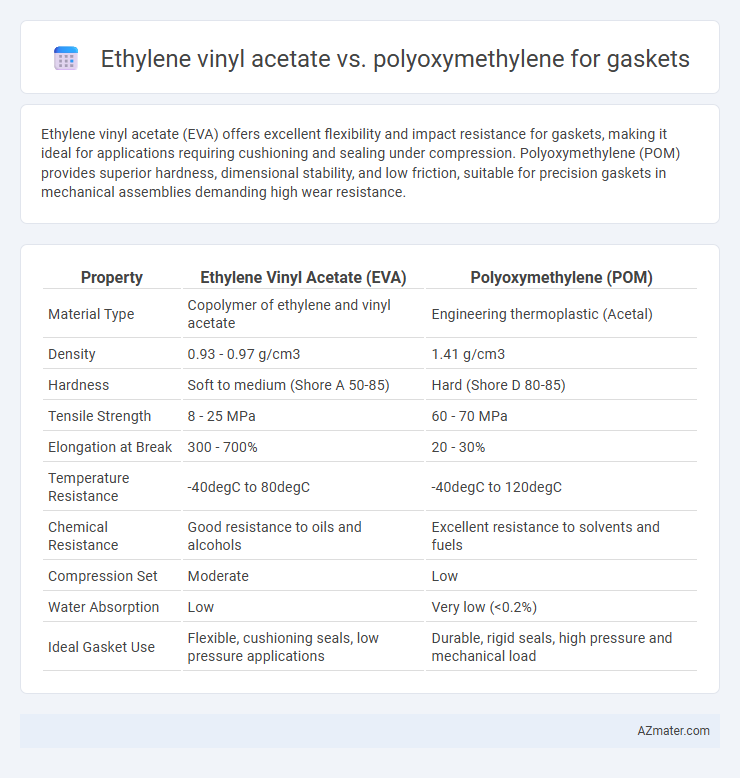
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance for gaskets, making it ideal for applications requiring cushioning and sealing under compression. Polyoxymethylene (POM) provides superior hardness, dimensional stability, and low friction, suitable for precision gaskets in mechanical assemblies demanding high wear resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polyoxymethylene (POM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate | Engineering thermoplastic (Acetal) |
| Density | 0.93 - 0.97 g/cm3 | 1.41 g/cm3 |
| Hardness | Soft to medium (Shore A 50-85) | Hard (Shore D 80-85) |
| Tensile Strength | 8 - 25 MPa | 60 - 70 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 300 - 700% | 20 - 30% |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 80degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and alcohols | Excellent resistance to solvents and fuels |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Low |
| Water Absorption | Low | Very low (<0.2%) |
| Ideal Gasket Use | Flexible, cushioning seals, low pressure applications | Durable, rigid seals, high pressure and mechanical load |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) exhibits excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and low-temperature performance, making it suitable for gaskets in automotive and packaging applications. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, offers high mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to wear and moisture, ideal for precision gasket components in industrial machinery. Choosing between EVA and POM depends on the gasket's operational environment, with EVA favored for cushioning and sealing flexibility, while POM is preferred for rigid, high-strength sealing solutions.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a copolymer known for its excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and low-temperature toughness, making it a versatile choice for gaskets in various industrial applications. EVA offers superior impact resistance and easy processability compared to Polyoxymethylene (POM), which is a rigid, high-strength polymer with excellent dimensional stability but less flexibility. The inherent softness and elasticity of EVA allow for improved sealing performance and cushioning in gasket applications where vibration and compression are factors.
Overview of Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic prized for its exceptional mechanical strength, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, making it an ideal choice for gaskets in demanding industrial applications. Unlike Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), POM offers superior chemical resistance and fatigue endurance, ensuring long-term reliability under continuous stress and exposure to solvents, oils, and fuels. Its low moisture absorption and high rigidity contribute to consistent sealing performance, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and precision machinery settings.
Chemical Resistance: EVA vs POM
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers moderate chemical resistance, performing well against oils, greases, and some solvents, but it may degrade when exposed to strong acids or hydrocarbons. Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to EVA, demonstrating excellent stability against fuels, lubricants, and various solvents, making it highly suitable for harsh chemical environments. For gaskets requiring long-term exposure to aggressive chemicals, POM provides enhanced durability and reliability over EVA.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) exhibits excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for gaskets requiring elasticity and vibration damping. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, provides superior tensile strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability, suitable for precision gasket applications needing high mechanical durability. Comparing the two, EVA is preferred for soft, compressible seals, while POM offers enhanced mechanical rigidity and wear resistance in more demanding gasket environments.
Temperature Tolerance of EVA and POM
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) gaskets offer temperature tolerance typically ranging from -40degC to 80degC, making them suitable for low to moderate thermal environments with good flexibility and resilience. Polyoxymethylene (POM) gaskets exhibit significantly higher temperature resistance, often withstanding continuous use up to 100degC to 120degC, along with superior dimensional stability under heat. Selecting between EVA and POM for gasket applications depends on thermal operating conditions, where EVA suits cooler environments and POM delivers enhanced performance in elevated temperature settings.
Durability and Longevity in Gasket Applications
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility and resistance to stress cracking, contributing to durable gaskets in moderate temperature environments. Polyoxymethylene (POM), known for its high tensile strength and superior wear resistance, provides longer-lasting gasket performance under mechanical stress and exposure to hydrocarbons. For gasket applications demanding enhanced durability and longevity, POM generally outperforms EVA due to its superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior cost efficiency for gaskets due to its lower raw material and processing expenses compared to polyoxymethylene (POM), which is more expensive due to its high-performance engineering properties. EVA provides adequate sealing performance for applications with moderate chemical resistance and flexibility requirements, driving down overall manufacturing and maintenance costs. In contrast, POM gaskets incur higher initial investment but offer enhanced mechanical strength and dimensional stability, suitable for demanding environments where long-term durability justifies the elevated expense.
Typical Industry Applications
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) gaskets are commonly used in automotive, packaging, and consumer goods industries due to their excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and airtight sealing properties. Polyoxymethylene (POM) gaskets are preferred in precision engineering, electronics, and industrial machinery applications for their high mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to solvents and wear. Both materials serve critical roles in sealing solutions, with EVA favored for cushioning and vibration damping, while POM ensures durability and chemical resistance in demanding environments.
Which Material is Best for Gasket Use?
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and low-temperature performance, making it suitable for gaskets in applications requiring cushioning and vibration dampening. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, provides superior mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and low friction, ideal for high-precision gasket seals in automotive and industrial equipment. Choosing the best material depends on specific gasket requirements: EVA excels in sealing with elasticity and chemical exposure, while POM is preferred for rigid, wear-resistant gasket applications demanding high strength and dimensional accuracy.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polyoxymethylene for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com