Uncoated paper offers higher opacity and better print quality compared to traditional newspaper paper, which is lightweight and more porous to reduce costs. Newspaper paper is typically made from recycled fibers, optimizing affordability and mass distribution despite lower durability.
Table of Comparison
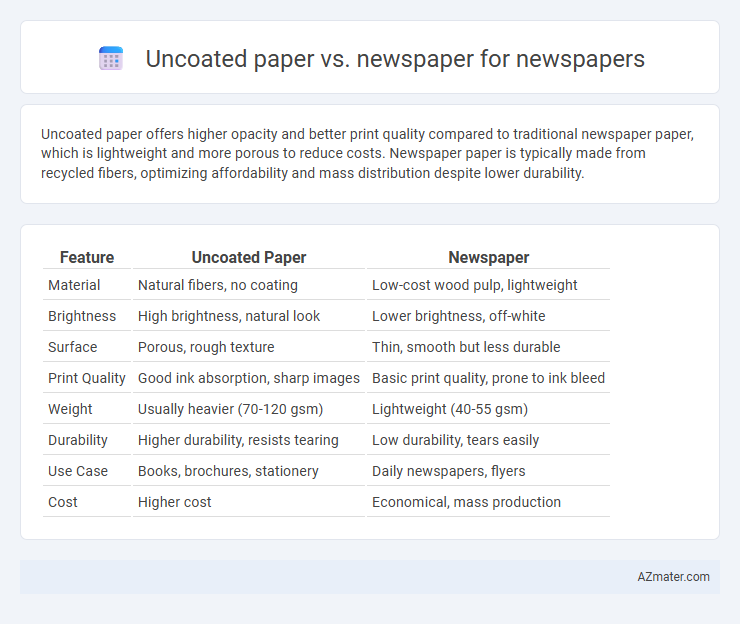
| Feature | Uncoated Paper | Newspaper |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural fibers, no coating | Low-cost wood pulp, lightweight |
| Brightness | High brightness, natural look | Lower brightness, off-white |
| Surface | Porous, rough texture | Thin, smooth but less durable |
| Print Quality | Good ink absorption, sharp images | Basic print quality, prone to ink bleed |
| Weight | Usually heavier (70-120 gsm) | Lightweight (40-55 gsm) |
| Durability | Higher durability, resists tearing | Low durability, tears easily |
| Use Case | Books, brochures, stationery | Daily newspapers, flyers |
| Cost | Higher cost | Economical, mass production |
Introduction to Printing Papers for Newspapers
Uncoated paper and newspaper paper serve distinct functions in printing with uncoated paper offering a smooth, porous surface ideal for high-quality text and image reproduction, enhancing readability and ink absorption. Newspaper paper, typically lightweight, uncoated, and made from recycled fibers, prioritizes cost-efficiency and rapid ink drying for mass-distribution printing. Both materials are formulated to balance print clarity, durability, and economic viability in the newspaper publishing industry.
What is Uncoated Paper?
Uncoated paper is a type of paper without a surface coating, offering a natural feel and better absorbency compared to coated varieties. It is often chosen for newspapers to provide enhanced print clarity and easier ink absorption, which helps prevent smudging and maintains legibility. This paper type supports sustainable printing by typically requiring fewer chemicals and enabling better recycling processes.
What is Newspaper Paper?
Newspaper paper, typically low-cost and lightweight, is designed for high-speed printing and rapid ink absorption, featuring a high percentage of uncoated pulp fibers. Uncoated paper, lacking a glossy finish, allows ink to penetrate directly into the fibers, enhancing readability but limiting image vibrancy compared to coated options. The porous texture of newspaper paper makes it ideal for mass production and daily distribution, balancing cost-efficiency with functional print quality.
Key Differences Between Uncoated Paper and Newspaper Paper
Uncoated paper offers a smooth, matte finish with higher brightness and opacity, making it ideal for high-quality print jobs requiring vivid colors and sharp text. Newspaper paper, also known as newsprint, is lightweight, lower brightness, and more porous, designed for fast absorption of ink to enable quick drying and cost-effective mass production. The main differences lie in durability, texture, and print quality, with uncoated paper providing superior performance for archival purposes while newspaper paper prioritizes affordability and rapid printing efficiency.
Print Quality: Uncoated vs Newspaper Paper
Uncoated paper offers a smoother surface that enhances ink absorption, resulting in sharper images and more vibrant colors compared to traditional newspaper paper. Newspaper paper, typically lower in weight and with a rougher texture, often produces a matte finish with less color saturation and detail definition. For high-quality newspaper printing, uncoated paper provides better print quality by minimizing ink bleed and improving overall clarity.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Uncoated paper used in newspaper printing generally offers moderate durability but tends to absorb ink more, which can lead to faster wear and color fading over time. Newspaper paper, typically made from lower-quality mechanical pulp, is less durable and prone to yellowing, tearing, and degradation when exposed to air and light. The longevity of uncoated paper is somewhat better than standard newsprint, making it preferable for archival purposes and longer-lasting publications.
Cost Implications for Publishers
Uncoated paper typically incurs higher production costs compared to standard newspaper-grade paper due to its weight and material quality, impacting overall publishing budgets. Newspaper paper, often made from lower-cost recycled fibers, offers significant savings in bulk printing while maintaining adequate print quality for daily circulation. Publishers must balance these cost factors with audience expectations and print durability requirements to optimize their expenditure and profitability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Uncoated paper for newspapers typically uses fewer chemical coatings and additives, resulting in better recyclability and less environmental toxicity compared to traditional newsprint, which often contains recycled fibers with inks and fillers that complicate recycling processes. Newspaper-grade paper is usually made from a higher percentage of post-consumer recycled content, reducing deforestation and lowering the carbon footprint associated with pulp production. The choice of uncoated paper enhances biodegradability and compostability, promoting sustainable waste management practices aligned with circular economy principles in the print media industry.
Reader Experience: Texture and Visual Appeal
Uncoated paper offers a softer texture and natural finish that enhances tactile engagement, making reading newspapers more comfortable and inviting. Newspaper print on traditional coated paper delivers sharper images and higher color vibrancy, improving visual appeal but often feels slick and less warm. Balancing texture and print clarity is crucial for publishers aiming to optimize reader experience in newspaper production.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Newspaper
Choosing the right paper for your newspaper involves comparing uncoated paper and traditional newspaper stock, focusing on factors like print quality, cost, and durability. Uncoated paper offers a smoother, more professional appearance with better ink absorption for sharper text and images, while traditional newspaper paper is more economical and lightweight, ideal for high-volume circulation. Evaluating your budget, target audience preferences, and desired print longevity ensures the best choice for effective news delivery.
Infographic: Uncoated paper vs Newspaper for Newspaper
 azmater.com
azmater.com