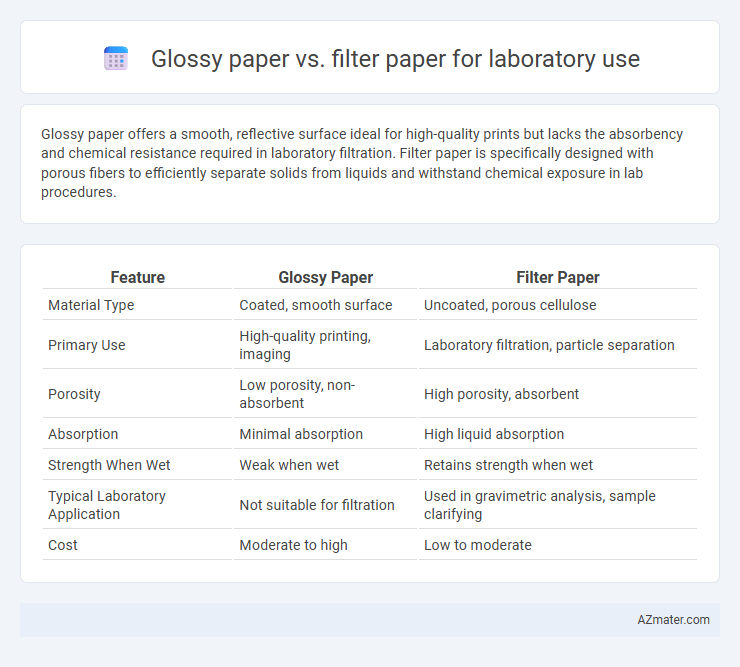
Glossy paper offers a smooth, reflective surface ideal for high-quality prints but lacks the absorbency and chemical resistance required in laboratory filtration. Filter paper is specifically designed with porous fibers to efficiently separate solids from liquids and withstand chemical exposure in lab procedures.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glossy Paper | Filter Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Coated, smooth surface | Uncoated, porous cellulose |
| Primary Use | High-quality printing, imaging | Laboratory filtration, particle separation |
| Porosity | Low porosity, non-absorbent | High porosity, absorbent |
| Absorption | Minimal absorption | High liquid absorption |
| Strength When Wet | Weak when wet | Retains strength when wet |
| Typical Laboratory Application | Not suitable for filtration | Used in gravimetric analysis, sample clarifying |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Laboratory Paper Types
Glossy paper in laboratories is primarily used for high-quality printing and visual presentations, offering a smooth, shiny surface that enhances image clarity but lacks absorbency. Filter paper serves a critical role in laboratory applications by providing porous, absorbent properties essential for separating solids from liquids during filtration processes. Understanding the distinct functions of glossy and filter papers aids in selecting the appropriate material for experimental accuracy and efficiency.
Glossy Paper: Composition and Properties
Glossy paper, primarily composed of coated cellulose fibers with a smooth, reflective surface achieved through calcium carbonate or kaolin clay, offers excellent print quality and moisture resistance in laboratory settings. Its dense, non-porous structure minimizes liquid absorption, making it less suitable for filtration but ideal for high-resolution imaging or documentation tasks. The paper's high brightness and smooth texture enhance the clarity of printed graphics and text, supporting precise visual analysis in scientific reports.
Filter Paper: Composition and Properties
Filter paper, primarily composed of cellulose fibers, exhibits high porosity and tensile strength, making it ideal for laboratory filtration tasks. Its uniform pore size allows efficient separation of fine particles from liquids while maintaining chemical inertness and heat resistance. Unlike glossy paper, filter paper's absorbency and filtration efficiency facilitate precise analytical and preparative applications in laboratory environments.
Common Laboratory Applications of Glossy Paper
Glossy paper in laboratory settings is primarily used for printing high-resolution images, charts, and detailed scientific figures, ensuring clarity and vibrant color reproduction, which is essential for presentations and documentation. It offers a smooth, reflective surface that enhances the visibility of complex graphical data, making it ideal for reports and educational materials. Unlike filter paper, which is designed for filtration and absorbency tasks, glossy paper is favored for visual representation rather than experimental procedures.
Common Laboratory Applications of Filter Paper
Filter paper is essential in laboratory settings for applications such as qualitative and quantitative analysis, separating solids from liquids during filtration, and collecting precipitates in gravimetric analysis. Its porous structure enables efficient retention of fine particles while allowing the passage of liquids, making it ideal for procedures like air pollution monitoring and microbiological studies. Unlike glossy paper, filter paper is engineered to withstand chemical exposure and high temperatures without compromising integrity or filtration efficiency.
Absorption and Filtration Capabilities
Glossy paper exhibits low absorption due to its smooth, coated surface, making it unsuitable for laboratory filtration tasks that require liquid retention or separation. Filter paper, with its porous structure, offers high absorption and efficient filtration capabilities essential for separating solids from liquids in laboratory processes. The choice between glossy and filter paper directly impacts the accuracy and efficiency of experimental filtration and sample preparation.
Chemical Compatibility and Reaction Impacts
Glossy paper exhibits low chemical resistance and can degrade or warp when exposed to strong acids, bases, or solvents, making it less suitable for chemical applications. Filter paper, specifically designed for laboratory use, offers high chemical compatibility and maintains structural integrity during exposure to various reagents, ensuring accurate filtration and minimal reaction interference. Selecting filter paper enhances experimental reliability by preventing contamination and undesired chemical reactions inherent to coated or treated surfaces found in glossy paper.
Precision and Accuracy in Laboratory Results
Glossy paper, commonly used for printing, lacks the absorbent quality required for laboratory applications, leading to potential inconsistencies in sample retention and therefore reduced precision and accuracy in results. Filter paper is specifically designed to provide consistent pore size and filtering properties, ensuring more reliable separation of solids from liquids, which enhances the reproducibility and accuracy of laboratory measurements. Selecting filter paper over glossy paper is critical for maintaining the integrity of quantitative and qualitative analyses in scientific experiments.
Cost, Availability, and Environmental Considerations
Glossy paper offers lower initial cost and is widely available but is less suitable for laboratory filtration due to its coated surface that impedes permeability. Filter paper, designed for laboratory use, has higher cost and may be less readily available but ensures efficient filtration and is often made from biodegradable materials, aligning better with environmental considerations. Choosing filter paper supports laboratory accuracy and sustainability despite its higher price and occasional supply constraints.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Paper for Your Laboratory Needs
Glossy paper offers high-quality print clarity ideal for presentations and documentation, while filter paper excels in filtration tasks due to its porosity and chemical resistance. Selecting the appropriate paper depends on the specific laboratory application--glossy paper suits data reporting and visual displays, whereas filter paper is essential for separating solids from liquids in experiments. Understanding each paper's properties ensures optimal performance and accuracy in laboratory processes.
Infographic: Glossy paper vs Filter paper for Laboratory use
 azmater.com
azmater.com