Rice paper offers a smooth surface with moderate ink absorption, producing fine, detailed lines ideal for calligraphy. Blotting paper absorbs ink quickly and extensively, preventing smudging but reducing line sharpness.
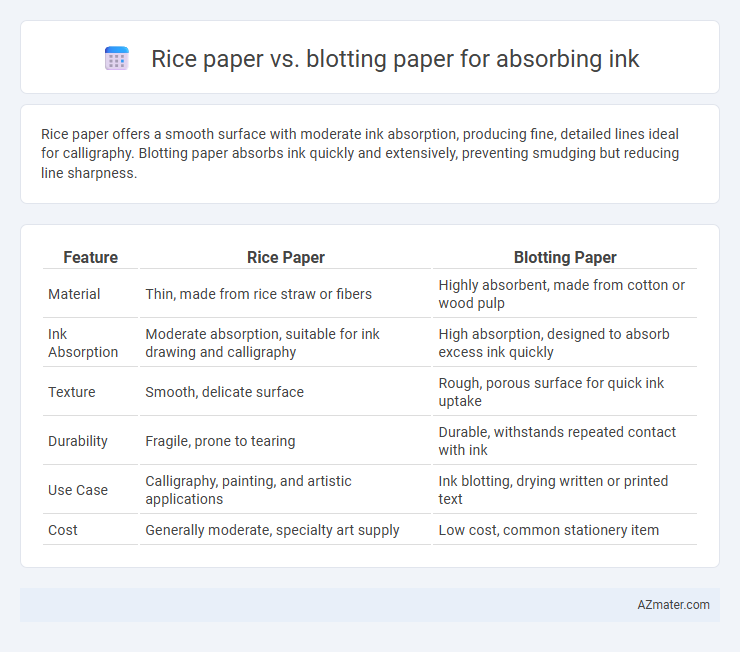
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rice Paper | Blotting Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thin, made from rice straw or fibers | Highly absorbent, made from cotton or wood pulp |
| Ink Absorption | Moderate absorption, suitable for ink drawing and calligraphy | High absorption, designed to absorb excess ink quickly |
| Texture | Smooth, delicate surface | Rough, porous surface for quick ink uptake |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to tearing | Durable, withstands repeated contact with ink |
| Use Case | Calligraphy, painting, and artistic applications | Ink blotting, drying written or printed text |
| Cost | Generally moderate, specialty art supply | Low cost, common stationery item |
Introduction: Rice Paper vs Blotting Paper
Rice paper, made from natural fibers such as mulberry or hemp, offers a smooth surface ideal for calligraphy and ink painting, but it absorbs ink slowly and minimally to preserve fine details. Blotting paper, crafted from highly absorbent cellulose fibers, excels at quickly soaking up excess ink, preventing smudges and drying errors in writing and printing processes. The choice between rice paper and blotting paper depends on whether ink retention for artistic precision or rapid absorption to avoid smearing is the primary goal.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Rice paper, traditionally made from paddy straw or bamboo fibers, undergoes a natural pulping process followed by thin pressing and drying, resulting in a smooth and delicate texture ideal for moderate ink absorption and brushwork precision. Blotting paper is produced by compressing cotton or cellulose fibers without sizing agents, creating a highly porous and thick sheet engineered specifically to absorb excess ink quickly and prevent smudging. The composition differences--rice paper's plant fibers versus blotting paper's dense cellulose network--and manufacturing methods directly influence their ink absorption capacity and drying speed.
Absorption Capacity: Which Performs Better?
Rice paper exhibits moderate absorption capacity, allowing it to soak up ink while maintaining surface integrity, making it ideal for calligraphy and artistic expressions. Blotting paper outperforms rice paper in absorption due to its porous and fibrous structure specifically designed to quickly draw excess ink, preventing smudging on documents. For applications requiring rapid and high ink absorption, blotting paper is superior, whereas rice paper suits controlled ink usage with aesthetic considerations.
Texture and Surface Characteristics
Rice paper has a smooth, delicate texture with a slightly translucent surface, making it less absorbent and ideal for controlled ink application in calligraphy and painting. Blotting paper features a porous, fibrous texture designed specifically to quickly absorb excess ink or moisture, preventing smudging and ensuring clean lines. The surface characteristics of blotting paper allow for rapid capillary action, whereas rice paper's denser fiber arrangement results in slower ink absorption and more detailed ink flow.
Ink Compatibility and Reactions
Rice paper exhibits high absorbency with water-based and traditional sumi inks, allowing smooth ink flow and vibrant strokes ideal for calligraphy and brush painting. Blotting paper is specifically designed to absorb excess oil-based inks and fountain pen ink quickly, preventing smudging, but it often causes feathering or spreading with water-based inks. Differences in fiber composition and surface texture between rice paper's cellulose fibers and blotting paper's porous structure directly affect ink compatibility and drying reactions.
Uses in Calligraphy and Art
Rice paper, renowned for its smooth texture and absorbent quality, is ideal for calligraphy where ink flow control and delicate brush strokes are essential, allowing vibrant and precise marks. Blotting paper excels at rapidly absorbing excess ink, preventing smudging and drying artwork or calligraphy sheets efficiently. Artists and calligraphers often use rice paper for creation and blotting paper as a finishing tool to maintain clarity and prevent ink bleeding.
Durability and Handling
Rice paper offers moderate durability with a smooth surface ideal for fine ink absorption, making it suitable for delicate calligraphy and artwork that require precise handling. Blotting paper, known for its high absorbency and thicker texture, excels in quickly soaking up excess ink without tearing, providing sturdier support during repeated blotting. While rice paper demands careful handling due to its thin, fragile nature, blotting paper withstands more rigorous use, making it preferable for frequent or heavy ink absorption tasks.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rice paper, made from natural fibers like rice straw and bamboo, offers a biodegradable and renewable option for absorbing ink, minimizing environmental impact compared to synthetic materials. Blotting paper, often produced from recycled cotton or wood pulp, also supports sustainability through its renewable sources and recyclability but may involve more intensive chemical processing. Choosing rice paper can reduce carbon footprint and waste due to its plant-based origin and compostability, whereas blotting paper's eco-friendliness depends heavily on sourcing and manufacturing practices.
Cost and Availability
Rice paper, commonly used in traditional art and calligraphy, is moderately priced and widely available in specialty art stores and Asian markets, making it a cost-effective choice for absorbing ink in creative applications. Blotting paper, designed specifically for absorbing excess ink, tends to be more expensive and is primarily found in stationery or office supply stores, often sold in smaller quantities which can affect overall cost efficiency. While both papers effectively absorb ink, blotting paper's higher cost is balanced by its targeted absorbency properties, whereas rice paper offers more versatility and broader availability at a lower price point.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Paper for Ink Absorption
Rice paper offers a smooth surface with moderate absorbency suitable for calligraphy and brush painting, allowing for controlled ink flow and subtle shading effects. Blotting paper features high absorbency and porous texture designed specifically to quickly absorb excess ink, preventing smudging and providing crisp drying. Selecting the right paper depends on the desired ink behavior: use rice paper for artistic expression with gradual ink absorption and blotting paper for efficient ink drying and prevention of bleed-through.
Infographic: Rice paper vs Blotting paper for Absorbing ink
 azmater.com
azmater.com