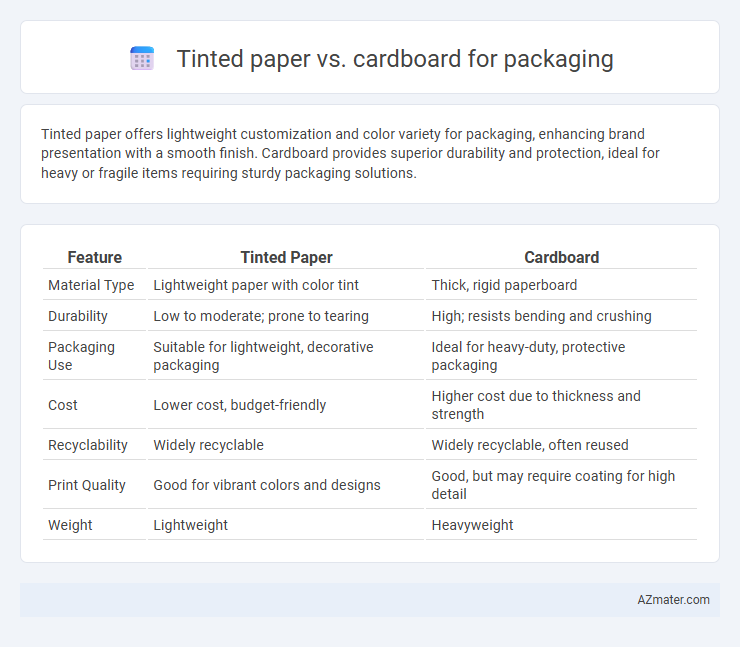
Tinted paper offers lightweight customization and color variety for packaging, enhancing brand presentation with a smooth finish. Cardboard provides superior durability and protection, ideal for heavy or fragile items requiring sturdy packaging solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tinted Paper | Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Lightweight paper with color tint | Thick, rigid paperboard |
| Durability | Low to moderate; prone to tearing | High; resists bending and crushing |
| Packaging Use | Suitable for lightweight, decorative packaging | Ideal for heavy-duty, protective packaging |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost due to thickness and strength |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable | Widely recyclable, often reused |
| Print Quality | Good for vibrant colors and designs | Good, but may require coating for high detail |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavyweight |
Introduction: Understanding Packaging Materials
Tinted paper offers lightweight protection and visual appeal for packaging, enhancing brand recognition through customizable hues and textures. Cardboard provides robust structural support and durability, ideal for safeguarding heavier products during shipping and storage. Choosing between tinted paper and cardboard depends on the balance of aesthetic presentation and functional strength required for specific packaging needs.
What is Tinted Paper?
Tinted paper is a type of paper that has been infused or dyed with color during its manufacturing process, providing a consistent hue throughout the sheet rather than just a surface coating. It is lightweight and versatile, often used to enhance the aesthetic appeal or brand identity of packaging materials without significantly increasing weight or cost. Unlike cardboard, which is thicker and more rigid for structural support, tinted paper offers visual differentiation and smooth texture ideal for wrapping or inner packaging layers.
What is Cardboard?
Cardboard is a thick, durable paper-based material commonly used in packaging for its strength and rigidity, typically made from multiple layers of paper pulp pressed together. It provides excellent protection for shipping and storage due to its cushioning properties and resistance to bending or crushing. Unlike thin, decorative tinted paper, cardboard is designed primarily for functionality and structural support in packaging applications.
Visual Appeal: Tinted Paper vs Cardboard
Tinted paper offers vibrant and customizable colors that enhance brand identity and visual appeal, making it ideal for luxury or boutique packaging. Cardboard provides a natural, rustic look with a matte finish, often used for eco-friendly or minimalist branding. While tinted paper attracts attention with its smooth texture and rich hues, cardboard emphasizes authenticity and sustainability through its tactile, earthy aesthetic.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Tinted paper offers moderate durability suitable for lightweight packaging, but cardboard outperforms it with superior strength and resistance to impact, making it ideal for heavy-duty protection. Cardboard's multi-layered structure provides enhanced rigidity and cushioning, essential for shipping and long-term storage. Tinted paper may serve aesthetic purposes but lacks the structural integrity required for robust packaging applications compared to corrugated or solid fiberboard options.
Cost Effectiveness Analysis
Tinted paper offers a lightweight and visually appealing packaging option with lower material costs but may sacrifice durability compared to cardboard. Cardboard provides superior strength and protection, often reducing damage-related expenses despite higher upfront material and shipping costs due to increased weight. Balancing tinting customization against the sturdiness of cardboard is crucial for optimizing overall packaging cost efficiency.
Printability and Customization Options
Tinted paper offers superior printability for packaging due to its smooth surface, allowing for sharp, vibrant graphics and accurate color reproduction. Cardboard provides robust customization options through embossing, debossing, and various coatings that enhance texture and durability but may sacrifice fine detail in printed designs. Choosing between tinted paper and cardboard depends on balancing the need for high-quality visual appeal versus structural strength and tactile customization.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Tinted paper offers a lightweight, recyclable option with lower energy consumption in production compared to cardboard, making it more eco-friendly for sustainable packaging. Cardboard provides superior durability and protection but often requires more resources and energy to manufacture and recycle, impacting its environmental footprint. Selecting tinted paper enhances sustainability by reducing raw material use and facilitating easier recycling processes in packaging applications.
Best Use Cases for Tinted Paper
Tinted paper excels in packaging applications requiring vibrant visual appeal and lightweight protection, making it ideal for luxury brands, gift wraps, and boutique retail products. Its ability to enhance color contrast without adding bulk suits it well for promotional materials and high-end cosmetic packaging where aesthetics drive consumer interest. Compared to cardboard, tinted paper offers superior print quality and flexibility, but less structural support, limiting its use to secondary packaging or decorative sleeves rather than heavy-duty shipping containers.
Best Use Cases for Cardboard
Cardboard excels in packaging applications requiring durability, protection, and structural support, making it ideal for shipping boxes, retail packaging, and heavy or fragile items. Its rigidity and cushioning properties ensure product safety during transit, while its recyclability and cost-effectiveness add environmental and economic benefits. Cardboard packaging is preferred for e-commerce deliveries, food containers, and customizable branding opportunities.
Infographic: Tinted paper vs Cardboard for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com