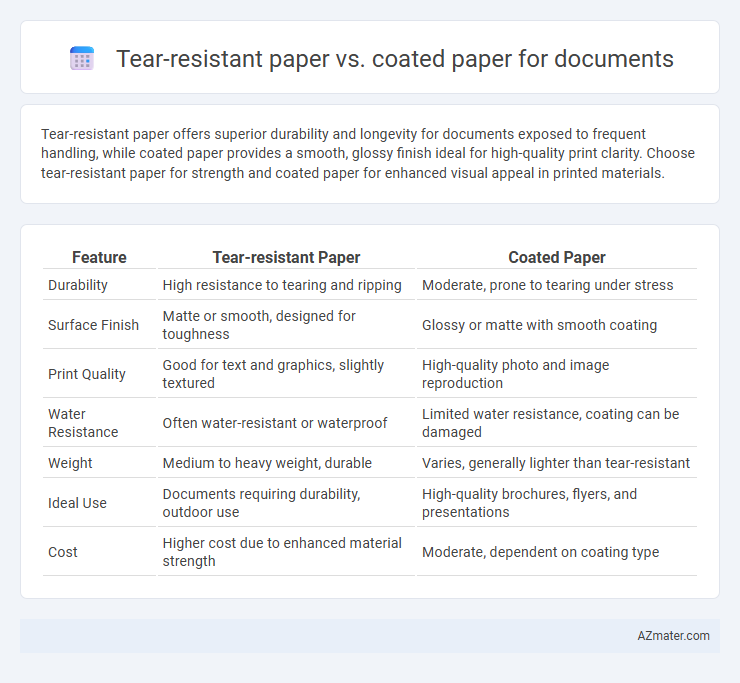
Tear-resistant paper offers superior durability and longevity for documents exposed to frequent handling, while coated paper provides a smooth, glossy finish ideal for high-quality print clarity. Choose tear-resistant paper for strength and coated paper for enhanced visual appeal in printed materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tear-resistant Paper | Coated Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to tearing and ripping | Moderate, prone to tearing under stress |
| Surface Finish | Matte or smooth, designed for toughness | Glossy or matte with smooth coating |
| Print Quality | Good for text and graphics, slightly textured | High-quality photo and image reproduction |
| Water Resistance | Often water-resistant or waterproof | Limited water resistance, coating can be damaged |
| Weight | Medium to heavy weight, durable | Varies, generally lighter than tear-resistant |
| Ideal Use | Documents requiring durability, outdoor use | High-quality brochures, flyers, and presentations |
| Cost | Higher cost due to enhanced material strength | Moderate, dependent on coating type |
Introduction: Understanding Tear-Resistant and Coated Papers
Tear-resistant paper is engineered with durable fibers and synthetic additives to enhance its strength and resistance against ripping, making it ideal for documents requiring longevity and frequent handling. Coated paper features a surface layer of clay or other substances that improve print quality by offering a smooth finish and vibrant color reproduction, suited for high-quality brochures and visual materials. Both paper types serve distinct purposes in document production, balancing durability and aesthetic appeal based on specific use cases.
Defining Tear-Resistant Paper: Features and Applications
Tear-resistant paper is specially engineered with synthetic fibers or resin coatings to enhance durability and prevent tearing, making it ideal for documents subjected to frequent handling or harsh conditions. Unlike coated paper, which has a smooth, glossy finish ideal for high-quality printing and visual appeal, tear-resistant paper prioritizes strength and longevity, often used for maps, tickets, labels, and outdoor documents. Its ability to withstand moisture, abrasion, and rough treatment distinguishes it in applications demanding resilience and extended usability.
What is Coated Paper? Types and Uses
Coated paper is paper that has been treated with a surface coating to improve its weight, brightness, smoothness, and ink holdout, making it ideal for high-quality printing. The main types of coated paper include gloss, matte, and satin, each offering different finishes suited for brochures, magazines, and flyers where vibrant images and sharp text are essential. Used primarily in advertising, publishing, and packaging, coated paper enhances visual appeal and durability compared to uncoated or tear-resistant paper, which is more focused on strength and longevity.
Durability Comparison: Tear-Resistant vs Coated Paper
Tear-resistant paper offers superior durability compared to coated paper, as it is specifically engineered to withstand physical stress without ripping or tearing easily, making it ideal for documents that require long-lasting use and frequent handling. Coated paper, while providing a smooth surface for high-quality print finishes and enhanced visual appeal, is more susceptible to tearing under tension or repeated folding. In environments where document longevity and resistance to damage are critical, tear-resistant paper provides a more reliable solution than standard coated paper.
Print Quality and Visual Appeal: Side-by-Side Analysis
Tear-resistant paper offers durability and resilience, maintaining print quality over time without smudging or fading, making it ideal for frequently handled documents. Coated paper enhances visual appeal with a smooth, glossy or matte finish that intensifies ink vibrancy and sharpness, producing crisp images and bold text. While coated paper excels in printing high-resolution graphics, tear-resistant paper provides balanced print clarity alongside superior longevity.
Cost Analysis: Tear-Resistant Paper vs Coated Paper
Tear-resistant paper typically has a higher upfront cost due to its durable materials and manufacturing process compared to coated paper, which is generally less expensive but more prone to damage and replacement. Over time, the durability of tear-resistant paper can reduce overall document replacement and maintenance expenses, providing cost-efficiency for high-handling applications. Coated paper offers lower initial investment, but increased wear and tear may result in higher long-term costs for frequent use or archival documents.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Tear-resistant paper is often made from synthetic fibers or reinforced materials that increase durability but may involve higher energy consumption and limited recyclability compared to coated paper, which typically uses a cellulose base with clay or polymer coatings. Coated paper, while providing superior print quality and smoothness, can present challenges in recycling processes due to its coating layers, potentially leading to increased landfill waste. Selecting between tear-resistant and coated paper depends on balancing durability requirements with sustainable practices such as sourcing recycled content and verifying certifications like FSC or PEFC to minimize environmental footprints.
Suitability for Document Storage and Archiving
Tear-resistant paper offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it highly suitable for long-term document storage and archiving where physical handling is frequent. Coated paper, while providing better print quality and a smoother surface, is more prone to surface damage and may degrade faster under heavy use or environmental stress. For archival purposes, tear-resistant paper ensures prolonged preservation without compromising structural integrity, whereas coated paper's aesthetic benefits are better suited for short to medium-term display documents.
Common Use Cases: Selecting the Right Paper Type
Tear-resistant paper is ideal for documents requiring durability and frequent handling, such as maps, instruction manuals, and outdoor labels, ensuring longevity without damage. Coated paper, favored for high-quality prints like brochures, flyers, and professional reports, enhances color vibrancy and detail with a smooth finish. Choosing between these types depends on the document's purpose: durability and resilience vs. visual appeal and print sharpness.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Paper for Your Documents
Tear-resistant paper offers superior durability and longevity, ideal for important documents requiring frequent handling or archival storage. Coated paper provides a smooth finish with vibrant print quality, making it suitable for marketing materials and presentations where visual appeal is critical. Selecting the best paper depends on prioritizing either durability for long-term use or enhanced aesthetics for professional impact.
Infographic: Tear-resistant paper vs Coated paper for Document
 azmater.com
azmater.com