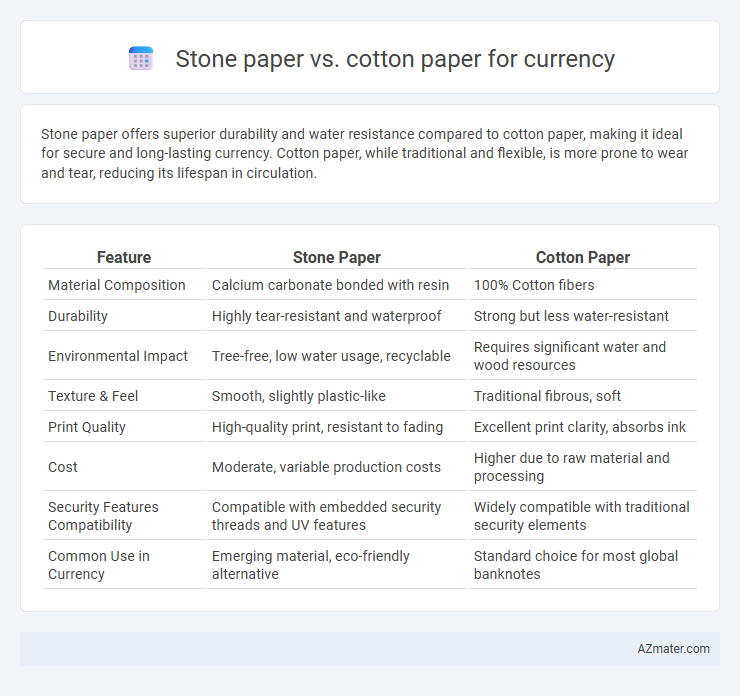
Stone paper offers superior durability and water resistance compared to cotton paper, making it ideal for secure and long-lasting currency. Cotton paper, while traditional and flexible, is more prone to wear and tear, reducing its lifespan in circulation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stone Paper | Cotton Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Calcium carbonate bonded with resin | 100% Cotton fibers |
| Durability | Highly tear-resistant and waterproof | Strong but less water-resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Tree-free, low water usage, recyclable | Requires significant water and wood resources |
| Texture & Feel | Smooth, slightly plastic-like | Traditional fibrous, soft |
| Print Quality | High-quality print, resistant to fading | Excellent print clarity, absorbs ink |
| Cost | Moderate, variable production costs | Higher due to raw material and processing |
| Security Features Compatibility | Compatible with embedded security threads and UV features | Widely compatible with traditional security elements |
| Common Use in Currency | Emerging material, eco-friendly alternative | Standard choice for most global banknotes |
Introduction to Stone Paper and Cotton Paper
Stone paper, composed primarily of calcium carbonate bonded with non-toxic resin, offers a durable and water-resistant alternative to traditional cotton paper used in currency production. Cotton paper, made from cotton linters and fibers, provides flexibility and has been the standard for high-quality banknotes due to its texture and strength. The use of stone paper in currency aims to enhance longevity and resistance to tearing, moisture, and environmental wear compared to conventional cotton-based notes.
Historical Background of Currency Paper
Currency paper has evolved significantly, with cotton paper traditionally dominating due to its durability and resistance to wear and tear since the 18th century. Stone paper, made from calcium carbonate and resin, emerged more recently as an eco-friendly alternative with superior water and tear resistance. Historical use of cotton fiber in currency allowed intricate security features and longevity, whereas stone paper represents innovation in sustainable materials for modern currency production.
Material Composition: Stone vs Cotton
Stone paper, made from calcium carbonate bonded with non-toxic resin, offers exceptional durability and water resistance compared to traditional cotton paper composed of 100% cotton fibers known for flexibility and breathability. The mineral-based stone paper resists tearing and fading under environmental stress, making it ideal for high-circulation currency requiring longevity. Conversely, cotton paper's fibrous structure provides a tactile texture favored for security features but is more prone to wear and moisture damage over time.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Stone paper exhibits superior durability and water resistance compared to cotton paper, making it highly resistant to tearing, creasing, and environmental damage. Cotton paper, traditionally used for currency, offers good strength and flexibility but is more vulnerable to moisture, wear, and microbial degradation over extended use. The longevity of stone paper currency often surpasses that of cotton-based notes, resulting in longer circulation life and reduced replacement costs.
Security Features Integration
Stone paper offers superior durability and water resistance, making it an excellent substrate for integrating advanced security features such as microtext, holograms, and UV-reactive inks without degradation over time. Cotton paper, traditionally used in currency production, allows deep fiber embedding of security threads and watermarks, providing proven tamper-evident characteristics. The choice between stone and cotton paper impacts the effectiveness and longevity of embedded security features, with stone paper excelling in resilience and cotton paper excelling in traditional fiber-based authentication methods.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Stone paper for currency production offers a sustainable alternative to traditional cotton paper by utilizing calcium carbonate bonded with non-toxic resin, significantly reducing deforestation and water consumption. Cotton paper manufacturing relies heavily on water, energy, and chemicals, contributing to higher environmental degradation and carbon emissions. The durability and recyclable nature of stone paper minimize waste and prolong currency lifespan, enhancing overall environmental benefits compared to cotton-based currency materials.
Printing Quality and Aesthetic Differences
Stone paper offers superior printing quality for currency with its smooth, non-porous surface that produces sharp, vibrant images and precise details, enhancing anti-counterfeiting features. Cotton paper provides a traditional textured feel and natural fiber aesthetic, lending an authentic, tactile quality that influences visual perception and durability. The choice between stone and cotton paper impacts both the clarity of intricate designs and the overall visual appeal of currency notes.
Costs of Production and Scalability
Stone paper production incurs higher initial equipment costs but benefits from lower raw material expenses due to the use of abundant calcium carbonate and non-wood fibers. Cotton paper requires significant agricultural inputs and energy-intensive processing, driving up costs and limiting scalability due to crop dependency and longer production cycles. Stone paper's quicker manufacturing process and reduced resource demand enable more efficient scaling for currency production, although cotton paper's durability in circulation remains a factor in overall cost-effectiveness.
Case Studies: Countries Adopting Alternative Papers
Vietnam and the Philippines have implemented stone paper for currency production, highlighting its tear resistance and waterproof properties compared to traditional cotton paper. Case studies reveal that stone paper currency reduces environmental impact through the elimination of wood pulp and chemical bleaching used in cotton paper manufacturing. Research from these countries indicates increased durability and cost-effectiveness in circulation, promoting stone paper as a viable alternative for sustainable currency solutions.
Future Trends in Currency Paper Technology
Stone paper offers enhanced durability, water resistance, and eco-friendly advantages over traditional cotton paper, which has long been the standard for currency production. Innovations in stone paper technology are leading to increased adoption by central banks seeking sustainable and long-lasting banknotes that reduce environmental impact. Future trends indicate a shift towards hybrid materials combining stone paper's synthetic properties with cotton's tactile feel to improve security features and user experience in currency notes.
Infographic: Stone paper vs Cotton paper for Currency
 azmater.com
azmater.com