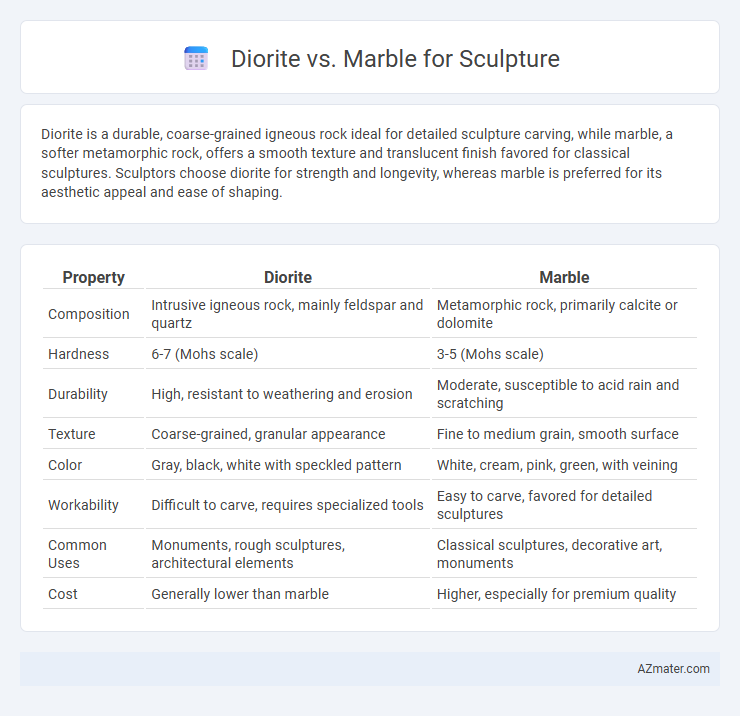
Diorite is a durable, coarse-grained igneous rock ideal for detailed sculpture carving, while marble, a softer metamorphic rock, offers a smooth texture and translucent finish favored for classical sculptures. Sculptors choose diorite for strength and longevity, whereas marble is preferred for its aesthetic appeal and ease of shaping.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Diorite | Marble |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Intrusive igneous rock, mainly feldspar and quartz | Metamorphic rock, primarily calcite or dolomite |
| Hardness | 6-7 (Mohs scale) | 3-5 (Mohs scale) |
| Durability | High, resistant to weathering and erosion | Moderate, susceptible to acid rain and scratching |
| Texture | Coarse-grained, granular appearance | Fine to medium grain, smooth surface |
| Color | Gray, black, white with speckled pattern | White, cream, pink, green, with veining |
| Workability | Difficult to carve, requires specialized tools | Easy to carve, favored for detailed sculptures |
| Common Uses | Monuments, rough sculptures, architectural elements | Classical sculptures, decorative art, monuments |
| Cost | Generally lower than marble | Higher, especially for premium quality |
Introduction to Diorite and Marble in Sculpture
Diorite, a coarse-grained igneous rock known for its durability and fine texture, has been prized in sculpture for its ability to hold intricate details and smooth finishes. Marble, a metamorphic rock primarily composed of calcite, offers a unique translucency and softness that allows artists to achieve delicate, refined shapes and a polished surface. Both stones have a rich history in sculpture, with diorite favored for monumental works requiring strength and marble chosen for its aesthetic appeal and workability.
Geological Origins and Composition
Diorite, an intrusive igneous rock formed from slow-cooling magma, primarily consists of plagioclase feldspar and hornblende, giving it a coarse-grained texture ideal for detailed sculpting. Marble is a metamorphic rock originating from limestone subjected to intense heat and pressure, predominantly composed of recrystallized calcite, resulting in a smooth, homogenous surface favored for fine artistry. Understanding the geological origins and mineral compositions of diorite and marble is essential for selecting the appropriate material based on durability and aesthetic requirements in sculpture.
Visual Characteristics: Color & Texture
Diorite features a granular texture with a speckled pattern of black, white, and gray minerals, offering a strong contrast and a rugged, coarse visual appeal ideal for bold sculptures. Marble presents a smooth, fine-grained texture with a translucent quality and a wide range of colors from pure white to various shades of green, pink, and black, creating elegant, refined sculptures with soft veining. The choice between diorite and marble depends on desired visual impact: diorite's dramatic speckling versus marble's polished, flowing veining.
Workability for Sculptors
Diorite is a dense, hard igneous rock that poses significant challenges in carving due to its toughness, requiring sculptors to use specialized tools and extended time for detailed work. Marble, known for its fine grain and relative softness, offers superior workability, allowing for intricate detailing and smoother finishes with traditional chiseling techniques. Sculptors often prefer marble over diorite for projects demanding precision and fluidity in form, while diorite suits more rugged, durable sculptures where longevity is prioritized.
Durability and Longevity
Diorite offers exceptional durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for sculptures exposed to outdoor elements due to its dense, hard composition. Marble, while prized for its aesthetic appeal and smooth texture, is softer and more susceptible to erosion and acid rain, which can affect the longevity of outdoor sculptures. Sculptors seeking long-lasting works with minimal maintenance often prefer diorite for its superior hardness and resilience.
Historical Use in Art and Architecture
Diorite, known for its extreme hardness and durability, was favored by ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Mesopotamians for creating statues and architectural elements that demanded longevity, such as the famous Code of Hammurabi stele. Marble, prized by Greek and Roman sculptors, offered a softer, more workable medium that allowed for intricate details and smooth finishes in sculptures and monumental buildings like the Parthenon. Both stones have played crucial roles in art history, with diorite symbolizing permanence and strength, while marble emphasized beauty and refinement in classical sculpture and architecture.
Notable Sculptures and Artists
Diorite, prized for its hardness and durability, was famously used by ancient Egyptian sculptors for the seated statue of Pharaoh Khafre and Mesopotamian artists creating stelae. Marble, valued for its smooth texture and translucence, is renowned in classical sculpture, exemplified by Michelangelo's David and Praxiteles' Aphrodite of Knidos. Notable artists favored marble for detailed human forms while diorite's toughness suited monumental and ceremonial works requiring longevity.
Cost and Availability
Diorite is generally more expensive and less readily available than marble due to its rarity and hardness, making it a costlier choice for sculpture. Marble, widely quarried and available in numerous varieties worldwide, tends to be more affordable and accessible for artists and sculptors. The higher availability of marble also contributes to its frequent use and lower overall cost in sculptural projects.
Environmental Impact and Sourcing
Diorite is a durable, coarse-grained igneous rock sourced primarily from quarries with relatively low environmental disturbance compared to marble, which involves energy-intensive extraction and processing due to its softer, more fragile composition. Marble quarrying often results in significant landscape alteration, high water consumption, and waste generation, posing greater ecological risks than the typically less invasive mining of diorite. Choosing diorite over marble can reduce carbon footprints and preserve biodiversity, making it a more environmentally conscious option for sustainable sculpture projects.
Choosing Between Diorite and Marble for Artistic Projects
Diorite offers exceptional durability and a coarse-grained texture ideal for detailed, long-lasting sculptures, while marble is prized for its smooth, fine grain and ability to capture delicate, lifelike details with a polished finish. Marble's translucency enhances the aesthetic appeal of artistic projects, making it the preferred choice for classical and intricate sculptures, whereas diorite's toughness supports outdoor installations and large-scale works requiring structural strength. Artists should consider the specific project requirements such as desired texture, detail precision, and environmental exposure when choosing between diorite and marble for sculptural art.
Infographic: Diorite vs Marble for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com