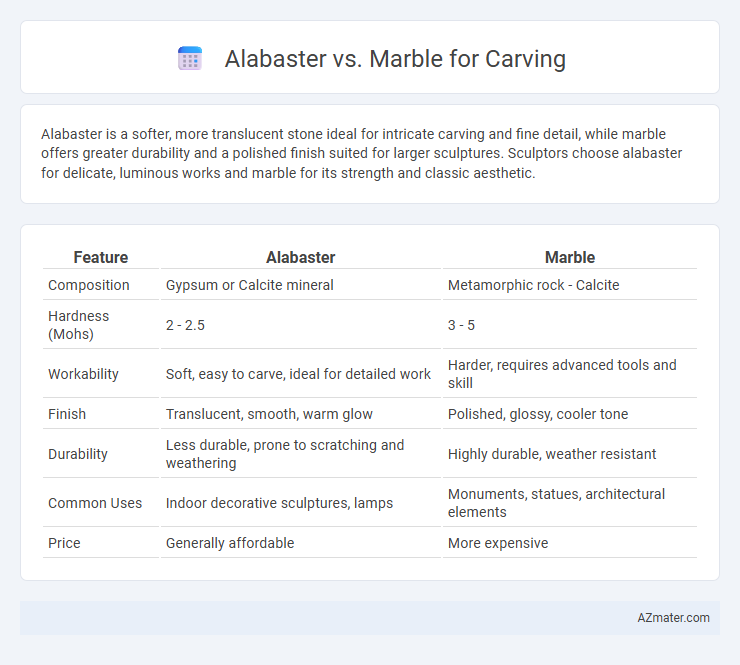
Alabaster is a softer, more translucent stone ideal for intricate carving and fine detail, while marble offers greater durability and a polished finish suited for larger sculptures. Sculptors choose alabaster for delicate, luminous works and marble for its strength and classic aesthetic.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Alabaster | Marble |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Gypsum or Calcite mineral | Metamorphic rock - Calcite |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 2 - 2.5 | 3 - 5 |
| Workability | Soft, easy to carve, ideal for detailed work | Harder, requires advanced tools and skill |
| Finish | Translucent, smooth, warm glow | Polished, glossy, cooler tone |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to scratching and weathering | Highly durable, weather resistant |
| Common Uses | Indoor decorative sculptures, lamps | Monuments, statues, architectural elements |
| Price | Generally affordable | More expensive |
Understanding Alabaster and Marble
Alabaster is a soft, fine-grained mineral composed primarily of gypsum or calcite, prized for its smooth texture and translucency, making it ideal for detailed carving and intricate designs. Marble, a metamorphic rock consisting mainly of calcite, features a crystalline structure that provides durability and a varied color palette, suitable for larger, more robust sculptures. Understanding the distinct physical properties of alabaster and marble helps artists choose the right material based on the desired finish, workability, and project scale.
Key Differences in Appearance
Alabaster exhibits a smooth, creamy texture with a translucent quality that allows light to pass through, giving sculptures a soft, glowing effect. Marble features a harder, crystalline structure with distinct veining patterns in colors ranging from white to green, pink, or black, providing a more dramatic and polished appearance. The subtle translucency of alabaster contrasts with marble's polished shine, making each material uniquely suited for different artistic expressions in carving.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Alabaster is a softer, more fragile stone, rating around 3 on the Mohs hardness scale, making it easier to carve but less durable over time compared to marble, which has a hardness of about 3 to 5 and offers greater resistance to weathering and chipping. Marble's denser crystalline structure provides superior strength, making it ideal for detailed sculptures that require long-term durability in both indoor and outdoor environments. While alabaster is prized for its translucency and smooth texture, marble's robustness ensures longevity and structural integrity in fine art and architectural carvings.
Ease of Carving: Alabaster vs Marble
Alabaster is significantly easier to carve than marble due to its softer composition, allowing intricate details to be shaped with less effort and finer tools. Marble, being denser and harder, requires more specialized tools and skill, making the carving process slower and more labor-intensive. Artists often choose alabaster for delicate, detailed sculptures, while marble is preferred for durability and polished finishes.
Cost and Availability
Alabaster is generally more affordable and widely accessible than marble, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious sculptors. Its softness allows for easier carving but can be less durable compared to the denser, more expensive marble varieties. Marble, often sourced from quarries in Italy and Greece, commands higher prices due to its durability and prestige, though its availability can be limited depending on the specific type.
Common Uses in Sculpture
Alabaster is favored for its softness and translucent qualities, making it ideal for detailed sculptures, indoor decorative art, and intricate relief work. Marble is preferred by sculptors for its durability, fine grain, and ability to achieve a high polish, commonly used in classical statues, monumental sculptures, and outdoor installations. Both materials serve distinct artistic purposes, with alabaster used mainly for delicate, small-scale works and marble for enduring, large-scale masterpieces.
Maintenance and Longevity
Alabaster offers easier maintenance due to its softness and porosity, requiring regular sealing to prevent staining and damage from moisture. Marble, being denser and harder, provides greater durability and longevity for carvings, although it requires occasional cleaning with pH-neutral products to preserve its polished surface. Both materials must be protected from acidic substances, but marble withstands environmental wear better over time, making it ideal for long-lasting sculptures.
Weight and Handling Considerations
Alabaster is significantly lighter than marble, making it easier to handle and carve, especially for detailed and intricate sculptures. Marble's dense and heavy composition requires more effort and strength during the carving process, but it offers greater durability and a polished finish. Artists often choose alabaster for projects demanding portability and fine detail, while marble is preferred for large, enduring works due to its robustness.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Alabaster has been prized since ancient Egypt for its smooth, translucent quality ideal for detailed carving, often used in funerary art and religious artifacts. Marble gained prominence in classical Greek and Roman sculpture, symbolizing strength and elegance in monuments and temples, reinforcing its cultural status in Western art history. Both materials embody unique artistic traditions, reflecting their distinct roles in cultural heritage and craftsmanship across civilizations.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Project
Alabaster, a softer and more translucent stone, is ideal for intricate carving and detailed artwork due to its ease of shaping and smooth finish. Marble, being harder and more durable, suits larger sculptures and projects requiring longevity and a polished surface that resists weathering. Choosing the right stone depends on the project's scale, desired texture, and exposure conditions, with alabaster preferred for delicate indoor pieces and marble favored for robust, long-lasting creations.
Infographic: Alabaster vs Marble for Carving
 azmater.com
azmater.com