Newsprint is a low-cost, lightweight paper designed for high-speed printing and quick ink absorption, making it ideal for daily newspapers. Cardboard offers greater durability and rigidity but is heavier and more expensive, typically used for packaging rather than newspaper printing.
Table of Comparison
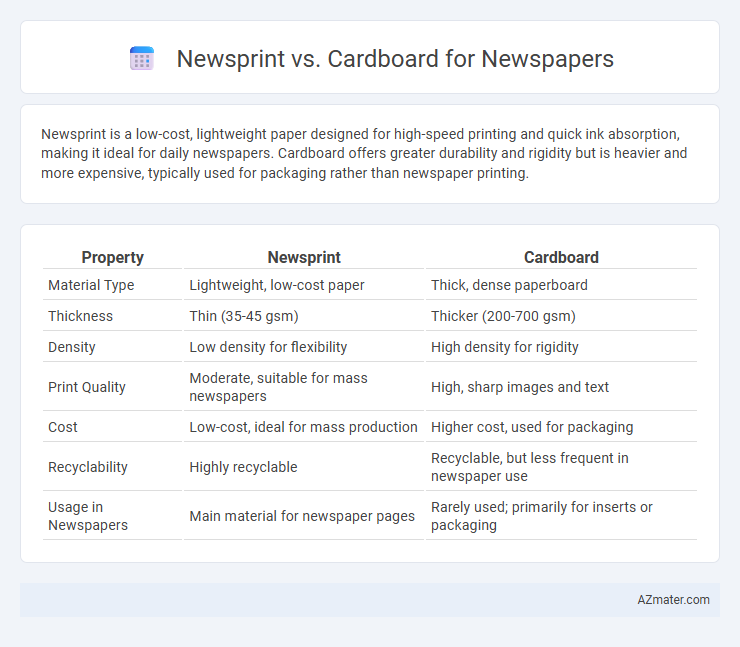
| Property | Newsprint | Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Lightweight, low-cost paper | Thick, dense paperboard |
| Thickness | Thin (35-45 gsm) | Thicker (200-700 gsm) |
| Density | Low density for flexibility | High density for rigidity |
| Print Quality | Moderate, suitable for mass newspapers | High, sharp images and text |
| Cost | Low-cost, ideal for mass production | Higher cost, used for packaging |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable | Recyclable, but less frequent in newspaper use |
| Usage in Newspapers | Main material for newspaper pages | Rarely used; primarily for inserts or packaging |
Introduction: Newsprint vs Cardboard in Newspaper Production
Newsprint serves as the primary medium for newspaper printing due to its lightweight, low cost, and high opacity, which allows for clear text and image reproduction. Cardboard, however, is thicker and more durable, often used for packaging rather than the internal pages of newspapers. The choice between newsprint and cardboard in newspaper production hinges on balancing printing clarity, cost efficiency, and material strength requirements.
Material Composition: Newsprint and Cardboard Explained
Newsprint is primarily made from wood pulp containing lower-quality fibers, resulting in a lightweight, thin, and highly porous material ideal for high-speed printing and mass distribution of newspapers. Cardboard, on the other hand, consists of multiple layers of thicker, denser fiberboard, often including recycled paper fibers and added coatings, providing superior strength and durability suitable for packaging and protective applications. The distinct material compositions of newsprint and cardboard directly influence their print quality, texture, and functional uses in newspaper production and related industries.
Print Quality: Visual and Text Clarity Comparison
Newsprint offers a smooth surface that enhances the sharpness of images and text, ensuring vibrant visual reproduction suitable for daily newspapers. Cardboard, with its rougher texture and thicker composition, can cause ink absorption issues leading to less defined edges and muted colors in printed materials. For optimal print quality focused on visual and text clarity, newsprint remains superior due to its specialized coating and lightweight fibers designed specifically for high-resolution newspaper printing.
Cost Efficiency: Price Differences and Budget Impact
Newsprint offers significant cost efficiency for newspapers due to its lower price compared to cardboard, making it ideal for high-volume printing. Cardboard, being more expensive and thicker, increases production costs and impacts overall budget allocation negatively when used for newspaper printing. Choosing newsprint helps optimize expenses while maintaining sufficient print quality for daily news distribution.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Recycling
Newsprint uses lower-quality fibers and contains fewer additives, making it more biodegradable and easier to recycle compared to cardboard, which consists of thicker layers and often includes additional coatings that slow decomposition. The production of newsprint typically consumes less energy and water, reducing its overall carbon footprint relative to cardboard manufacturing, which demands more raw materials and processing. Recycling newsprint is more efficient in sustaining paper recovery systems, supporting circular economy goals by minimizing landfill waste and conserving forest resources.
Durability: Strength and Longevity Analysis
Newsprint offers limited durability with lower tensile strength and quick degradation, making it suitable for short-term newspaper use. Cardboard provides superior strength and longevity due to its thicker fibers and higher density, enhancing resistance to wear and moisture. These properties make cardboard more durable for archival and packaging purposes compared to the fragile nature of newsprint.
Production Process: Manufacturing Differences
Newsprint is produced using mechanical pulping methods primarily from softwood fibers, resulting in a lightweight, low-cost paper with high opacity ideal for newspaper printing. Cardboard manufacturing involves the layering and bonding of multiple pulp-based sheets or recycled fibers into a thicker, more durable material through processes like corrugation or lamination. The distinct production techniques influence their respective strength, thickness, and suitability for either newsprint dissemination or protective packaging applications.
Weight and Handling: Distribution Considerations
Newsprint is significantly lighter than cardboard, typically weighing between 35 to 55 grams per square meter, which facilitates easier handling and reduces transportation costs during newspaper distribution. Cardboard, with a much higher weight ranging from 200 to 500 grams per square meter depending on thickness, offers increased durability but complicates logistics due to its bulkiness and heavier load. Distributors prioritize newsprint for mass circulation because its lightweight composition enables more efficient stacking, faster handling, and lower freight expenses compared to the cumbersome nature of cardboard.
Reader Experience: Texture, Flexibility, and Usability
Newsprint offers a lightweight texture that enhances ease of handling and quick page-turning, promoting a comfortable reading experience for newspapers. Cardboard, with its rigid and thicker surface, provides durability but can hinder flexibility, making it less ideal for smooth, continuous reading. For usability, newsprint's breathable quality prevents excessive glare and reduces eye strain, while cardboard's stiffness limits foldability and can disrupt reader engagement.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Modern Newspapers
Newsprint remains the best choice for modern newspapers due to its cost-effectiveness, lightweight nature, and suitability for high-speed printing presses. Cardboard, while more durable and eco-friendly, is often too thick and expensive for mass newspaper production. The balance of quality, affordability, and print efficiency makes newsprint the preferred material in the newspaper industry.
Infographic: Newsprint vs Cardboard for Newspaper
 azmater.com
azmater.com