Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear-proof qualities, making it ideal for high-quality, long-lasting printing. Recycled paper is eco-friendly, cost-effective, and supports sustainable production but may lack the durability and print clarity of synthetic alternatives.
Table of Comparison
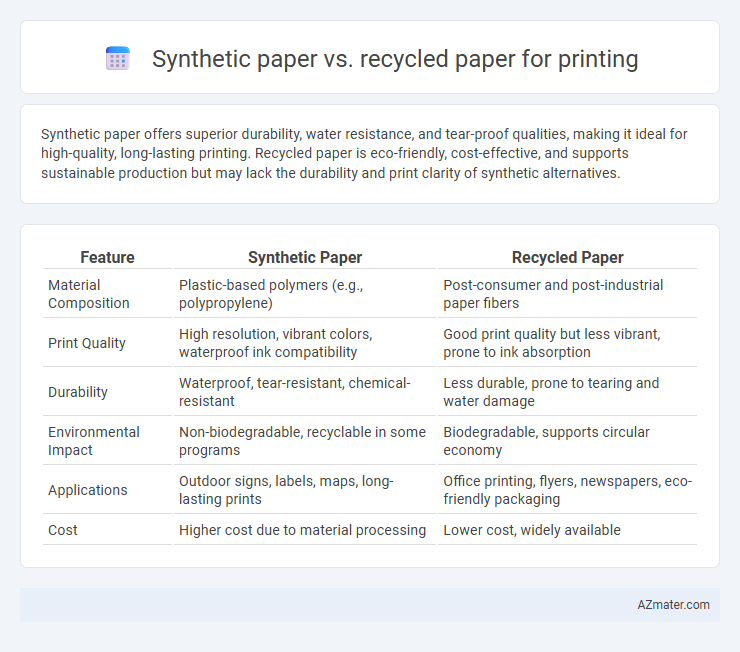
| Feature | Synthetic Paper | Recycled Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plastic-based polymers (e.g., polypropylene) | Post-consumer and post-industrial paper fibers |
| Print Quality | High resolution, vibrant colors, waterproof ink compatibility | Good print quality but less vibrant, prone to ink absorption |
| Durability | Waterproof, tear-resistant, chemical-resistant | Less durable, prone to tearing and water damage |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable in some programs | Biodegradable, supports circular economy |
| Applications | Outdoor signs, labels, maps, long-lasting prints | Office printing, flyers, newspapers, eco-friendly packaging |
| Cost | Higher cost due to material processing | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Synthetic and Recycled Paper
Synthetic paper, made from plastic polymers like polypropylene, offers exceptional durability, water resistance, and tear-proof qualities, making it ideal for long-lasting printed materials. Recycled paper is derived from processed post-consumer waste, emphasizing environmental sustainability by reducing deforestation and landfill impact while maintaining decent print quality. Both materials cater to different needs in printing, with synthetic paper excelling in resilience and recycled paper promoting eco-friendly practices.
What is Synthetic Paper?
Synthetic paper is a durable, waterproof material made from plastic polymers such as polypropylene or polyethylene, offering superior tear resistance compared to traditional wood-pulp recycled paper. Unlike recycled paper, which is made from reclaimed fibers of used paper products, synthetic paper provides excellent print clarity and longevity in harsh environments, making it ideal for labels, maps, and outdoor applications. Its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure ensures printed materials maintain high-quality visuals without degradation over time.
What is Recycled Paper?
Recycled paper is produced from used paper fibers that have been collected, processed, and repurposed to create new paper products, reducing the reliance on virgin wood pulp. It often contains post-consumer waste and manufacturing scraps, making it an eco-friendly choice for sustainable printing operations. While recycled paper may vary in texture and brightness, it supports resource conservation and minimizes environmental impact compared to synthetic alternatives.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Synthetic paper for printing is made from plastic resins, offering durability and water resistance but relying on non-renewable petroleum-based resources. Recycled paper reduces the demand for virgin wood fibers, minimizing deforestation and lowering energy consumption by up to 40% compared to virgin paper production. Environmental impact assessments highlight that recycled paper significantly decreases greenhouse gas emissions and landfill waste, whereas synthetic paper's non-biodegradable nature contributes to long-term environmental pollution concerns.
Durability and Longevity
Synthetic paper offers superior durability and longevity compared to recycled paper, resisting water, tearing, and fading even under harsh conditions. Its waterproof and tear-resistant properties make it ideal for long-term applications such as labels, maps, and outdoor signage. Recycled paper, while eco-friendly, generally lacks this level of robustness and tends to degrade faster when exposed to moisture and physical stress.
Print Quality and Color Reproduction
Synthetic paper offers superior print quality and vibrant color reproduction due to its smooth, non-porous surface that prevents ink bleeding and enhances image sharpness. Recycled paper often exhibits a rougher texture and lower brightness, which can result in muted colors and less precise print detail. Choosing synthetic paper is ideal for high-resolution printing and vivid graphics, while recycled paper suits eco-friendly printing needs with moderate color fidelity.
Cost Differences and Considerations
Synthetic paper typically costs 2 to 3 times more than recycled paper due to its durable, water-resistant properties and longer lifespan. Recycled paper offers a budget-friendly option with prices averaging 30% less, though it may compromise on durability and print quality. When selecting between synthetic and recycled paper, consider factors like print job volume, durability needs, and environmental impact to balance upfront costs and long-term value.
Applications in Printing Industry
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear-proof qualities, making it ideal for labels, maps, and outdoor signage in the printing industry. Recycled paper provides an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution suited for everyday printing tasks, such as brochures, flyers, and office documents. Choosing between synthetic and recycled paper depends on the required print longevity, environmental impact, and application-specific performance.
Pros and Cons of Synthetic Paper
Synthetic paper offers durability, water resistance, and tear resistance, making it ideal for outdoor labels, maps, and packaging that require long-lasting print quality. Its synthetic composition prevents ink smudging and provides a smooth surface for vibrant color reproduction, enhancing professional printing results. However, synthetic paper tends to be less eco-friendly compared to recycled paper, is usually more expensive, and may face compatibility issues with certain printers and ink types.
Pros and Cons of Recycled Paper
Recycled paper offers significant environmental benefits by reducing deforestation, conserving energy, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin paper, making it a sustainable choice for printing. However, recycled paper can sometimes suffer from lower brightness, reduced strength, and potential ink absorption issues, which may impact print quality and durability. Cost-effectiveness varies depending on the grade of recycled fiber used, but it generally provides a balance between eco-friendliness and performance for many printing applications.
Infographic: Synthetic paper vs Recycled paper for Printing
 azmater.com
azmater.com