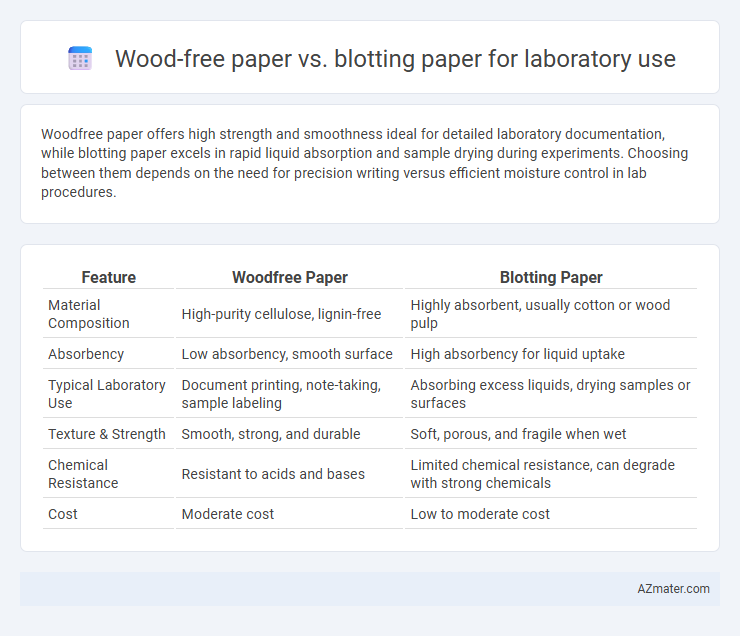
Woodfree paper offers high strength and smoothness ideal for detailed laboratory documentation, while blotting paper excels in rapid liquid absorption and sample drying during experiments. Choosing between them depends on the need for precision writing versus efficient moisture control in lab procedures.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Woodfree Paper | Blotting Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-purity cellulose, lignin-free | Highly absorbent, usually cotton or wood pulp |
| Absorbency | Low absorbency, smooth surface | High absorbency for liquid uptake |
| Typical Laboratory Use | Document printing, note-taking, sample labeling | Absorbing excess liquids, drying samples or surfaces |
| Texture & Strength | Smooth, strong, and durable | Soft, porous, and fragile when wet |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and bases | Limited chemical resistance, can degrade with strong chemicals |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Low to moderate cost |
Introduction to Laboratory Papers
Woodfree paper offers high brightness and smooth surface making it ideal for printing laboratory results, while blotting paper excels in absorbing liquids quickly for sample preparation and drying purposes. Laboratory use demands precise characteristics; woodfree paper ensures clarity and durability in documentation, whereas blotting paper's porous structure facilitates efficient liquid absorption and transfer. Choosing between these papers depends on whether the primary need is for documentation or wet-laboratory procedures.
What is Woodfree Paper?
Woodfree paper is a high-quality, chemical pulp paper that contains minimal lignin, which prevents yellowing and enhances durability, making it ideal for laboratory documentation and archival purposes. Unlike blotting paper used primarily for absorbing liquids and controlling moisture during experiments, woodfree paper provides a smooth, consistent surface for printing and note-taking in scientific settings. Its acid-free composition ensures long-term stability, crucial for maintaining accurate laboratory records and sensitive data.
What is Blotting Paper?
Blotting paper is a highly absorbent type of paper primarily used in laboratories to soak up excess liquids, such as during chromatography or when drying samples. Unlike woodfree paper, which is smooth and designed for printing or writing without ink bleeding, blotting paper has a porous texture that efficiently captures moisture without tearing or disintegrating. Its unique absorbency makes it essential for precise sample handling, ensuring accuracy in experimental procedures.
Manufacturing Processes: Woodfree vs Blotting Paper
Woodfree paper is produced through chemical pulping that removes lignin to ensure high purity and brightness, resulting in a smooth surface ideal for detailed scientific documentation. Blotting paper, manufactured from highly absorbent cellulose fibers often without chemical bleaching, is specifically designed to quickly absorb liquids and maintain sample integrity in laboratory applications. The distinct manufacturing processes yield woodfree paper with durable writing qualities while blotting paper emphasizes permeability and rapid fluid uptake.
Physical Properties Comparison
Woodfree paper exhibits a smooth surface with high brightness and low absorbency, making it ideal for precise printing and writing in laboratory documentation. Blotting paper features a porous texture with exceptional absorbency and high capillarity, efficiently soaking up liquids during experiments. The tensile strength of woodfree paper is generally higher, providing durability, whereas blotting paper is more fragile but optimized for rapid liquid absorption in laboratory procedures.
Absorbency and Moisture Handling
Woodfree paper exhibits low absorbency with a smooth surface, making it ideal for writing and printing but less effective in absorbing liquids during laboratory applications. Blotting paper demonstrates high absorbency due to its porous texture, efficiently handling moisture by rapidly soaking up excess liquids in experiments or sample preparation. Choosing blotting paper ensures superior moisture management in labs, while woodfree paper serves better for documentation and non-absorbent needs.
Chemical Compatibility and Resistance
Woodfree paper, commonly used in laboratories, offers high chemical compatibility and excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents due to its purified cellulose content, making it ideal for general filtration and analytical applications. Blotting paper, although highly absorbent, exhibits lower chemical resistance and is more susceptible to degradation when exposed to harsh chemicals or solvents, limiting its suitability for rigorous chemical testing or filtration tasks. Selecting woodfree paper over blotting paper enhances durability and accuracy in chemical-sensitive laboratory procedures.
Typical Laboratory Applications
Woodfree paper is commonly used in laboratories for high-quality printing, note-taking, and documentation due to its smooth surface and acid-free properties, ensuring longevity and clarity of records. Blotting paper excels in applications requiring absorption of excess liquids, such as in chromatography, drying wet samples, and filtering small quantities of solutions. While woodfree paper supports documentation and record-keeping, blotting paper is essential for sample preparation and liquid management tasks in laboratory settings.
Cost and Availability
Woodfree paper offers a cost-effective and widely available option for laboratory use, providing consistent quality due to its chemical pulp composition free of lignin. Blotting paper, while generally more expensive, is specialized for absorbing liquids quickly and is less commonly stocked, potentially limiting immediate availability. Laboratories balancing budget and rapid absorption needs often opt for woodfree paper for routine tasks and reserve blotting paper for specific applications requiring high absorbency.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Laboratory Needs
Woodfree paper offers a smooth, durable surface ideal for writing and printing laboratory notes with minimal ink absorption, ensuring clarity and precision. Blotting paper excels in absorbing excess liquids quickly, making it indispensable for filtering and drying applications where rapid moisture removal is crucial. Selecting between woodfree and blotting paper depends on the specific laboratory function: choose woodfree paper for documentation and blotting paper for absorption tasks.
Infographic: Woodfree paper vs Blotting paper for Laboratory use
 azmater.com
azmater.com