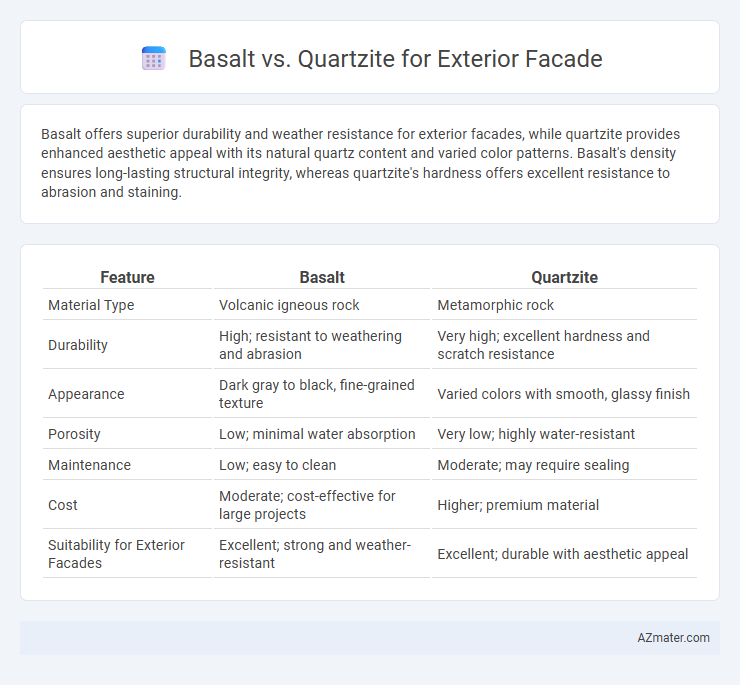
Basalt offers superior durability and weather resistance for exterior facades, while quartzite provides enhanced aesthetic appeal with its natural quartz content and varied color patterns. Basalt's density ensures long-lasting structural integrity, whereas quartzite's hardness offers excellent resistance to abrasion and staining.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Basalt | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Volcanic igneous rock | Metamorphic rock |
| Durability | High; resistant to weathering and abrasion | Very high; excellent hardness and scratch resistance |
| Appearance | Dark gray to black, fine-grained texture | Varied colors with smooth, glassy finish |
| Porosity | Low; minimal water absorption | Very low; highly water-resistant |
| Maintenance | Low; easy to clean | Moderate; may require sealing |
| Cost | Moderate; cost-effective for large projects | Higher; premium material |
| Suitability for Exterior Facades | Excellent; strong and weather-resistant | Excellent; durable with aesthetic appeal |
Introduction to Basalt and Quartzite as Facade Materials
Basalt, a dense volcanic rock known for its durability and deep black to gray hues, offers excellent weather resistance and thermal insulation, making it ideal for exterior facades. Quartzite, a naturally occurring metamorphic rock formed from sandstone, features a hard, glassy surface and a variety of colors ranging from white to pink, providing both aesthetic versatility and high durability against environmental factors. Both materials are favored in architectural applications for their strength, longevity, and low maintenance requirements in exterior cladding.
Geological Formation and Characteristics
Basalt, formed from rapid cooling of lava at the Earth's surface, exhibits fine-grained texture and exceptional durability, making it resistant to weathering and ideal for exterior facades. Quartzite originates from the metamorphism of sandstone under intense heat and pressure, resulting in a highly dense, interlocking crystalline structure that offers outstanding hardness and resistance to abrasion. Both stones provide unique geological characteristics, with basalt's volcanic origin yielding a dense, dark appearance, while quartzite's metamorphic nature grants a range of colors and a glassy luster suited for aesthetic and structural facade applications.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Basalt offers a sleek, dark, and uniform aesthetic with deep grey to black tones ideal for modern, minimalist exterior facades, while quartzite showcases a broader spectrum of colors ranging from whites and grays to vibrant blues, pinks, and greens that enhance visual interest. The natural shimmer and layered texture of quartzite create dynamic facades that catch light differently throughout the day, contrasting with basalt's consistent matte finish for a more subdued, sophisticated look. Both materials provide durable, weather-resistant surfaces, but quartzite's diverse color palette often makes it the preferred choice for designers seeking bold, eye-catching exterior facades.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Basalt offers exceptional durability and weather resistance due to its dense, fine-grained volcanic origin, making it highly resistant to abrasion, freeze-thaw cycles, and chemical erosion. Quartzite also provides strong durability, with a natural hardness ranking near diamond, ensuring resistance to scratches, heat, and acid rain exposure. When comparing exterior facades, basalt's low porosity and compression strength outperform quartzite's slightly higher porosity, making basalt superior in harsh weather conditions.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Basalt offers exceptional durability and low maintenance for exterior facades due to its dense, weather-resistant properties that resist erosion and staining over time. Quartzite, while harder and highly resistant to scratches, may require periodic sealing to maintain its appearance and protect against weathering effects. Both stones provide long-lasting solutions, but basalt generally demands less upkeep, making it ideal for projects prioritizing minimal maintenance and extended facade lifespan.
Installation Techniques and Challenges
Basalt and quartzite each present unique installation techniques and challenges for exterior facades, with basalt requiring specialized cutting tools due to its hardness and dense structure, and quartzite demanding careful handling to prevent surface chipping. Basalt's volcanic origin contributes to its high durability and difficulty in drilling, necessitating the use of diamond-tipped saws and anchors for secure attachment, whereas quartzite's layered metamorphic composition allows for easier shaping but poses risks of delamination if improperly installed. Contractors must consider these material-specific factors to ensure long-term stability and aesthetic appeal, with basalt excelling in structural resilience and quartzite favored for its natural variegated appearance.
Cost Comparison: Basalt vs Quartzite
Basalt typically costs less than quartzite for exterior facades due to its widespread availability and easier quarrying process, making it a budget-friendly option for large projects. Quartzite's higher price reflects its superior hardness, durability, and attractive, unique patterns, which can justify the investment for premium applications. Cost comparison must consider not only material price per square foot but also installation complexity and long-term maintenance, with basalt offering lower upfront expenses and quartzite providing enhanced longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Basalt, a volcanic igneous rock, offers superior durability and low porosity, making it highly resistant to weathering and reducing the need for frequent replacements, which minimizes environmental impact. Quartzite, a metamorphic rock formed from sandstone, exhibits impressive hardness and resistance to abrasion but typically requires more energy-intensive quarrying and processing compared to basalt. Choosing basalt for exterior facades contributes to sustainability by lowering carbon emissions through its longevity and ability to be sourced closer to project sites, whereas quartzite's environmental footprint depends heavily on transportation and extraction methods.
Suitable Applications in Exterior Design
Basalt and quartzite are both durable natural stones ideal for exterior facades, with basalt excelling in modern architectural designs due to its dense, fine-grained texture and resistance to weathering. Quartzite offers superior hardness and vibrant color variations, making it well-suited for high-traffic areas and decorative cladding that demands longevity and aesthetic appeal. Selecting between basalt and quartzite depends on the project's requirements for thermal performance, abrasion resistance, and desired visual impact in exterior design.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Facade
Basalt offers superior durability and resistance to weathering, making it an excellent choice for exterior facades exposed to harsh climates. Quartzite features a striking, natural crystalline texture and high compressive strength, providing both aesthetic appeal and longevity. Selecting the right stone depends on factors such as local weather conditions, desired color palette, and maintenance requirements for your facade.
Infographic: Basalt vs Quartzite for Exterior Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com