Thermal paper is coated with a heat-sensitive layer that darkens when heated, making it ideal for shipping labels due to its durability and resistance to smudging without the need for ink. Copy paper lacks this coating, causing printed labels to fade quickly and suffer from poor moisture and abrasion resistance, making it less suitable for shipping applications.
Table of Comparison
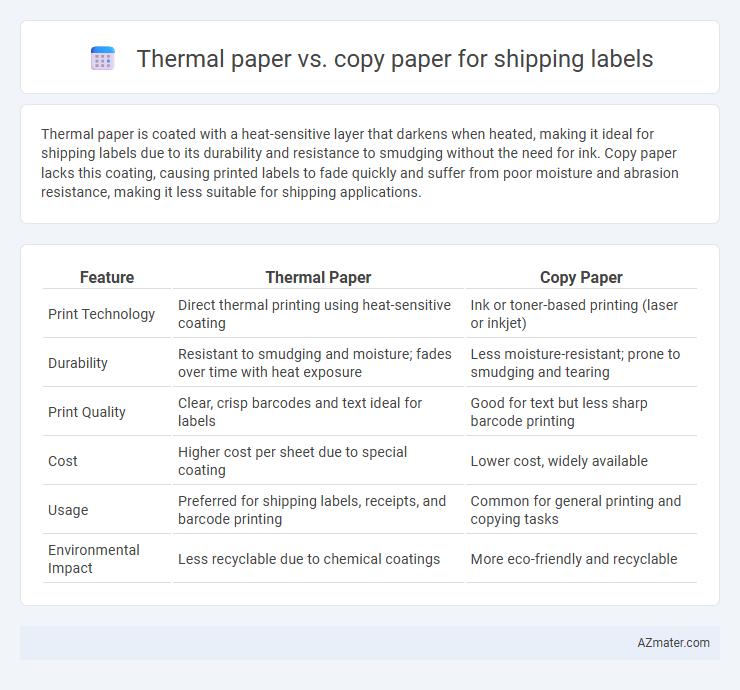
| Feature | Thermal Paper | Copy Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Print Technology | Direct thermal printing using heat-sensitive coating | Ink or toner-based printing (laser or inkjet) |
| Durability | Resistant to smudging and moisture; fades over time with heat exposure | Less moisture-resistant; prone to smudging and tearing |
| Print Quality | Clear, crisp barcodes and text ideal for labels | Good for text but less sharp barcode printing |
| Cost | Higher cost per sheet due to special coating | Lower cost, widely available |
| Usage | Preferred for shipping labels, receipts, and barcode printing | Common for general printing and copying tasks |
| Environmental Impact | Less recyclable due to chemical coatings | More eco-friendly and recyclable |
Introduction to Shipping Label Paper Types
Thermal paper and copy paper represent two primary types of shipping label materials, each suited to different printing technologies and usage scenarios. Thermal paper is coated with a heat-sensitive layer that produces images when exposed to heat, making it ideal for direct thermal printers often used in fast-paced shipping environments due to its durability and smudge resistance. Copy paper, typically used with inkjet or laser printers, requires adhesive backing and offers versatility but may fade or smudge under certain conditions, impacting label readability during transit.
What is Thermal Paper?
Thermal paper is a specialized paper coated with a chemical that changes color when exposed to heat, making it ideal for printing shipping labels without the need for ink or toner. This heat-sensitive feature ensures fast, clear, and durable printouts, which remain legible under various environmental conditions. Compared to copy paper, thermal paper improves efficiency and reduces costs in shipping label production due to its direct thermal printing technology.
What is Copy Paper?
Copy paper is a versatile, standard office paper primarily designed for use in inkjet and laser printers, making it suitable for printing shipping labels with sharp text and images. Unlike thermal paper, which reacts to heat for printing, copy paper relies on toner or ink, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of printing devices and providing durability for shipping labels. Its smooth surface and consistent thickness help maintain print quality during handling and shipping processes.
Printing Methods: Thermal vs Inkjet/Laser
Thermal paper uses direct thermal printing technology that applies heat to create images, making it ideal for shipping labels due to its fast, smudge-resistant output and no need for ink or toner. In contrast, copy paper requires inkjet or laser printers that rely on ink cartridges or toner to transfer images, which can lead to smudging and fading over time when used for labels. Thermal printing offers greater durability and clarity essential for barcode scanning and shipping accuracy.
Durability and Longevity of Labels
Thermal paper offers superior durability and longevity for shipping labels due to its heat-sensitive coating that resists smudging, fading, and moisture damage. Copy paper lacks this protective layer, making it prone to ink smearing and reduced legibility under exposure to handling, light, and moisture. For shipping labels requiring extended readability and durability, thermal paper ensures better performance and reliability throughout the delivery process.
Cost Comparison: Thermal Paper vs Copy Paper
Thermal paper typically offers lower long-term costs for shipping labels due to its direct printing process, which eliminates the need for ink or toner compared to copy paper. While copy paper requires regular replacement of ink cartridges or toner, thermal printers use heat-sensitive paper that reduces consumable expenses despite higher initial printer costs. Overall, thermal paper's cost efficiency becomes more evident in high-volume shipping operations, where bulk purchasing and reduced maintenance drive significant savings.
Print Quality and Readability
Thermal paper offers superior print quality and readability for shipping labels due to its heat-sensitive coating, producing sharp, high-contrast images without the need for ink or toner. Copy paper, lacking this coating, often results in lighter prints that may fade over time and reduce barcode scan accuracy, negatively impacting shipping efficiency. The durability and clarity of thermal paper significantly improve label legibility and scanner compatibility in various shipping environments.
Environmental Impact Considerations
Thermal paper for shipping labels often contains BPA or BPS, chemicals linked to environmental and health concerns, while copy paper is generally chlorine-bleached and may involve significant water and energy use during production. Thermal paper is less recyclable due to its coating, leading to increased landfill waste, whereas copy paper, especially if recycled or certified by FSC, supports better sustainability practices. Choosing recycled or certified copy paper reduces deforestation and pollution, presenting a more eco-friendly option for shipping label printing.
Compatibility with Shipping Label Printers
Thermal paper is specifically designed for direct thermal printers used in shipping label printers, ensuring clear, smudge-free prints without the need for ink or toner. Copy paper, on the other hand, is incompatible with thermal printers as it cannot produce the required heat-reactive image, resulting in poor print quality or no image transfer. Using thermal paper guarantees optimal compatibility and durability for shipping labels subjected to handling and varying environmental conditions.
Choosing the Best Paper for Your Shipping Needs
Thermal paper offers superior durability and smudge resistance, making it ideal for shipping labels exposed to moisture and handling during transit. Copy paper lacks the heat-sensitive coating, resulting in faded or illegible prints that can cause scanning errors and delivery delays. Selecting thermal paper ensures reliable barcode readability, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in your shipping process.
Infographic: Thermal paper vs Copy paper for Shipping label
 azmater.com
azmater.com