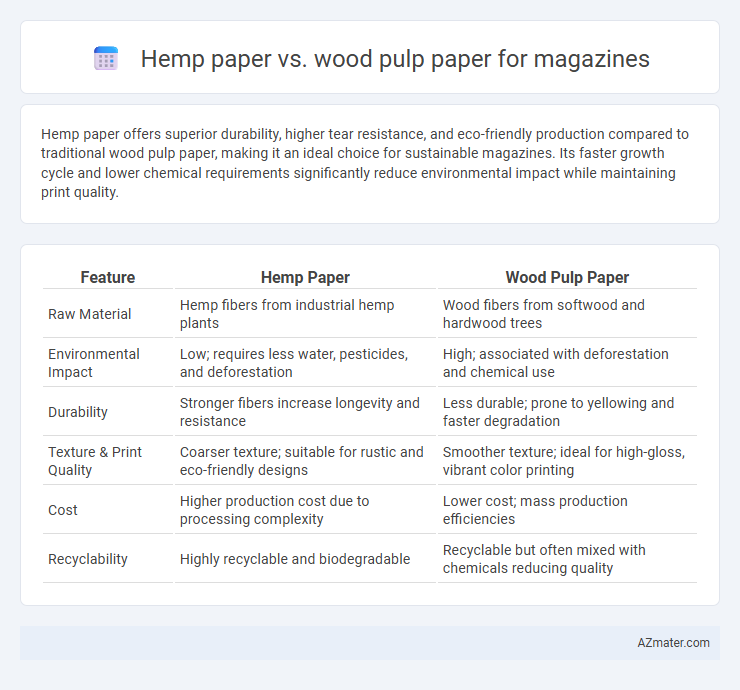
Hemp paper offers superior durability, higher tear resistance, and eco-friendly production compared to traditional wood pulp paper, making it an ideal choice for sustainable magazines. Its faster growth cycle and lower chemical requirements significantly reduce environmental impact while maintaining print quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Paper | Wood Pulp Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Hemp fibers from industrial hemp plants | Wood fibers from softwood and hardwood trees |
| Environmental Impact | Low; requires less water, pesticides, and deforestation | High; associated with deforestation and chemical use |
| Durability | Stronger fibers increase longevity and resistance | Less durable; prone to yellowing and faster degradation |
| Texture & Print Quality | Coarser texture; suitable for rustic and eco-friendly designs | Smoother texture; ideal for high-gloss, vibrant color printing |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to processing complexity | Lower cost; mass production efficiencies |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable and biodegradable | Recyclable but often mixed with chemicals reducing quality |
Introduction: The Shift from Wood Pulp to Hemp Paper
Hemp paper offers a sustainable alternative to traditional wood pulp paper, reducing deforestation and environmental impact significantly. The fiber content in hemp is longer and stronger, resulting in more durable, higher-quality magazine pages that resist yellowing and wear over time. Growing hemp requires less water and fewer pesticides compared to timber, making it a more eco-friendly source for paper production in the magazine industry.
Historical Overview of Paper Production
Hemp paper, first produced in China around 100 BCE, provided durable and sustainable material long before wood pulp paper emerged in the mid-19th century as the primary substrate for magazines. Wood pulp paper, made from mechanically or chemically processed trees, revolutionized mass magazine production due to its lower cost and abundant availability. Despite hemp's early historical use, the industrial-scale adoption of wood pulp paper largely replaced hemp in magazine printing until recent environmental considerations renewed interest in hemp's eco-friendly properties.
Cultivation: Hemp vs. Trees
Hemp cultivation for paper production requires significantly less water and time compared to trees, with hemp maturing in 3-4 months while trees take decades to reach harvest. Hemp grows densely, yields 3-4 times more fiber per acre, and enhances soil health through phytoremediation and reduced pesticide needs. Tree farming often involves deforestation and slower regrowth cycles, leading to higher environmental impact in terms of carbon emissions and biodiversity loss.
Processing Methods: Hemp Pulp vs. Wood Pulp
Hemp pulp production involves chemical and mechanical processes to break down hemp fibers, resulting in a higher cellulose content and less lignin compared to wood pulp. Wood pulp processing typically requires extensive chemical treatments, such as kraft or sulfite methods, to remove lignin and hemicellulose, which contributes to environmental concerns due to chemical waste. The comparatively simpler hemp pulping technique leads to a more sustainable and eco-friendly magazine paper production with enhanced durability and brightness.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Hemp paper production generates significantly less carbon dioxide and consumes fewer pesticides compared to traditional wood pulp paper, contributing to a lower environmental footprint for magazines. Hemp fibers grow rapidly, yielding up to four times more pulp per acre than trees, which require decades to mature, thereby reducing deforestation and habitat loss. The biodegradability and recyclability of hemp paper further enhance its sustainability, making it a greener alternative for environmentally conscious magazine publishing.
Paper Quality and Printability for Magazines
Hemp paper offers superior durability and a smoother surface compared to wood pulp paper, enhancing print quality with sharper images and vibrant colors ideal for magazines. Its higher fiber length and density reduce ink bleed and improve detail retention, resulting in a more refined and professional appearance. Wood pulp paper, while more common and cost-effective, tends to have lower tensile strength and increased acidity, which can affect the longevity and clarity of printed magazine content.
Cost Analysis: Production and Scalability
Hemp paper production entails higher initial costs due to expensive harvesting and processing techniques compared to conventional wood pulp paper, which benefits from established large-scale industrial infrastructure. The scalability of wood pulp paper is significantly more efficient, leveraging a mature supply chain and abundant raw material availability, resulting in lower overall production expenses for magazines. However, hemp's faster growth cycle and higher fiber yield per acre offer potential long-term cost reductions and sustainability advantages as processing technology advances.
Durability and Longevity of Hemp vs. Wood-Based Magazines
Hemp paper exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to traditional wood pulp paper due to its longer fibers and natural resistance to decomposition, making it ideal for magazines intended to withstand frequent handling. Hemp-based magazines resist yellowing and brittleness over time, preserving print quality and structural integrity far longer than wood-derived counterparts. This enhanced durability reduces the need for frequent replacements, supporting sustainability and cost-effectiveness in publishing.
Market Availability and Industry Adoption
Hemp paper, derived from the fibrous stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional wood pulp paper but currently represents a niche market with limited availability compared to the well-established wood pulp paper industry. Wood pulp paper dominates magazine production due to mature supply chains, lower costs, and widespread industry adoption despite environmental concerns linked to deforestation and chemical processing. Growing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures are gradually increasing hemp paper's presence in eco-conscious magazine publications, though large-scale market penetration remains constrained by higher production costs and limited industrial infrastructure.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Magazine Publishing
Hemp paper offers superior durability and eco-friendly benefits compared to traditional wood pulp paper, positioning it as a promising alternative in sustainable magazine publishing. Advances in processing technology are reducing hemp paper costs, making it more accessible for mass production and environmentally conscious publishers. Innovations in biodegradable inks and composite materials further enhance hemp paper's appeal, supporting future magazine editions focused on reducing carbon footprints and promoting circular economy principles.
Infographic: Hemp paper vs Wood pulp paper for Magazine
 azmater.com
azmater.com