Synthetic paper offers superior water resistance and durability, making it ideal for long-lasting books that withstand heavy use. Bamboo paper provides eco-friendly sustainability with natural texture, perfect for environmentally conscious publications seeking a unique tactile experience.
Table of Comparison
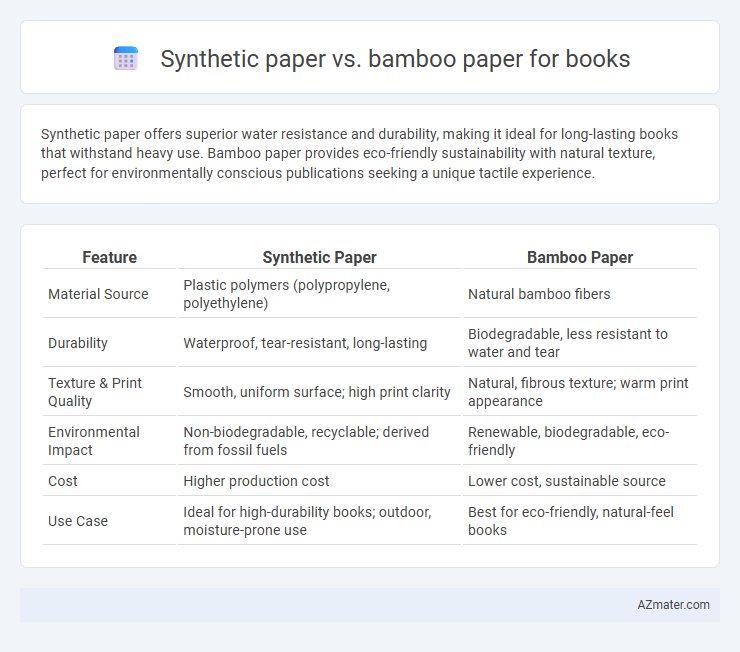
| Feature | Synthetic Paper | Bamboo Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Plastic polymers (polypropylene, polyethylene) | Natural bamboo fibers |
| Durability | Waterproof, tear-resistant, long-lasting | Biodegradable, less resistant to water and tear |
| Texture & Print Quality | Smooth, uniform surface; high print clarity | Natural, fibrous texture; warm print appearance |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable; derived from fossil fuels | Renewable, biodegradable, eco-friendly |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower cost, sustainable source |
| Use Case | Ideal for high-durability books; outdoor, moisture-prone use | Best for eco-friendly, natural-feel books |
Introduction to Synthetic and Bamboo Paper
Synthetic paper is a durable, water-resistant material made from plastic resins designed to mimic the texture and printability of traditional paper, ideal for long-lasting books exposed to moisture or rough handling. Bamboo paper, crafted from bamboo pulp, offers an eco-friendly alternative with natural antibacterial properties and a smooth texture that supports high-quality printing while promoting sustainability. Both materials serve niche markets in book production, with synthetic paper emphasizing durability and bamboo paper focusing on environmental benefits.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Synthetic paper is made from polypropylene or polyethylene resins, resulting in a durable, water-resistant material produced through extrusion and calendaring processes. Bamboo paper is composed of natural bamboo fibers, obtained by mechanically or chemically pulping bamboo stalks, then pressed and dried to form sheets. The manufacturing process of synthetic paper emphasizes polymer melting and shaping, whereas bamboo paper relies on traditional pulp and sheet formation techniques enhancing eco-friendliness.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Synthetic paper, made from petrochemical-based polymers, presents challenges in biodegradability and recycling, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. Bamboo paper, derived from fast-growing, renewable bamboo plants, offers enhanced sustainability through its rapid renewability, lower water usage, and reduced chemical processing. Life cycle assessments consistently show bamboo paper's significantly lower carbon footprint and environmental impact compared to synthetic alternatives, making it a more eco-friendly choice for book production.
Durability and Longevity
Synthetic paper offers superior durability and water resistance compared to bamboo paper, making it ideal for books exposed to frequent handling or harsh environments. Bamboo paper, while eco-friendly and biodegradable, tends to degrade faster and is more susceptible to wear and tear over time. For longevity, synthetic paper maintains structural integrity and resists fading, ensuring books last significantly longer than those printed on bamboo paper.
Print Quality and Compatibility
Synthetic paper offers superior print quality due to its smooth, non-absorbent surface that ensures vibrant colors and sharp text, making it ideal for high-resolution printing. Bamboo paper provides a natural texture that may slightly absorb ink, resulting in softer prints but excellent compatibility with eco-friendly and biodegradable inks. Both papers support various printing technologies, but synthetic paper excels in ink adhesion and durability, while bamboo paper enhances sustainable printing projects.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Synthetic paper typically incurs higher production costs due to its specialized polymers, resulting in a higher purchase price compared to bamboo paper. Bamboo paper, derived from fast-growing bamboo plants, offers a more affordable and sustainable alternative with lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. For book production, bamboo paper provides a cost-effective solution without compromising quality, enhancing overall affordability for publishers.
Recycling and Biodegradability
Synthetic paper, made from plastic resins like polypropylene, offers durability and water resistance but presents challenges in recycling due to its plastic composition, often requiring specialized facilities that are not widely available. Bamboo paper, derived from fast-growing bamboo plants, is biodegradable and recyclable within conventional paper recycling systems, making it an eco-friendly alternative with a lower environmental impact. Choosing bamboo paper supports sustainable forestry and reduces landfill waste through natural decomposition, whereas synthetic paper's persistence in the environment raises concerns about long-term pollution.
Applications in Book Publishing
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear resistance, making it ideal for specialty books such as manuals, cookbooks, and outdoor guides that require longevity and frequent handling. Bamboo paper, known for its eco-friendly properties and natural texture, is preferred in artisanal and eco-conscious book publishing, enhancing the tactile experience while supporting sustainable sourcing. Both materials cater to niche markets in book publishing, with synthetic paper emphasizing functionality and bamboo paper emphasizing sustainability and aesthetics.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumers increasingly favor bamboo paper for books due to its eco-friendly attributes, biodegradability, and sustainable sourcing, aligning with growing environmental awareness. Synthetic paper appeals to niche markets for its durability, water resistance, and tear-proof qualities, making it suitable for long-lasting or outdoor reading materials. Market trends indicate a rising demand for bamboo paper driven by sustainability trends, while synthetic paper maintains steady use where practical functionality is a priority.
Future Outlook for Book Paper Materials
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear-proof qualities, making it a promising alternative for eco-friendly and long-lasting book materials. Bamboo paper, prized for its rapid renewability and lower environmental impact, aligns with growing sustainability demands in the publishing industry. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach leveraging synthetic paper's resilience and bamboo paper's biodegradability will drive innovation in book paper production.
Infographic: Synthetic paper vs Bamboo paper for Book
 azmater.com
azmater.com