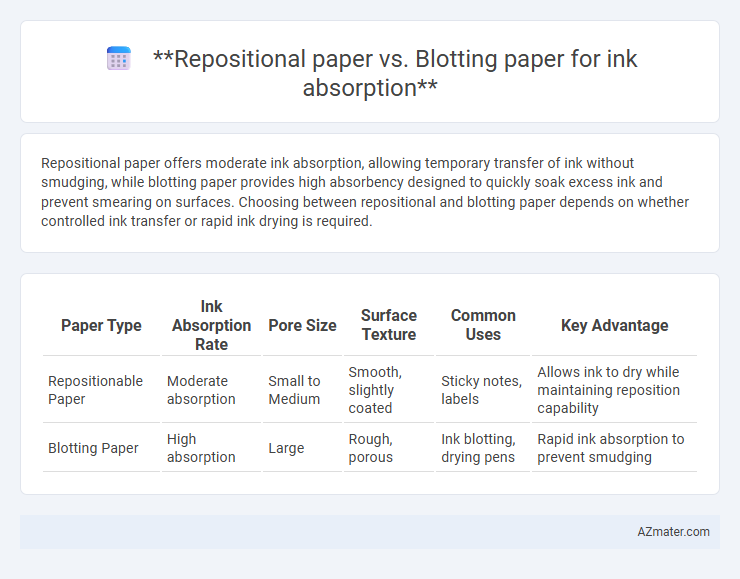
Repositional paper offers moderate ink absorption, allowing temporary transfer of ink without smudging, while blotting paper provides high absorbency designed to quickly soak excess ink and prevent smearing on surfaces. Choosing between repositional and blotting paper depends on whether controlled ink transfer or rapid ink drying is required.
Table of Comparison
| Paper Type | Ink Absorption Rate | Pore Size | Surface Texture | Common Uses | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repositionable Paper | Moderate absorption | Small to Medium | Smooth, slightly coated | Sticky notes, labels | Allows ink to dry while maintaining reposition capability |
| Blotting Paper | High absorption | Large | Rough, porous | Ink blotting, drying pens | Rapid ink absorption to prevent smudging |
Introduction to Ink Absorption Techniques
Repositional paper and blotting paper serve distinct roles in ink absorption techniques, with blotting paper primarily designed to rapidly absorb excess ink from writing surfaces, preventing smudging and promoting quick drying. Repositional paper, often used in crafts and printing, allows temporary adhesion and ink transfer without saturating the surface, facilitating precise control over ink application. Understanding the material composition and absorption rates of these papers is crucial for optimizing ink performance in various artistic and industrial contexts.
What is Repositional Paper?
Repositional paper is a specialized type of paper designed to allow temporary adhesion, enabling ink to be transferred or repositioned without permanent attachment. Unlike blotting paper, which primarily absorbs excess ink to prevent smudging, repositional paper facilitates controlled ink transfer for applications such as stamping or crafting. Its surface treatment optimizes ink absorption and release properties, ensuring clean, transferable impressions without blotting or bleeding.
What is Blotting Paper?
Blotting paper is a highly absorbent material designed to quickly soak up excess ink from writing surfaces, preventing smudging and promoting faster drying times. It is typically made from cellulose fibers that provide a porous texture ideal for ink absorption without spreading the liquid. Unlike repositionable paper, which allows for temporary attachment and movement, blotting paper solely functions to absorb ink efficiently, ensuring clean and precise writing results.
Key Differences in Material Composition
Repositional paper is coated with a low-tack adhesive layer, allowing ink to be absorbed lightly and enabling temporary adhesion without smudging. Blotting paper is made from highly absorbent, porous cellulose fibers that quickly soak up excess ink to prevent spreading and promote drying. The key difference lies in the adhesive presence on repositional paper versus the uncoated, ultra-absorbent texture of blotting paper.
Ink Absorption Efficiency Compared
Repositional paper exhibits moderate ink absorption efficiency, allowing for temporary adhesion without immediate ink diffusion, making it ideal for tracing and transferring images. In contrast, blotting paper demonstrates superior ink absorption due to its porous and fibrous structure, quickly drawing excess ink from surfaces to prevent smudging and enhance drying time. The distinct absorption rates between the two papers cater to different applications where precise ink management is crucial, with blotting paper excelling in rapid ink removal and repositional paper facilitating controlled ink handling.
Reusability and Environmental Impact
Repositional paper offers moderate ink absorption with the advantage of being reusable multiple times, reducing paper waste and lowering environmental impact compared to single-use blotting paper. Blotting paper, designed for rapid ink absorption, provides efficient drying but is typically disposable, contributing to more frequent waste generation. Choosing repositional paper supports sustainability by minimizing resource consumption, while blotting paper prioritizes functionality at the expense of higher environmental footprints.
Applications in Art and Writing
Repositional paper offers precise ink absorption with minimal feathering, making it ideal for detailed art projects and temporary annotations in writing. Blotting paper excels in rapid ink absorption, preventing smudging and ensuring clean, crisp lines essential for calligraphy and traditional penmanship. Artists and writers select repositional paper for controlled ink work and blotting paper for efficient drying and maintenance of ink quality.
Cost Effectiveness of Each Paper Type
Repositional paper offers moderate ink absorption with the advantage of reusability, making it cost-effective for short-term projects and frequent adjustments. Blotting paper, characterized by high absorbency and disposable nature, ensures efficient ink drying, suitable for high-volume or professional use but incurs higher ongoing costs due to single use. Evaluating cost-effectiveness depends on balancing the frequency of use and required ink absorption, where repositional paper reduces material costs, while blotting paper enhances workflow efficiency.
Pros and Cons: Repositional vs Blotting Paper
Repositional paper excels in temporary adhesion, allowing easy removal and repositioning of inked materials without residue, but its ink absorption is limited, often causing smudging on fresh ink. Blotting paper absorbs ink rapidly, preventing smears and enhancing drying time; however, it may cause ink feathering or bleed-through on thin paper surfaces, reducing print clarity. Choosing between repositional and blotting paper depends on whether ink control or repositioning flexibility is prioritized in the application.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Ink Needs
Repositional paper offers moderate ink absorption, ideal for temporary marks or annotations without smudging, while blotting paper excels in quickly absorbing excess ink to prevent smears and drying delays. For precise ink control in calligraphy or fountain pen use, blotting paper ensures faster drying times, whereas repositional paper supports adjustments without permanent ink transfer. Selecting the appropriate paper depends on whether rapid ink absorption or adjustable ink placement suits your specific writing or artistic requirements.
Infographic: Repositional paper vs Blotting paper for Ink absorption
 azmater.com
azmater.com