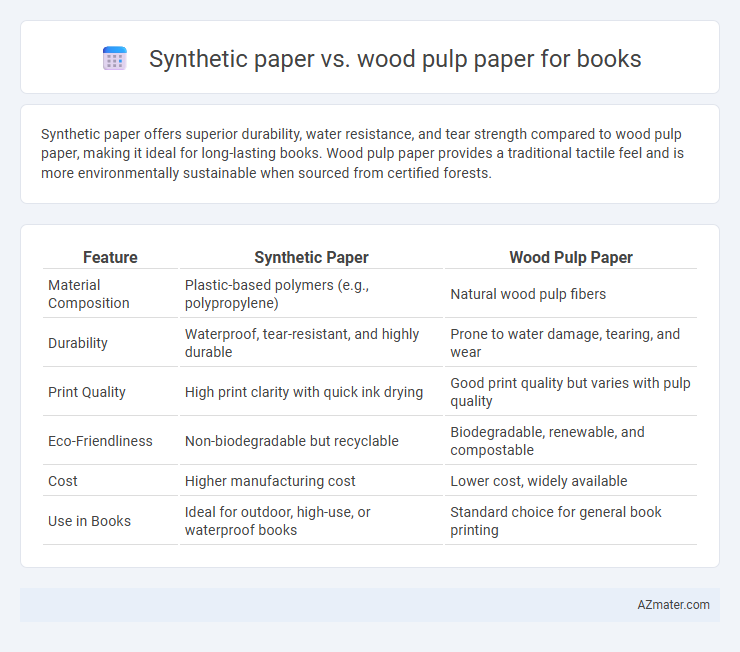
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear strength compared to wood pulp paper, making it ideal for long-lasting books. Wood pulp paper provides a traditional tactile feel and is more environmentally sustainable when sourced from certified forests.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Paper | Wood Pulp Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plastic-based polymers (e.g., polypropylene) | Natural wood pulp fibers |
| Durability | Waterproof, tear-resistant, and highly durable | Prone to water damage, tearing, and wear |
| Print Quality | High print clarity with quick ink drying | Good print quality but varies with pulp quality |
| Eco-Friendliness | Non-biodegradable but recyclable | Biodegradable, renewable, and compostable |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Use in Books | Ideal for outdoor, high-use, or waterproof books | Standard choice for general book printing |
Introduction to Book Papers: Synthetic vs Wood Pulp
Synthetic paper offers durability, water resistance, and tear-proof qualities that make it ideal for books requiring longevity and frequent handling, contrasting with wood pulp paper known for its traditional texture, biodegradability, and cost-effectiveness. Wood pulp paper, derived from cellulose fibers, delivers excellent print quality and is widely used for standard paperback and hardcover books due to its natural feel and recyclability. Choosing between synthetic and wood pulp paper depends on factors such as environmental impact, budget, and the specific functional needs of the book.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Synthetic paper consists primarily of plastic resins such as polypropylene combined with mineral fillers, producing a durable, water-resistant sheet formed through extrusion or calendering processes. Wood pulp paper derives from cellulose fibers extracted from trees, undergoing pulping, bleaching, and drying stages to create a porous, biodegradable sheet suitable for printing. The manufacturing of synthetic paper emphasizes polymer processing techniques, while wood pulp paper relies on mechanical and chemical treatments to preserve natural fiber integrity.
Durability and Longevity
Synthetic paper, made from plastic polymers like polypropylene, offers superior durability and resistance to water, tearing, and chemicals compared to wood pulp paper. Wood pulp paper, derived from cellulose fibers, tends to degrade over time due to exposure to moisture and acidic conditions, leading to yellowing and brittleness. For long-lasting books, synthetic paper ensures extended lifespan and preserves print quality under harsh conditions.
Print Quality and Visual Appeal
Synthetic paper offers superior print quality with sharper image resolution and vibrant color retention due to its non-porous surface, making text and graphics appear clearer and more striking compared to wood pulp paper. Wood pulp paper tends to absorb ink more, which can cause slight bleeding and dullness, affecting the visual appeal of printed material. For books where high-definition visuals and longer-lasting vibrancy are critical, synthetic paper provides a more consistent and professional look.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic paper, made from polypropylene or polyethylene, offers durability and water resistance but presents challenges for biodegradability and recycling compared to wood pulp paper, which is biodegradable and compostable due to its natural cellulose fibers. Wood pulp paper, sourced from sustainably managed forests certified by FSC or PEFC, supports carbon sequestration and reduces environmental footprints through renewable resources. However, synthetic paper's longer lifespan can reduce overall paper consumption, while wood pulp paper's biodegradability aligns better with circular economy principles and lower microplastic pollution.
Cost Comparison and Affordability
Synthetic paper typically costs 2 to 3 times more than wood pulp paper due to its manufacturing process involving durable polymers like polypropylene. Wood pulp paper remains more affordable for bulk book production, with prices averaging $0.50 to $1 per pound compared to synthetic paper's $1.50 to $3 per pound. While synthetic paper offers longevity and water resistance, wood pulp paper is favored for cost-effective printing and widespread availability.
Water and Tear Resistance
Synthetic paper offers superior water resistance compared to traditional wood pulp paper, preventing ink smudging and page damage even in wet conditions. Its tear resistance is significantly higher due to the durable plastic polymers used, making books more resilient to frequent handling and rough use. Wood pulp paper, while biodegradable, tends to absorb moisture easily and tears more readily, limiting its longevity in environments prone to water exposure or heavy wear.
Applications in Book Publishing
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear resistance compared to traditional wood pulp paper, making it ideal for textbooks, manuals, and outdoor reading materials in book publishing. It enhances the longevity and readability of books used in high-traffic or harsh environments, such as educational institutions and field guides. Wood pulp paper remains preferred for novels, literary works, and mass-market books due to its cost-effectiveness, recyclability, and natural feel, balancing quality with economic efficiency in large-scale production.
Reader Experience and Handling
Synthetic paper offers superior durability and water resistance, enhancing reader experience by preventing pages from tearing or wrinkling during extensive handling. Wood pulp paper provides a traditional tactile feel and natural warmth favored by readers but is more prone to wear, yellowing, and damage over time. Choosing synthetic paper improves longevity and readability in various environments, while wood pulp paper maintains the classic book aesthetic valued by many readers.
Future Trends in Book Paper Materials
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear resistance compared to traditional wood pulp paper, making it ideal for long-lasting book materials in future publishing. Advancements in eco-friendly synthetic fibers and biodegradable polymers are driving the shift toward sustainable synthetic paper alternatives. As the demand for recyclable and weather-resistant book pages grows, synthetic paper is poised to redefine industry standards, balancing longevity with environmental responsibility.
Infographic: Synthetic paper vs Wood pulp paper for Book
 azmater.com
azmater.com