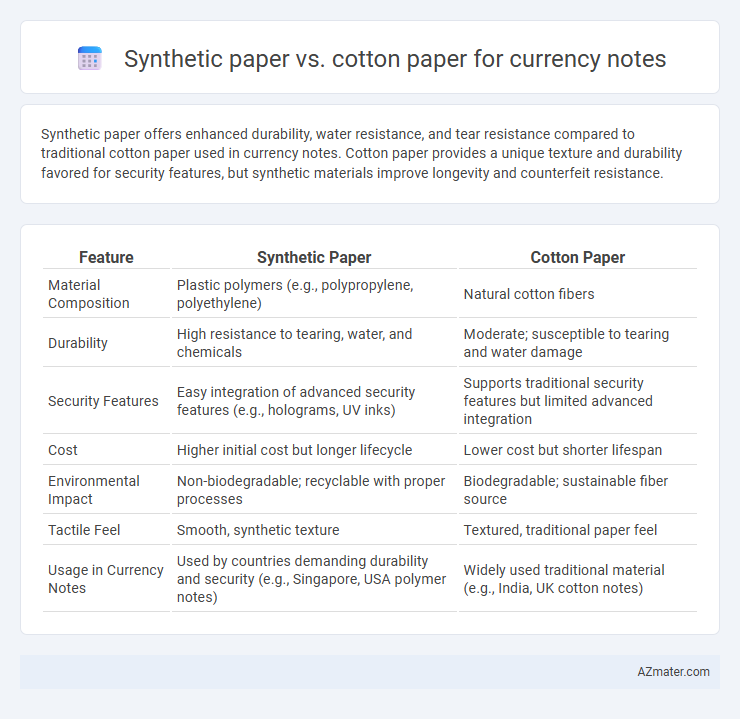
Synthetic paper offers enhanced durability, water resistance, and tear resistance compared to traditional cotton paper used in currency notes. Cotton paper provides a unique texture and durability favored for security features, but synthetic materials improve longevity and counterfeit resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Paper | Cotton Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plastic polymers (e.g., polypropylene, polyethylene) | Natural cotton fibers |
| Durability | High resistance to tearing, water, and chemicals | Moderate; susceptible to tearing and water damage |
| Security Features | Easy integration of advanced security features (e.g., holograms, UV inks) | Supports traditional security features but limited advanced integration |
| Cost | Higher initial cost but longer lifecycle | Lower cost but shorter lifespan |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable; recyclable with proper processes | Biodegradable; sustainable fiber source |
| Tactile Feel | Smooth, synthetic texture | Textured, traditional paper feel |
| Usage in Currency Notes | Used by countries demanding durability and security (e.g., Singapore, USA polymer notes) | Widely used traditional material (e.g., India, UK cotton notes) |
Introduction to Currency Paper Materials
Currency notes are predominantly made from specialized materials designed to enhance durability, security, and longevity. Synthetic paper, composed of polymer substrates like biaxially oriented polypropylene (BOPP), offers superior resistance to tearing, water, and abrasion compared to traditional cotton paper, which is made from cotton fibers providing a distinct texture and flexibility. Central banks often choose synthetic materials for advanced security features and extended lifecycle, while cotton paper remains valued for its tactile feel and established anti-counterfeiting capabilities.
Overview of Synthetic Paper for Currency
Synthetic paper for currency notes offers enhanced durability, water resistance, and tamper-evident features compared to traditional cotton paper, making it ideal for high-circulation environments. Its polymer-based composition improves longevity by resisting tearing, smudging, and fading, which reduces replacement costs and extends note life. Advanced synthetic substrates also support sophisticated security elements such as transparent windows and embedded holograms, strengthening anti-counterfeiting measures.
Characteristics of Cotton Paper in Banknotes
Cotton paper used in banknotes is favored for its durability, high tensile strength, and ability to incorporate security features like watermarks and security threads, which enhance counterfeit resistance. Its fibrous texture provides a unique tactile feel that helps in quick authentication by both machines and humans. The cellulose fibers in cotton paper also allow for long-lasting ink adhesion, ensuring that the currency remains clear and legible through extensive handling and circulation.
Durability Comparison: Synthetic vs Cotton
Synthetic paper exhibits superior durability compared to cotton paper in currency notes due to its resistance to tearing, water, and chemicals, extending the lifespan of notes significantly. Cotton paper, while offering a natural feel and security feature integration, tends to degrade faster under continuous handling and environmental exposure. The enhanced durability of synthetic substrates reduces replacement costs and maintains note integrity in circulation longer than traditional cotton fibers.
Security Features in Synthetic and Cotton Papers
Synthetic paper used in currency notes incorporates advanced security features such as embedded polymer threads, transparent windows, micro-printing, and tactile elements that resist counterfeiting and wear. Cotton paper, traditionally favored for its durability and texture, includes fiber optics, watermarks, and security fibers that enable authentication but are more vulnerable to physical damage over time. The integration of synthetic substrates enhances the longevity and security of notes by providing superior resistance to moisture, tearing, and tampering compared to cotton-based currency papers.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Analysis
Synthetic paper used for currency notes offers superior durability and water resistance, reducing the frequency of replacements and lowering long-term environmental waste compared to traditional cotton paper. Cotton paper, derived from natural fibers, is biodegradable and renewable but requires intensive water and pesticide use during cultivation, contributing to higher environmental footprints. Sustainable currency production balances synthetic material longevity with eco-friendly recycling programs to minimize resource consumption and pollution.
Cost Efficiency: Production and Lifecycle
Synthetic paper offers higher cost efficiency in currency note production due to its durability, reducing the frequency of replacement compared to cotton paper. Cotton paper, while traditional, incurs higher lifecycle costs because it wears out faster and requires more frequent reprinting and circulation replenishment. The long-term savings of synthetic paper stem from lower maintenance, resistance to wear, and improved lifespan in high-handling environments.
User Experience: Handling and Perception
Synthetic paper used in currency notes offers enhanced durability and resistance to water and wear, providing a smooth texture that facilitates easy handling and folding without tearing. Cotton paper, favored for its traditional fibrous feel, delivers a tactile, soft texture that users often associate with authenticity and quality, though it is more prone to damage from moisture and frequent handling. The perception of synthetic currency is modern and practical, while cotton-based notes maintain a classic, trusted appearance valued in everyday transactions.
Global Trends and Case Studies
Synthetic paper offers enhanced durability, water resistance, and longevity compared to traditional cotton paper, making it increasingly favored in currency note production worldwide. Countries like Australia, Canada, and Nigeria have successfully adopted polymer substrates, resulting in reduced counterfeiting and extended currency lifespan according to case studies by the Reserve Bank of Australia and the Bank of Canada. Global trends indicate a shift towards synthetic paper use driven by cost-effectiveness, environmental sustainability, and improved security features in modern banknotes.
Future Outlook for Currency Paper Materials
Synthetic paper is increasingly favored in currency note production due to its durability, resistance to water, and enhanced security features, offering a longer lifecycle compared to traditional cotton paper. Innovations in polymer substrates and nanotechnology integration promise even greater counterfeit resistance and environmental sustainability in future currency materials. As central banks worldwide seek cost-effective, secure, and eco-friendly solutions, synthetic paper is positioned to dominate the currency paper market through continuous material advancements.
Infographic: Synthetic paper vs Cotton paper for Currency note
 azmater.com
azmater.com