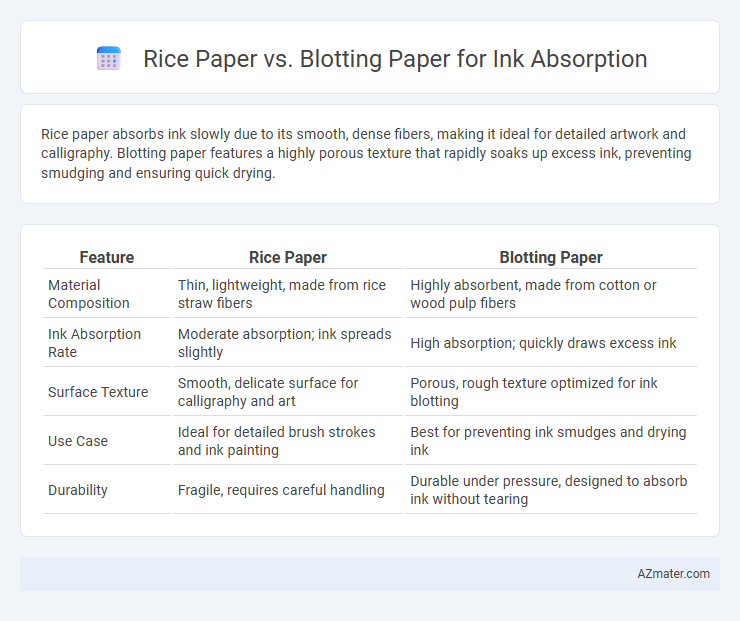
Rice paper absorbs ink slowly due to its smooth, dense fibers, making it ideal for detailed artwork and calligraphy. Blotting paper features a highly porous texture that rapidly soaks up excess ink, preventing smudging and ensuring quick drying.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rice Paper | Blotting Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Thin, lightweight, made from rice straw fibers | Highly absorbent, made from cotton or wood pulp fibers |
| Ink Absorption Rate | Moderate absorption; ink spreads slightly | High absorption; quickly draws excess ink |
| Surface Texture | Smooth, delicate surface for calligraphy and art | Porous, rough texture optimized for ink blotting |
| Use Case | Ideal for detailed brush strokes and ink painting | Best for preventing ink smudges and drying ink |
| Durability | Fragile, requires careful handling | Durable under pressure, designed to absorb ink without tearing |
Introduction: Understanding Rice Paper and Blotting Paper
Rice paper, made from the fibers of the rice plant or similar plant materials, is prized for its smooth texture and slight translucency, commonly used in calligraphy and watercolor art. Blotting paper, composed of highly absorbent cellulose fibers, is specifically designed to quickly absorb excess ink and prevent smudging on documents or artwork. The distinct fiber composition and porosity of rice paper versus blotting paper result in varying ink absorption rates, making each suitable for different artistic and practical applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Rice paper, made primarily from pounded rice straw or mulberry fibers, features a thin, translucent texture with minimal sizing, enabling moderate ink absorption and smooth dispersion. Blotting paper, composed of highly absorbent cellulose fibers processed through extensive pressing and creping during manufacturing, exhibits a dense, porous surface optimized for rapid and high-volume ink absorption. The fundamental difference in composition--natural plant fibers versus refined pulp--and manufacturing techniques results in rice paper offering controlled ink spread with artistic qualities, while blotting paper maximizes ink uptake to prevent smudging on writing surfaces.
Ink Absorption Mechanisms
Rice paper absorbs ink through capillary action within its thin, fibrous structure, allowing quick ink dispersion and smooth lines ideal for calligraphy and art. Blotting paper, composed of thick, highly porous cellulose fibers, relies on its high absorbency to draw excess ink from the surface, preventing smudging and facilitating drying. The key difference lies in rice paper's controlled absorption for artistic precision, while blotting paper maximizes ink uptake to manage moisture.
Texture and Surface Properties
Rice paper features a smooth, delicate texture with a slightly porous surface that allows moderate ink absorption, making it ideal for fine brushwork and calligraphy. Blotting paper possesses a coarse, fibrous texture with highly absorbent surface properties designed to quickly soak up excess ink and prevent smudging. The contrast in surface morphology directly impacts ink dispersion, with rice paper offering controlled ink spread and blotting paper enabling rapid ink retention for drying purposes.
Suitability for Different Types of Ink
Rice paper offers excellent absorption for water-based inks, allowing vibrant colors to spread smoothly and creating delicate brush strokes ideal for calligraphy and watercolor art. Blotting paper excels at absorbing excess ink from fountain pens and gel pens, preventing smudging and facilitating quick drying without bleeding. Choosing between rice paper and blotting paper depends on the ink type: rice paper suits water-based and dye inks, while blotting paper is optimal for oil-based or liquid calligraphy inks requiring rapid absorption.
Advantages of Rice Paper for Ink Work
Rice paper offers superior ink absorption for calligraphy and brush painting due to its smooth, delicate fibers that allow precise control and sharp ink lines. It prevents excessive bleeding and feathering, preserving the clarity and vibrancy of strokes compared to blotting paper, which absorbs ink too rapidly and unevenly. The natural texture of rice paper enhances artistic expression by providing a stable surface that balances ink retention and drying time effectively.
Benefits of Blotting Paper in Absorption
Blotting paper offers superior ink absorption due to its highly porous structure, which quickly wicks away excess ink, preventing smudging and promoting faster drying times compared to rice paper. Its unique cellulose fiber composition enhances capillary action, making it ideal for maintaining clean and crisp writing or artwork. Blotting paper's effectiveness in controlling ink spread supports precision in calligraphy, drafting, and other ink-based applications.
Common Uses in Art and Calligraphy
Rice paper, known for its smooth texture and lightweight properties, is prized in calligraphy and traditional Asian art for its ability to absorb ink evenly, producing crisp, vibrant strokes ideal for brushwork. Blotting paper, thicker and more porous, excels at quickly absorbing excess ink, preventing smudging and allowing artists and calligraphers to control dryness and preserve the integrity of fine details. Both papers serve complementary roles in art and calligraphy, with rice paper favored for the creation of detailed ink work and blotting paper used primarily for drying and correcting ink applications.
Durability and Reusability Comparison
Rice paper exhibits moderate ink absorption with smooth texture, ideal for calligraphy but tends to degrade faster due to its thin fibers, limiting durability and reusability. Blotting paper offers superior ink absorption with high porosity and thicker composition, enhancing durability by resisting wear and allowing multiple uses without significant loss of performance. For projects requiring repeated blotting and longevity, blotting paper outperforms rice paper in maintaining structural integrity and consistent ink absorption capabilities.
Choosing the Best Paper for Your Needs
Rice paper offers a smooth surface and moderate ink absorption, ideal for fine calligraphy and watercolor techniques, while blotting paper excels in rapidly absorbing excess ink to prevent smudging and drying times. When choosing between rice paper and blotting paper, consider the purpose: rice paper enhances ink flow and detail for artistic expression, whereas blotting paper serves as a practical tool for managing wet ink and protecting finished work. Assessing factors like ink type, drying speed, and desired texture helps determine the best paper to meet both creative and functional needs.
Infographic: Rice paper vs Blotting paper for Ink absorption
 azmater.com
azmater.com