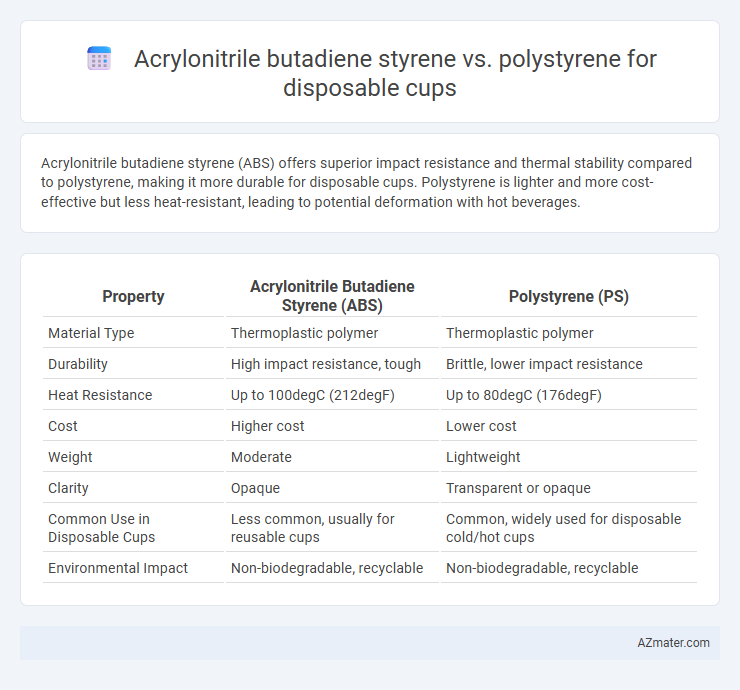
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and thermal stability compared to polystyrene, making it more durable for disposable cups. Polystyrene is lighter and more cost-effective but less heat-resistant, leading to potential deformation with hot beverages.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Durability | High impact resistance, tough | Brittle, lower impact resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 100degC (212degF) | Up to 80degC (176degF) |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Weight | Moderate | Lightweight |
| Clarity | Opaque | Transparent or opaque |
| Common Use in Disposable Cups | Less common, usually for reusable cups | Common, widely used for disposable cold/hot cups |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
Introduction to Disposable Cup Materials
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and durability compared to polystyrene (PS), making it suitable for reusable and more robust disposable cups. Polystyrene is lightweight and cost-effective, commonly used for single-use disposable cups due to its ease of molding and rigidity. Both materials provide distinct advantages in thermal insulation and manufacturing efficiency, influencing their selection in disposable cup production.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent impact resistance, toughness, and chemical stability, making it suitable for durable disposable cups. Compared to Polystyrene (PS), ABS offers superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, ensuring better performance under varied temperature conditions. Its robust molecular structure enables enhanced durability and reduced brittleness, which is critical for maintaining cup integrity during use.
Overview of Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene (PS) is a lightweight, rigid thermoplastic polymer widely used for disposable cups due to its clarity, ease of molding, and cost-effectiveness. Its excellent insulating properties make it ideal for both hot and cold beverages, while its resistance to moisture helps maintain cup integrity. Compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), PS offers better transparency but lower impact resistance and heat tolerance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and toughness compared to polystyrene (PS), making ABS more durable for disposable cups. PS exhibits higher stiffness and better clarity but is more brittle, which can result in cracks or breaks under stress. The enhanced mechanical strength of ABS ensures improved performance in applications requiring greater durability and resistance to deformation.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits superior thermal resistance and higher impact strength compared to polystyrene, making it more suitable for disposable cups that require durability under varying temperatures. Polystyrene, while lightweight and cost-effective, tends to have lower thermal resistance and can deform or become brittle when exposed to hot liquids. Therefore, ABS cups perform better in hot beverage applications, maintaining structural integrity and user comfort during use.
Chemical Resistance of ABS vs PS
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polystyrene (PS), making ABS more suitable for disposable cups exposed to various solvents and detergents. ABS resists alcohols, oils, and mild acids better than PS, which tends to degrade or become brittle when in contact with many chemicals. This enhanced durability of ABS ensures greater longevity and safety for chemical exposure in disposable cup applications.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polystyrene (PS) differ significantly in their environmental impact when used for disposable cups. ABS is less commonly used but offers higher durability and thermal resistance, resulting in longer product life and potentially reduced waste generation. Polystyrene, especially in its expanded form (EPS), contributes to significant pollution due to its low biodegradability and high volume in landfill, posing greater challenges in waste management and environmental toxicity.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) generally incurs higher raw material and production costs compared to polystyrene (PS), making ABS less economically feasible for disposable cups in large-scale, cost-sensitive applications. Polystyrene offers lower manufacturing expenses and greater market availability, resulting in reduced unit costs and enhanced affordability for mass production. However, ABS provides superior impact resistance and durability, which can justify its higher price point in niche markets valuing quality over cost.
Suitability for Food and Beverage Applications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and thermal stability, making it more suitable for hot beverage cups compared to polystyrene (PS), which tends to deform under heat. PS is commonly used for cold drink cups due to its clarity and cost-effectiveness but lacks the durability needed for hot applications. Food-grade ABS complies with FDA regulations for food contact, providing enhanced safety and performance in disposable cup manufacturing.
Conclusions: Best Choice for Disposable Cups
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and durability compared to polystyrene (PS), making it a more reliable choice for disposable cups subjected to rough handling. Polystyrene is lightweight and cost-effective but lacks the thermal stability and mechanical strength needed for hot or heavy liquids. Therefore, ABS is the best choice for disposable cups requiring enhanced durability and heat resistance.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polystyrene for Disposable cup
 azmater.com
azmater.com