability and aesthetic qualities for monuments.
Physical Properties Comparison
Greenstone exhibits high durability, moderate hardness, and excellent weather resistance, making it suitable for long-lasting monuments. Basalt features superior compressive strength, finer grain texture, and higher density, which contributes to its robustness and resistance to erosion. Both stones offer exceptional physical properties, but basalt generally provides enhanced strength and longevity for outdoor monumental applications.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Greenstone exhibits high durability with excellent resistance to weathering, making it suitable for monuments exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Basalt is also known for its exceptional strength and resistance to abrasion, often outperforming greenstone in freeze-thaw cycles and chemical weathering. Both stones provide long-lasting monument surfaces, but basalt's denser structure offers superior longevity in extreme climates.
Aesthetic Qualities and Color Differences
Greenstone exhibits a unique, deep green hue with subtle mineral flecks that provide a polished, elegant finish ideal for monuments seeking a natural yet refined appearance. Basalt, characterized by its uniform dark gray to black color, offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with a matte or slightly rough texture that emphasizes durability and minimalism. The choice between Greenstone and Basalt for monuments hinges on desired visual impact, with Greenstone appealing to those favoring vibrant, earth-toned elegance and Basalt suiting designs prioritizing monochromatic strength and contemporary style.
Historical Significance in Monument Building
Greenstone has been historically valued in monument building for its durability and distinctive green hue, often associated with ceremonial and royal artifacts in ancient cultures such as the Maori in New Zealand. Basalt, known for its dense, fine-grained structure, was commonly used in monumental architecture across civilizations like the Egyptians and Mesopotamians due to its longevity and ability to withstand weathering. Both materials embody cultural significance, with greenstone symbolizing spiritual connection and basalt representing strength and permanence in historical monuments.
Workability and Carving Characteristics
Greenstone offers exceptional workability for monuments due to its fine-grained texture, allowing detailed and intricate carvings with smooth finishes. Basalt, while durable and dense, presents more challenges in carving because of its hardness, requiring specialized tools and techniques for precision work. The choice between greenstone and basalt impacts the intricacy and refinement of monument designs, with greenstone favored for elaborate sculptures and basalt preferred for robust, enduring structures.
Cost and Availability of Materials
Greenstone offers moderate cost advantages due to its relative abundance in certain regions, making it more accessible for local monument projects. Basalt, while generally more expensive due to extraction and transport challenges, provides superior durability that can offset initial expenditure through long-term maintenance savings. Material availability heavily depends on geographic location, with greenstone more common in specific areas and basalt found globally but distributed unevenly.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Greenstone and basalt offer distinct environmental advantages for monuments, with greenstone often sourced locally, reducing transportation emissions and supporting regional ecosystems. Basalt's durability and natural resistance to weathering extend monument lifespan, minimizing the need for frequent restoration and associated resource consumption. Both materials are abundant and non-toxic, but greenstone's lower embodied energy during extraction and processing gives it a slight sustainability edge in eco-conscious construction.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Greenstone and Basalt
Greenstone offers unique aesthetic appeal with its rich green hues and historical significance in monument construction, while basalt provides superior durability and weather resistance due to its dense, fine-grained structure. Selecting between greenstone and basalt depends on whether the priority is visual heritage or long-term resilience in outdoor environments. For monuments requiring minimal maintenance and enduring strength, basalt is generally the preferred choice, whereas greenstone suits projects emphasizing cultural symbolism and distinctive coloration.
Infographic: Greenstone vs Basalt for Monument
 azmater.com
azmater.com