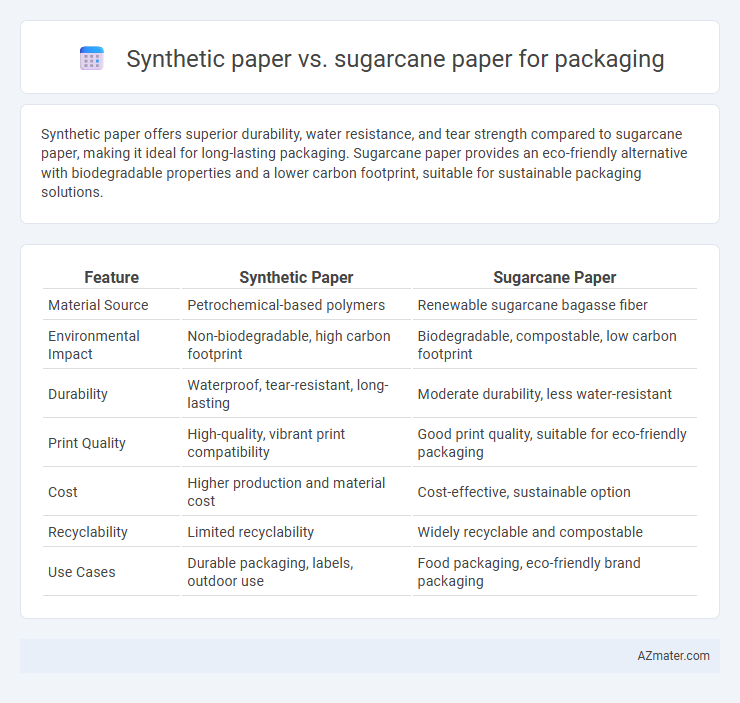
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear strength compared to sugarcane paper, making it ideal for long-lasting packaging. Sugarcane paper provides an eco-friendly alternative with biodegradable properties and a lower carbon footprint, suitable for sustainable packaging solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Paper | Sugarcane Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Petrochemical-based polymers | Renewable sugarcane bagasse fiber |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, high carbon footprint | Biodegradable, compostable, low carbon footprint |
| Durability | Waterproof, tear-resistant, long-lasting | Moderate durability, less water-resistant |
| Print Quality | High-quality, vibrant print compatibility | Good print quality, suitable for eco-friendly packaging |
| Cost | Higher production and material cost | Cost-effective, sustainable option |
| Recyclability | Limited recyclability | Widely recyclable and compostable |
| Use Cases | Durable packaging, labels, outdoor use | Food packaging, eco-friendly brand packaging |
Introduction to Synthetic and Sugarcane Papers
Synthetic paper is a durable, water-resistant material made from plastic resins such as polypropylene, offering enhanced strength and tear resistance ideal for packaging that demands longevity and moisture protection. Sugarcane paper, derived from bagasse--a byproduct of sugarcane processing--is an eco-friendly alternative emphasizing sustainability and biodegradability, increasingly adopted for environmentally conscious packaging solutions. The choice between synthetic and sugarcane papers depends on application requirements, balancing synthetic paper's robustness and sugarcane paper's renewable resource benefits.
Environmental Impact: Synthetic vs Sugarcane Paper
Synthetic paper, made from plastic resins like polypropylene, offers durability and water resistance but poses significant environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradable nature and reliance on fossil fuels. Sugarcane paper, derived from bagasse, a byproduct of sugar extraction, is biodegradable, compostable, and utilizes renewable resources, significantly reducing carbon footprint and landfill waste. When evaluating packaging sustainability, sugarcane paper outperforms synthetic alternatives by minimizing environmental pollution and enhancing circular economy practices.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Synthetic paper manufacturing involves extrusion of polymers such as polypropylene into thin, durable sheets using processes like biaxial stretching, resulting in water-resistant and tear-proof material. Sugarcane paper is produced by recycling bagasse, the fibrous residue left after extracting juice from sugarcane, through pulping, bleaching, and pressing, emphasizing renewable resource utilization and lower carbon footprint. Synthetic paper relies on petrochemical inputs and energy-intensive processes, while sugarcane paper supports sustainable agriculture and waste valorization with comparatively lower environmental impacts.
Material Properties and Performance
Synthetic paper offers superior water resistance, tear strength, and durability, making it ideal for packaging requiring long-lasting protection and moisture resistance. Sugarcane paper, made from renewable bagasse fiber, provides excellent biodegradability and compostability, appealing to eco-friendly packaging solutions but with lower tensile strength and water resistance compared to synthetic paper. The choice between synthetic and sugarcane paper depends on balancing environmental impact with performance requirements such as durability, printability, and resistance to physical and environmental stress.
Biodegradability and Recycling Options
Synthetic paper, made from polypropylene or polyethylene, offers durability and water resistance but poses challenges in biodegradability, often taking several decades to break down naturally. Sugarcane paper, derived from bagasse, is fully biodegradable within months and supports composting processes, making it environmentally friendly for packaging waste disposal. Recycling options for synthetic paper are limited due to contamination with plastics, whereas sugarcane paper can be recycled alongside conventional paper products, enhancing circular economy benefits.
Cost Analysis for Packaging Applications
Synthetic paper typically incurs higher initial production costs compared to sugarcane paper due to its petroleum-based raw materials and energy-intensive manufacturing process. Sugarcane paper offers a more cost-effective alternative, leveraging abundant agricultural waste, which reduces both raw material expenses and environmental impact in packaging applications. When scaling packaging production, sugarcane paper's lower material cost and biodegradability contribute to reduced total cost of ownership despite potential trade-offs in durability.
Printability and Customization Features
Synthetic paper offers superior printability with high resolution and vibrant color reproduction due to its smooth, non-porous surface, making it ideal for intricate designs and detailed graphics. Sugarcane paper, while eco-friendly and biodegradable, tends to have a more textured surface that can affect ink absorption and limit sharpness in print details. Customization options for synthetic paper include various finishes like matte or gloss, while sugarcane paper primarily emphasizes natural, rustic aesthetics with fewer customizable surface treatments.
Regulatory and Food Safety Compliance
Synthetic paper offers excellent moisture resistance and durability but often raises concerns regarding environmental regulations and recyclability, which may impact its acceptance in food packaging under strict safety standards. Sugarcane paper, derived from renewable biomass, aligns closely with evolving regulatory frameworks promoting sustainable packaging and demonstrates compliance with food safety regulations due to its natural composition and reduced chemical additives. Both materials must meet FDA and EFSA guidelines for food contact materials, but sugarcane paper's biodegradable nature provides a regulatory advantage amid increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly food packaging solutions.
Market Trends in Sustainable Packaging
Synthetic paper maintains strong demand in packaging due to its durability and water resistance, especially in sectors requiring extended shelf life and moisture protection. Sugarcane paper gains rapid market traction driven by consumer preference for eco-friendly materials and biodegradable packaging, aligning with global sustainability goals and regulatory pressures. The sustainable packaging market increasingly favors sugarcane paper as brands seek renewable resources to reduce carbon footprint and meet circular economy standards.
Choosing the Right Paper for Packaging Needs
Synthetic paper offers durability, water resistance, and tear-proof qualities ideal for packaging that demands longevity and high performance. Sugarcane paper provides an eco-friendly alternative, made from renewable agricultural waste, featuring biodegradability and lower carbon footprint suitable for sustainable packaging solutions. Selecting the right paper depends on balancing factors such as environmental impact, product protection requirements, and cost-effectiveness for targeted packaging applications.
Infographic: Synthetic paper vs Sugarcane paper for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com