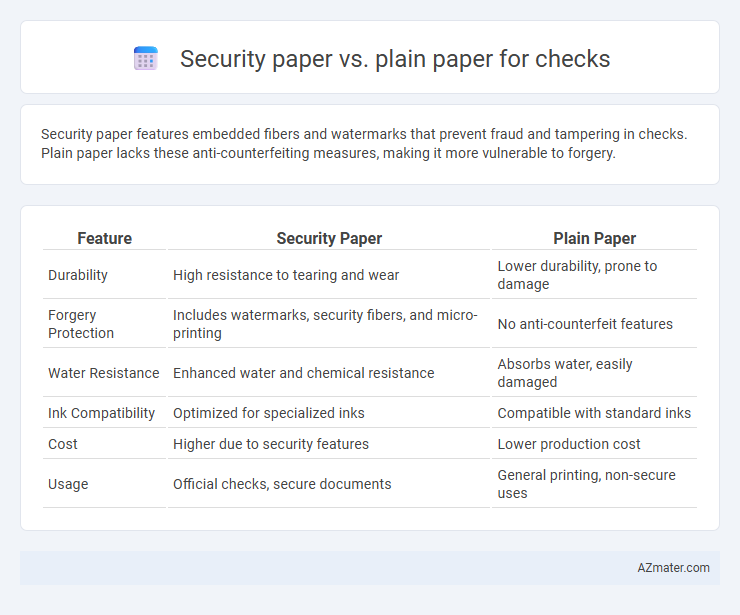
Security paper features embedded fibers and watermarks that prevent fraud and tampering in checks. Plain paper lacks these anti-counterfeiting measures, making it more vulnerable to forgery.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Security Paper | Plain Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to tearing and wear | Lower durability, prone to damage |
| Forgery Protection | Includes watermarks, security fibers, and micro-printing | No anti-counterfeit features |
| Water Resistance | Enhanced water and chemical resistance | Absorbs water, easily damaged |
| Ink Compatibility | Optimized for specialized inks | Compatible with standard inks |
| Cost | Higher due to security features | Lower production cost |
| Usage | Official checks, secure documents | General printing, non-secure uses |
Understanding Security Paper vs Plain Paper for Checks
Security paper for checks incorporates features like watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitivity to prevent counterfeiting and tampering, making it significantly safer than plain paper. Plain paper lacks these protective elements, increasing the risk of fraud, alterations, and unauthorized copying. Choosing security paper enhances the integrity and authenticity of financial documents by providing built-in safeguards against common security threats.
Key Features of Security Paper Checks
Security paper checks incorporate advanced features such as watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitivity to prevent tampering, counterfeiting, and alterations. These checks may also include embedded fibers, holograms, and security threads that provide visual and tactile verification, enhancing fraud detection. In contrast, plain paper checks lack these protective elements, making them more vulnerable to forgery and unauthorized modifications.
Risks of Using Plain Paper for Checks
Using plain paper for checks significantly increases the risk of fraud due to the lack of embedded security features such as watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitivity found in security paper. Plain paper checks are easier to alter, replicate, or counterfeit, leading to potential financial losses and compromised account information. Financial institutions often reject plain paper checks, causing processing delays and raising compliance issues with banking regulations.
Security Authentication Methods in Check Printing
Security paper used in check printing incorporates advanced authentication methods such as watermarks, microprinting, and UV-reactive fibers, which significantly reduce the risk of counterfeiting and fraud. Plain paper lacks these built-in security features, making it more vulnerable to tampering and unauthorized duplication. Incorporating security elements within the paper substrate enhances verification accuracy during bank processing and provides a reliable physical deterrent against fraudulent alterations.
Cost Differences: Security Paper vs Plain Paper
Security paper for checks typically costs significantly more than plain paper due to embedded features like watermarks, microprinting, and special fibers that enhance fraud prevention. Plain paper remains the cheaper option but lacks these security elements, increasing the risk of alteration or forgery. Businesses often weigh the higher upfront cost of security paper against potential losses from check fraud, making security paper a cost-effective investment for fraud-sensitive transactions.
Legal Compliance and Banking Requirements
Security paper for checks incorporates embedded features such as watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitivity, which enhance fraud prevention and ensure compliance with legal and banking regulations. Plain paper checks lack these protective elements, increasing the risk of alteration and rejection by banks, potentially leading to non-compliance with the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) and other financial standards. Financial institutions often mandate security paper to meet regulatory requirements for check processing and authentication, thereby safeguarding both issuers and payees against counterfeit and unauthorized transactions.
Counterfeit and Fraud Prevention Measures
Security paper for checks integrates advanced anti-counterfeiting features such as watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitivity, making it significantly more resistant to fraud compared to plain paper. Plain paper lacks these embedded security elements, rendering checks more vulnerable to alterations, forgery, and unauthorized reproductions. Financial institutions prioritize security paper to enhance verification processes and reduce the risk of counterfeit checks in transaction systems.
Use Cases: When to Use Security Paper Checks
Security paper checks are designed for high-risk transactions requiring enhanced protection against fraud, making them ideal for business payments, payroll disbursements, and government-issued checks. These checks feature watermarks, microprinting, and fraud-resistant inks that help verify authenticity and prevent unauthorized alterations. Plain paper checks are suitable for low-risk scenarios such as personal payments or informal agreements where immediate, extensive security features are not critical.
Environmental and Practical Considerations
Security paper used for checks incorporates embedded features like watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitivity that prevent fraud and tampering, reducing the risk of financial loss. Plain paper, while more environmentally friendly due to its recyclability and lower production impact, lacks these safeguards, making it less secure for financial transactions. Choosing security paper balances practical fraud prevention with a moderate environmental footprint, especially when sourced from sustainable materials or recycled fibers.
Choosing the Right Paper for Secure Transactions
Security paper for checks incorporates watermarks, microprinting, and special fibers that deter counterfeiting and alteration, ensuring transaction authenticity. Plain paper lacks these protective features, making checks vulnerable to forgery and fraud, which can lead to financial losses and legal complications. Selecting security paper enhances the integrity of financial documents by providing visible and covert safeguards against tampering during secure transactions.
Infographic: Security paper vs Plain paper for Check
 azmater.com
azmater.com