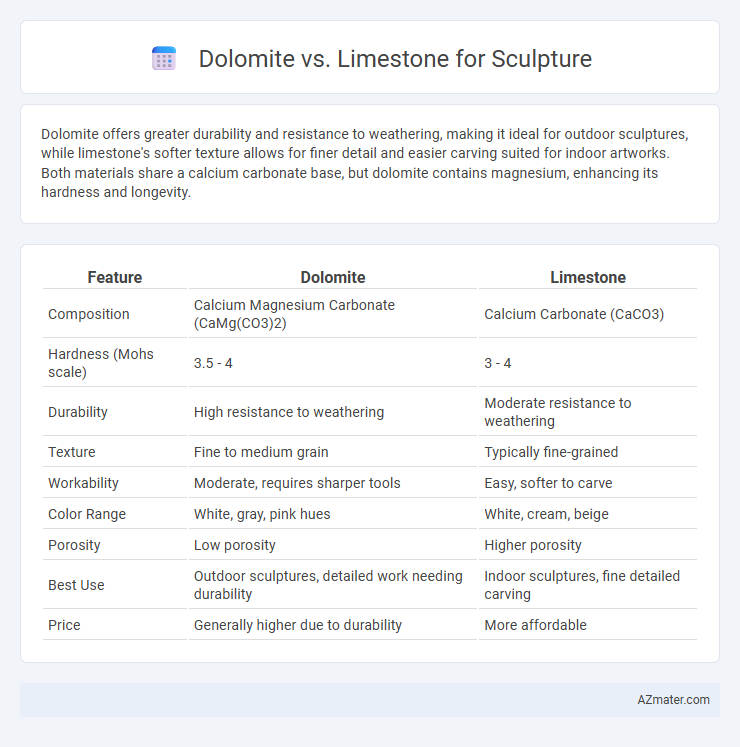
Dolomite offers greater durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for outdoor sculptures, while limestone's softer texture allows for finer detail and easier carving suited for indoor artworks. Both materials share a calcium carbonate base, but dolomite contains magnesium, enhancing its hardness and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dolomite | Limestone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium Magnesium Carbonate (CaMg(CO3)2) | Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 3.5 - 4 | 3 - 4 |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering | Moderate resistance to weathering |
| Texture | Fine to medium grain | Typically fine-grained |
| Workability | Moderate, requires sharper tools | Easy, softer to carve |
| Color Range | White, gray, pink hues | White, cream, beige |
| Porosity | Low porosity | Higher porosity |
| Best Use | Outdoor sculptures, detailed work needing durability | Indoor sculptures, fine detailed carving |
| Price | Generally higher due to durability | More affordable |
Introduction: Understanding Dolomite and Limestone
Dolomite and limestone are both sedimentary rocks commonly used in sculpture, each with distinct mineral compositions that influence their durability and workability. Dolomite contains calcium magnesium carbonate, providing greater hardness and resistance to weathering compared to limestone, which primarily consists of calcium carbonate. The choice between dolomite and limestone depends on the desired texture, finish, and environmental resilience for the sculptural work.
Geological Origins and Composition
Dolomite forms primarily from the alteration of limestone through magnesium-rich fluids, resulting in a carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate (CaMg(CO3)2). Limestone consists mainly of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), typically derived from marine organisms' skeletal fragments deposited over millions of years in shallow, warm marine environments. The higher magnesium content in dolomite contributes to its increased hardness and chemical stability, influencing sculptors' choice between the two materials based on durability and workability.
Physical Properties Comparison
Dolomite exhibits greater hardness and durability compared to limestone, making it more resistant to weathering and erosion in sculptures. Limestone, primarily composed of calcite, is softer and more porous, which allows for easier carving but results in reduced long-term structural integrity. The crystalline structure of dolomite provides enhanced resistance to acid rain, whereas limestone sculptures require more frequent maintenance to preserve fine details.
Workability for Sculptors
Dolomite offers greater hardness and durability compared to limestone, making it more resistant to weathering but slightly harder to carve. Limestone's softer texture and fine grain enable sculptors to achieve intricate details and smooth finishes with less effort, making it ideal for delicate work. Both materials provide excellent workability, though limestone is generally preferred for ease of carving, while dolomite is favored for sculptures requiring long-term structural integrity.
Surface Finish and Texture
Dolomite offers a finer, more crystalline texture than limestone, resulting in a smoother surface finish that enhances detailed sculptural work. Limestone's softer composition allows for easier carving but tends to produce a more porous and matte texture, which may weather differently over time. The choice between dolomite and limestone significantly impacts the durability and visual clarity of sculptures, with dolomite providing greater resistance to erosion and a polished appearance.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Dolomite exhibits superior durability and weather resistance compared to limestone, making it a preferred choice for outdoor sculptures exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its crystalline structure provides enhanced hardness and resistance to acid rain, reducing erosion and surface degradation over time. Limestone, while easier to carve, is more porous and susceptible to weathering, often leading to faster deterioration in sculptures exposed to moisture and pollutants.
Color Variations and Aesthetic Appeal
Dolomite offers a subtle range of creamy whites, pale grays, and soft pinks, creating a refined and elegant aesthetic ideal for detailed sculptures requiring smooth finishes. Limestone provides a broader spectrum of colors, including warm beige, honey, and earthy browns, enhancing rustic and naturalistic artworks with its textured surface. Both stones deliver unique visual appeal; choosing between dolomite and limestone depends on the desired color palette and stylistic expression in sculpture design.
Historical Use in Sculpture
Dolomite and limestone have both played significant roles in historical sculpture, with limestone favored by ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans for its softness and ease of carving. Dolomite, containing magnesium, offers greater durability and weather resistance, making it a preferred material in later periods for outdoor sculptures and architectural details. The Parthenon's use of dolomitic marble exemplifies its historical importance in creating enduring masterpieces.
Cost and Availability
Dolomite tends to be more expensive than limestone due to its denser composition and durability, making it a preferred choice for long-lasting sculptures. Limestone is generally more affordable and widely available, especially in regions like the United States and Europe, which makes it a popular material for large or budget-conscious art projects. Sculptors selecting between dolomite and limestone must weigh the cost difference against desired texture, hardness, and weather resistance.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Sculpture
Dolomite offers greater durability and resistance to weathering compared to limestone, making it ideal for outdoor sculptures exposed to harsh conditions. Limestone, with its softer texture and ease of carving, suits detailed indoor sculptures requiring intricate designs. Selecting the right stone depends on the sculpture's location, desired finish, and long-term maintenance requirements, with dolomite favored for strength and limestone for fine detail.
Infographic: Dolomite vs Limestone for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com