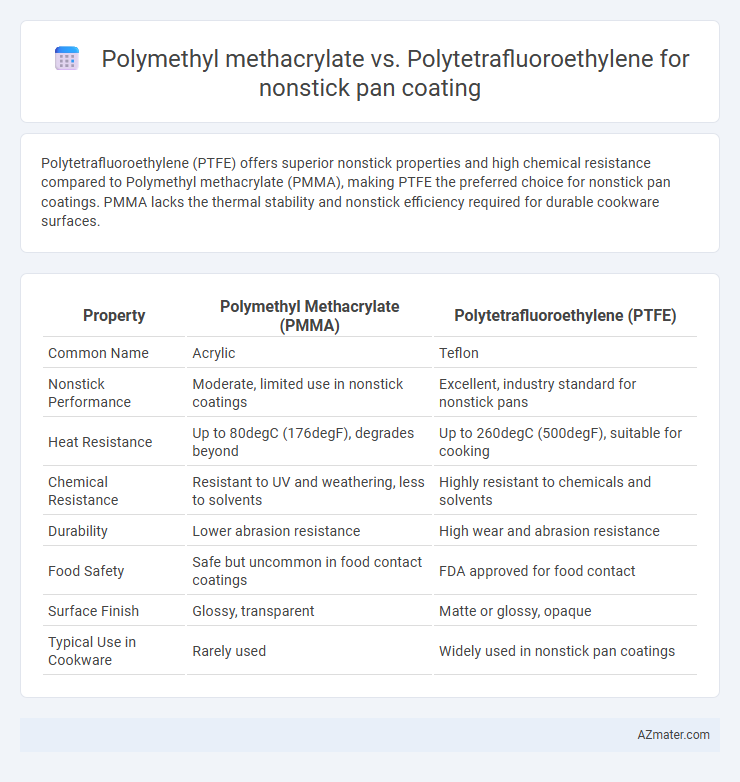
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior nonstick properties and high chemical resistance compared to Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making PTFE the preferred choice for nonstick pan coatings. PMMA lacks the thermal stability and nonstick efficiency required for durable cookware surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Common Name | Acrylic | Teflon |
| Nonstick Performance | Moderate, limited use in nonstick coatings | Excellent, industry standard for nonstick pans |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 80degC (176degF), degrades beyond | Up to 260degC (500degF), suitable for cooking |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to UV and weathering, less to solvents | Highly resistant to chemicals and solvents |
| Durability | Lower abrasion resistance | High wear and abrasion resistance |
| Food Safety | Safe but uncommon in food contact coatings | FDA approved for food contact |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, transparent | Matte or glossy, opaque |
| Typical Use in Cookware | Rarely used | Widely used in nonstick pan coatings |
Introduction to Nonstick Pan Coatings
Nonstick pan coatings primarily utilize Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) due to its exceptional low friction and resistance to high temperatures, making it ideal for cooking applications. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is less common in nonstick cookware but serves as a durable, transparent polymer that offers better scratch resistance though lower heat tolerance compared to PTFE. PTFE's chemical inertness and ability to prevent food adhesion contribute to its widespread use, whereas PMMA coatings may be found in specialty or multi-layer composite surfaces enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal.
What is Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)?
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic often used as a lightweight, shatter-resistant alternative to glass. Its chemical structure, derived from methyl methacrylate monomers, provides excellent resistance to UV light and weathering but lacks the nonstick properties essential for cookware coatings. In nonstick pan applications, PMMA is not favored due to its limited heat resistance and surface friction compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which offers superior nonstick performance and chemical inertness.
What is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer renowned for its exceptional nonstick properties, chemical resistance, and high thermal stability, making it a popular choice for nonstick pan coatings. Unlike polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which is primarily used in transparent applications like acrylic glass, PTFE provides superior durability and low friction surfaces essential for cookware. Its molecular structure creates a slick, inert surface that prevents food from adhering, enhancing cooking performance and ease of cleaning.
Key Properties of PMMA in Cookware Applications
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent transparency, high impact resistance, and chemical stability, making it a durable choice for nonstick pan coatings. Its superior heat resistance up to approximately 100degC enhances coating longevity without warping or degradation. PMMA's non-toxicity and ease of adherence to metal surfaces contribute to its widespread use in cookware, providing a safe and reliable cooking experience compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
Key Properties of PTFE in Cookware Applications
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is highly valued in nonstick cookware for its exceptional low coefficient of friction, providing superior food release and easy cleaning compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PTFE exhibits excellent thermal stability up to approximately 260degC, chemical inertness, and resistance to high temperatures without degrading, making it ideal for cooking surfaces exposed to direct heat. Its non-reactive nature prevents flavor transfer or toxic fumes under recommended conditions, setting PTFE apart as a superior coating material for nonstick pans.
Nonstick Performance: PMMA vs PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior nonstick performance compared to Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) due to its low coefficient of friction and exceptional resistance to sticking agents, making it ideal for cookware coatings. PMMA, while more rigid and chemically resistant, lacks the inherent slippery surface properties of PTFE, resulting in less effective nonstick behavior. PTFE coatings provide enhanced food release and easier cleaning, maintaining their performance under high temperatures up to 260degC (500degF), whereas PMMA exhibits limited heat resistance and lower nonstick efficiency.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior durability and longevity compared to Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) when used as a nonstick pan coating due to its high chemical resistance and ability to withstand temperatures up to 260degC without degradation. PMMA coatings, while clear and aesthetically pleasing, are more prone to scratching and thermal damage, limiting their lifespan in high-heat cooking applications. The carbon-fluorine bonds in PTFE provide enhanced stability against abrasion and heat, making it the preferred choice for long-lasting nonstick cookware.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is widely recognized for its excellent nonstick properties and chemical inertness, making it a safe and popular choice for cookware coatings at moderate temperatures below 260degC (500degF). Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), while less common as a pan coating, lacks the thermal stability of PTFE and can degrade at typical cooking temperatures, potentially releasing harmful byproducts. Users should avoid overheating PTFE-coated pans beyond recommended limits to prevent pyrolysis and exposure to toxic fumes, whereas PMMA's lower heat tolerance limits its practical use for safe nonstick applications.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers a lower cost and wider availability compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) in nonstick pan coatings, making it a budget-friendly option for mass production. PTFE, known for its superior nonstick properties and heat resistance, is generally more expensive due to complex manufacturing and limited raw materials. Market demand heavily favors PTFE for premium cookware, but PMMA's affordability ensures steady supply and competitive pricing for entry-level products.
Final Verdict: Which Coating is Better for Nonstick Pans?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) outperforms polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in nonstick pan coatings due to its superior heat resistance, chemical inertness, and exceptional nonstick properties. PTFE coatings provide durable, easy food release and withstand cooking temperatures up to 260degC (500degF), while PMMA degrades faster under high heat and offers less effective nonstick performance. For reliable, long-lasting nonstick cookware, PTFE remains the preferred choice based on durability and optimal cooking efficiency.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick pan coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com