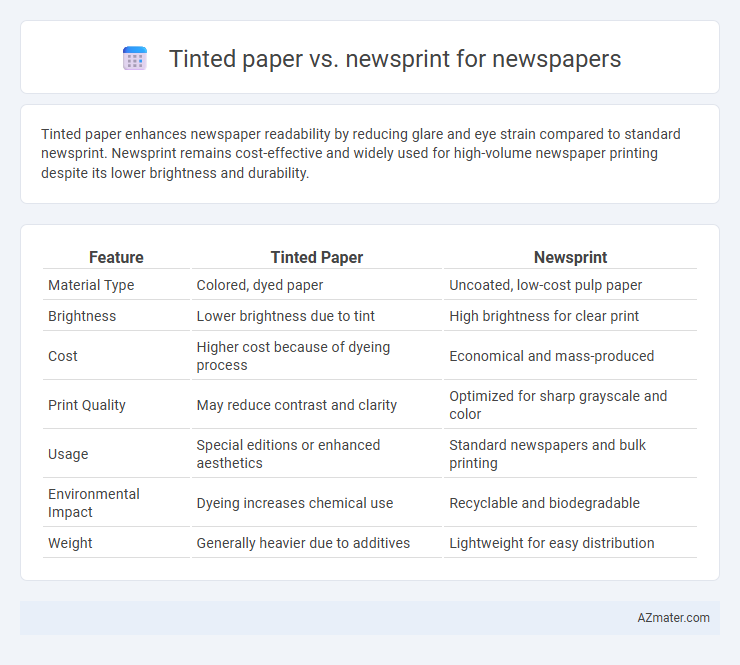
Tinted paper enhances newspaper readability by reducing glare and eye strain compared to standard newsprint. Newsprint remains cost-effective and widely used for high-volume newspaper printing despite its lower brightness and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tinted Paper | Newsprint |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Colored, dyed paper | Uncoated, low-cost pulp paper |
| Brightness | Lower brightness due to tint | High brightness for clear print |
| Cost | Higher cost because of dyeing process | Economical and mass-produced |
| Print Quality | May reduce contrast and clarity | Optimized for sharp grayscale and color |
| Usage | Special editions or enhanced aesthetics | Standard newspapers and bulk printing |
| Environmental Impact | Dyeing increases chemical use | Recyclable and biodegradable |
| Weight | Generally heavier due to additives | Lightweight for easy distribution |
Introduction to Newspaper Printing Materials
Tinted paper offers enhanced visual appeal and readability through subtle color tones, improving the reader's experience in newspaper printing. Newsprint remains the industry standard due to its cost-effectiveness, lightweight nature, and high absorbency suited for fast print runs. Choosing between tinted paper and newsprint depends on balancing aesthetic quality with budget constraints and printing efficiency.
What is Tinted Paper?
Tinted paper is a type of paper that features a subtle color or shade, used primarily to reduce glare and improve readability compared to standard white paper. Unlike newsprint, which is made from inexpensive, low-quality wood pulp and typically left uncolored, tinted paper offers enhanced contrast for printed text and images, making it ideal for special editions or premium newspaper sections. Its higher quality and colored composition contribute to increased durability and a more visually appealing presentation in print media.
What is Newsprint?
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper primarily made from wood pulp, designed for printing newspapers with high-speed presses. Its lightweight and porous nature allows for quick ink absorption, resulting in sharp text and images, but it tends to yellow and degrade over time. Compared to tinted paper, newsprint offers superior affordability and recyclability, making it the preferred choice for mass newspaper production.
Cost Comparison: Tinted Paper vs Newsprint
Tinted paper generally costs 20-30% more than standard newsprint due to the additional dyeing and processing steps involved. Newsprint remains the more economical choice for large-volume newspaper production, offering low material costs typically around $0.05 to $0.10 per sheet. Although tinted paper increases expenses, its visual appeal and branding benefits can justify the higher price for niche publications.
Print Quality and Readability
Tinted paper enhances print quality by providing a subtle background that reduces glare and eye strain, improving overall readability without compromising ink contrast. Newsprint, characterized by its lower brightness and rough texture, often results in less sharp images and text clarity due to ink absorption variations. Newspapers printed on tinted paper tend to maintain consistent readability under diverse lighting conditions, whereas newsprint may struggle with legibility, especially in low light or for small fonts.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tinted paper often uses dyes and coatings that can complicate recycling processes, leading to increased environmental impact compared to newsprint, which is typically uncoated and easier to recycle. Newsprint is generally produced from recycled fibers and requires less energy and water in manufacturing, making it a more sustainable choice for newspapers. The lower chemical additives and higher recyclability of newsprint contribute to reduced landfill waste and a smaller carbon footprint relative to tinted paper.
Durability and Shelf Life
Tinted paper offers enhanced durability compared to newsprint due to its higher fiber content and improved resistance to yellowing and wear, extending the newspaper's shelf life significantly. Newsprint, primarily made from low-cost, recycled fibers, tends to degrade faster, resulting in brittleness and fading within a few months under normal conditions. For archival purposes and prolonged readability, tinted paper is preferable as it maintains structural integrity longer and preserves print clarity over time.
Audience Perception and Reader Experience
Tinted paper enhances newspaper appeal by reducing glare and eye strain, creating a more comfortable reading environment that can increase reader engagement and satisfaction. Newsprint, characterized by its lower cost and traditional white or grayish tone, may lead to quicker eye fatigue and a perception of lower quality but is widely accepted for mass circulation. Audience perception tends to favor tinted paper for premium editions or niche markets, while newsprint remains dominant due to cost-effectiveness and familiarity.
Suitability for Color and Image Printing
Tinted paper generally offers better suitability for color and image printing compared to newsprint due to its smoother surface and higher brightness, which enhance color vibrancy and image clarity. Newsprint, made from lower-quality, recycled fibers, tends to absorb ink more readily, leading to duller colors and less sharp images. For newspapers prioritizing vivid visuals and detailed graphics, tinted paper provides a more effective medium despite its higher cost.
Final Verdict: Which Paper Is Best for Newspapers?
Tinted paper enhances visual appeal and readability with improved contrast, making it ideal for premium or special edition newspapers. Newsprint remains the most cost-effective and widely used option due to its affordability and recyclability, suitable for everyday mass circulation. The final verdict depends on balancing budget constraints and desired aesthetic impact, with newsprint favored for general use and tinted paper preferred for niche, high-quality publications.
Infographic: Tinted paper vs Newsprint for Newspaper
 azmater.com
azmater.com