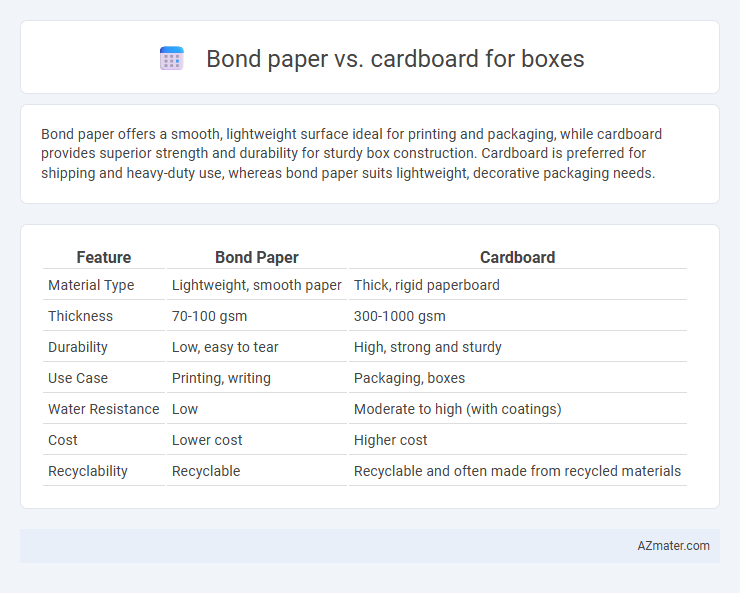
Bond paper offers a smooth, lightweight surface ideal for printing and packaging, while cardboard provides superior strength and durability for sturdy box construction. Cardboard is preferred for shipping and heavy-duty use, whereas bond paper suits lightweight, decorative packaging needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bond Paper | Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Lightweight, smooth paper | Thick, rigid paperboard |
| Thickness | 70-100 gsm | 300-1000 gsm |
| Durability | Low, easy to tear | High, strong and sturdy |
| Use Case | Printing, writing | Packaging, boxes |
| Water Resistance | Low | Moderate to high (with coatings) |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Recyclability | Recyclable | Recyclable and often made from recycled materials |
Introduction to Bond Paper and Cardboard
Bond paper is a high-quality, durable paper known for its smooth texture and strength, often used in official documents and printing applications, while cardboard is a thick, sturdy material made from multiple layers of fiberboard primarily used for packaging and structural support. Bond paper's lightweight and flexible properties differ significantly from cardboard's rigidity and cushioning capabilities, making each suitable for distinct purposes in box manufacturing. Understanding these material characteristics helps determine the best choice for packaging needs, balancing protection, presentation, and cost-effectiveness.
Key Differences Between Bond Paper and Cardboard
Bond paper, commonly used for printing and office purposes, is lightweight, smooth, and typically measures between 50-100 gsm, offering flexibility but limited durability. Cardboard, on the other hand, is a thick, rigid material made from multiple layers of paper pulp, designed to provide structural strength and protect contents in packaging applications. The key differences lie in their weight, thickness, durability, and intended use, with bond paper ideal for document printing and cardboard suited for manufacturing sturdy boxes.
Physical Properties Comparison
Bond paper exhibits a smooth texture, lightweight structure, and high flexibility, making it ideal for printed materials but less durable for heavy-duty packaging. Cardboard features a thicker, rigid composition with superior crush resistance and higher tensile strength, providing enhanced protection and sturdiness for box construction. The physical properties of cardboard, including greater thickness and stiffness, enable it to withstand impact and stacking pressures better than bond paper.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Bond paper, typically used for lightweight packaging and printing, offers moderate durability but lacks the robustness required for heavy-duty applications. Cardboard, especially corrugated varieties, provides superior strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for protecting products during shipping and handling. The fiber composition and thickness of cardboard significantly enhance its load-bearing capacity compared to the thinner, less rigid structure of bond paper.
Cost Considerations
Bond paper generally costs less than cardboard, making it a budget-friendly option for lightweight packaging or short-term use. Cardboard, though more expensive, offers greater durability and structural integrity, justifying the higher price for products requiring sturdy protection. Cost considerations should balance between the initial material cost and the functional requirements of the box's intended use.
Printability and Customization Options
Bond paper offers superior printability due to its smooth, uncoated surface that ensures sharp, vibrant images and crisp text, making it ideal for high-quality packaging designs. Cardboard, while more durable and suitable for structural integrity, often features a textured or coated surface that can limit print detail and color vibrancy, although it supports various finishing options like embossing and debossing for customization. Choosing between bond paper and cardboard for boxes depends on balancing the need for precise visual presentation with the requirement for durability and tactile design elements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bond paper, typically made from wood pulp, has a lower recyclability rate compared to cardboard, which is often composed of recycled fibers and supports multiple recycling cycles. Cardboard's higher durability and biodegradability make it a more sustainable packaging option, reducing landfill waste and promoting circular economy practices. The environmental impact of bond paper increases with deforestation and chemical processing, whereas cardboard production increasingly incorporates eco-friendly methods such as using renewable energy and recycled content.
Ideal Uses for Bond Paper in Packaging
Bond paper excels in packaging applications requiring lightweight and flexible materials, ideal for printing high-quality graphics and detailed labels on box surfaces. It offers excellent ink absorption, making it perfect for customized packaging such as gift boxes, product inserts, and promotional materials. Its smooth texture and durability enhance the visual appeal and protection of lightweight products without adding bulk.
Situations Where Cardboard Is Preferred
Cardboard is preferred for box packaging when durability and protection during shipping are essential, as its thick, rigid structure can withstand impact better than bond paper. In situations requiring custom printing for branding on larger surfaces, cardboard offers a more stable and professional appearance. For heavy or bulky items, cardboard boxes provide superior support and stacking capability compared to bond paper alternatives.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Boxes
Selecting the appropriate material for boxes depends on the intended use and durability requirements; bond paper offers smooth texture and printability ideal for lightweight, decorative packaging, while cardboard provides superior strength and rigidity suited for heavy-duty shipping and storage. Bond paper is typically used for presentation boxes or retail packaging where appearance matters, whereas cardboard is preferred for protective packaging due to its structural integrity and cushioning properties. Evaluating factors such as weight support, environmental impact, and cost efficiency ensures the right balance between aesthetics and functionality in box material selection.
Infographic: Bond paper vs Cardboard for Box
 azmater.com
azmater.com