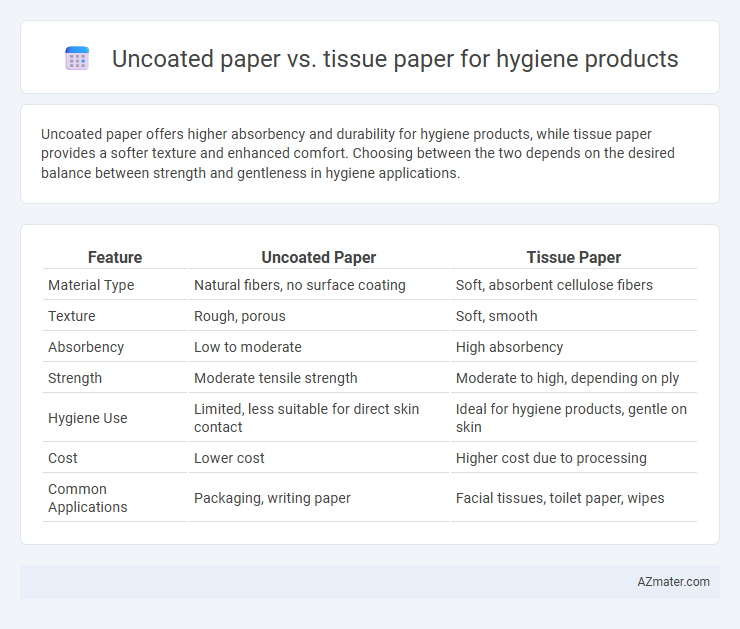
Uncoated paper offers higher absorbency and durability for hygiene products, while tissue paper provides a softer texture and enhanced comfort. Choosing between the two depends on the desired balance between strength and gentleness in hygiene applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Uncoated Paper | Tissue Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural fibers, no surface coating | Soft, absorbent cellulose fibers |
| Texture | Rough, porous | Soft, smooth |
| Absorbency | Low to moderate | High absorbency |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | Moderate to high, depending on ply |
| Hygiene Use | Limited, less suitable for direct skin contact | Ideal for hygiene products, gentle on skin |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to processing |
| Common Applications | Packaging, writing paper | Facial tissues, toilet paper, wipes |
Introduction to Hygiene Papers: Uncoated vs Tissue
Uncoated paper and tissue paper serve distinct roles in hygiene products, with uncoated paper offering enhanced durability and absorbency due to its thicker fibers and lack of surface treatment. Tissue paper, characterized by its softness and lightweight structure, provides superior comfort and gentleness ideal for sensitive skin applications such as facial tissues and toilet paper. Selecting between uncoated and tissue paper depends on balancing factors like absorbency, softness, and intended hygiene use, influencing product performance and consumer satisfaction.
Material Composition: Uncoated Paper and Tissue Paper
Uncoated paper is typically made from virgin or recycled wood pulp without any surface coatings, resulting in a natural, porous texture ideal for absorbency and breathability in hygiene products. Tissue paper, often composed of softwood and hardwood fibers blended for strength and softness, undergoes a creping process that enhances flexibility and absorbency, making it suitable for sensitive skin applications. The material composition differences directly impact the product's durability, softness, and moisture management, critical factors in hygiene product performance.
Absorbency Levels: Which Performs Better?
Uncoated paper and tissue paper differ significantly in absorbency levels, with tissue paper typically outperforming uncoated paper due to its specialized fiber composition and manufacturing process designed to enhance liquid retention. The porous structure and thinner layers of tissue paper allow it to quickly absorb and retain moisture, making it ideal for hygiene products like facial tissues and toilet paper. In contrast, uncoated paper, which lacks surface treatments, generally exhibits lower absorbency and is better suited for applications where moisture resistance is less critical.
Softness and Comfort: User Experience Compared
Uncoated paper lacks the fine finishing of tissue paper, resulting in a rougher texture that may irritate sensitive skin in hygiene products. Tissue paper, designed with softness and pliability, significantly enhances comfort and reduces abrasion during use. Consumer feedback consistently highlights tissue paper's superior gentle touch, making it the preferred choice for personal hygiene applications.
Strength and Durability: Uncoated Paper vs Tissue
Uncoated paper exhibits higher tensile strength and durability compared to tissue paper, making it more suitable for hygiene products requiring robust handling and resistance to tearing. Tissue paper is designed for softness and absorbency but generally lacks the structural integrity found in uncoated paper, limiting its use where strength is critical. The fiber composition and manufacturing process of uncoated paper contribute to its enhanced mechanical properties, ensuring longer-lasting performance in hygiene applications.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact
Uncoated paper used in hygiene products typically offers higher biodegradability due to the absence of chemical coatings, allowing faster decomposition and less environmental residue. Tissue paper, designed for softness and absorbency, is often biodegradable but can contain additives that may slow breakdown rates and increase environmental impact. Choosing uncoated paper generally reduces ecological footprint by minimizing plastic contamination and facilitating recycling or composting processes.
Cost Efficiency in Hygiene Product Manufacturing
Uncoated paper offers a cost-efficient option in hygiene product manufacturing due to its lower raw material and processing expenses compared to tissue paper. Tissue paper, while more delicate and absorbent, generally incurs higher production costs driven by specialized manufacturing and additional treatments for softness and hygiene standards. Choosing uncoated paper can reduce overall production costs, making it ideal for budget-sensitive hygiene products without compromising basic functionality.
Applications in Personal and Industrial Hygiene
Uncoated paper is widely used in personal hygiene products such as facial tissues, napkins, and paper towels due to its softness and high absorbency, making it ideal for skin contact and moisture management. Tissue paper, often manufactured with specialized treatments to enhance strength and softness, is preferred in industrial hygiene for tasks like cleaning, dusting, and sanitizing surfaces without abrasive effects. Both materials play crucial roles in hygiene applications, with uncoated paper dominating disposable personal care items and tissue paper being essential for effective industrial cleaning and maintenance.
Safety and Allergen Considerations
Uncoated paper used in hygiene products is typically free from chemical coatings, reducing the risk of skin irritation or allergenic reactions compared to coated or treated alternatives. Tissue paper designed for hygiene purposes often undergoes rigorous safety testing to ensure hypoallergenic properties, making it suitable for sensitive skin and minimizing allergen exposure. Both materials must comply with regulatory standards such as FDA or ISO to guarantee safety and reduce contaminants that could trigger allergic responses.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Uncoated paper in hygiene products is favored for its biodegradability and strength, driving market growth in eco-conscious consumer segments. Tissue paper remains dominant due to its softness and absorbency, aligning with consumer demand for comfort and gentle skin contact. Emerging trends show a rising preference for hybrid products that combine the durability of uncoated paper with the softness of tissue paper to meet diverse hygiene needs.
Infographic: Uncoated paper vs Tissue paper for Hygiene product
 azmater.com
azmater.com