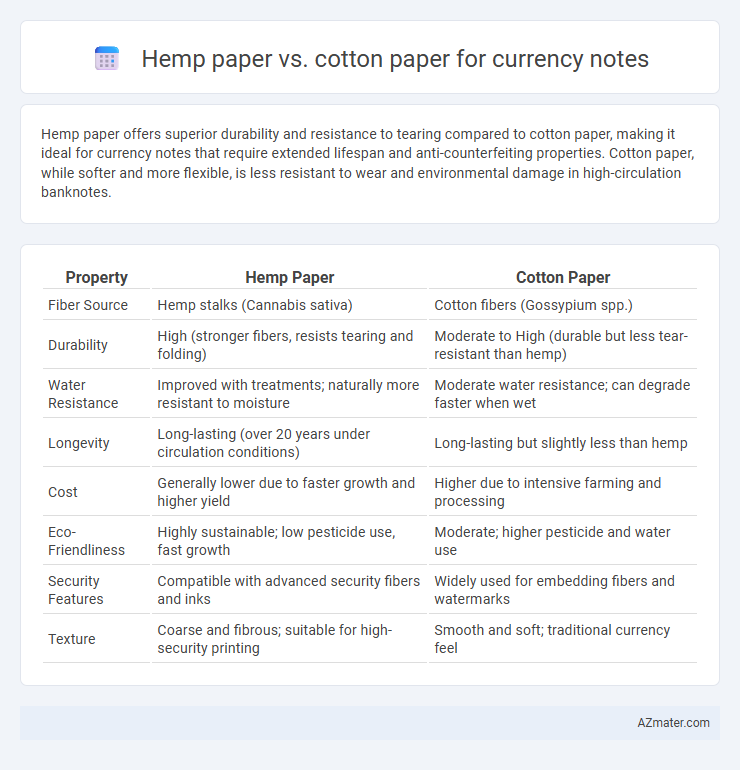
Hemp paper offers superior durability and resistance to tearing compared to cotton paper, making it ideal for currency notes that require extended lifespan and anti-counterfeiting properties. Cotton paper, while softer and more flexible, is less resistant to wear and environmental damage in high-circulation banknotes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Paper | Cotton Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Source | Hemp stalks (Cannabis sativa) | Cotton fibers (Gossypium spp.) |
| Durability | High (stronger fibers, resists tearing and folding) | Moderate to High (durable but less tear-resistant than hemp) |
| Water Resistance | Improved with treatments; naturally more resistant to moisture | Moderate water resistance; can degrade faster when wet |
| Longevity | Long-lasting (over 20 years under circulation conditions) | Long-lasting but slightly less than hemp |
| Cost | Generally lower due to faster growth and higher yield | Higher due to intensive farming and processing |
| Eco-Friendliness | Highly sustainable; low pesticide use, fast growth | Moderate; higher pesticide and water use |
| Security Features | Compatible with advanced security fibers and inks | Widely used for embedding fibers and watermarks |
| Texture | Coarse and fibrous; suitable for high-security printing | Smooth and soft; traditional currency feel |
Introduction to Currency Note Materials
Currency notes commonly utilize hemp paper and cotton paper due to their durability and security features. Hemp paper, derived from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, offers superior strength, resistance to wear, and natural anti-counterfeit properties compared to cotton paper made from textile fibers. The choice of material affects the note's lifespan, tactile feel, and ability to incorporate security threads and watermarks essential for preventing currency fraud.
Historical Use of Hemp and Cotton in Currency
Hemp paper was historically favored for currency notes due to its exceptional durability, resistance to wear, and high fiber strength, which ensured longer-lasting banknotes, as seen with early U.S. currency in the 18th and 19th centuries. Cotton paper later became the industry standard for modern currency, valued for its softness, flexibility, and ability to incorporate advanced security features like watermarks and security threads, which are crucial for anti-counterfeiting measures. Both hemp and cotton fibers have played significant roles in currency production, with hemp providing toughness and longevity, while cotton offers enhanced print quality and security adaptability.
Material Composition: Hemp Paper vs Cotton Paper
Hemp paper used in currency notes consists primarily of long, strong cellulose fibers derived from the hemp plant, providing exceptional durability and resistance to wear and tear. Cotton paper, in contrast, is made from cotton linters, offering a softer texture and high tensile strength but with shorter fibers compared to hemp. The unique fiber structure of hemp contributes to greater longevity and enhanced security features in banknotes compared to traditional cotton-based paper.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Hemp paper surpasses cotton paper in durability and lifespan, making it highly suitable for currency notes exposed to frequent handling and wear. Hemp fibers are longer and stronger, providing enhanced tear resistance and preventing quick degradation compared to cotton fibers. This results in currency notes that maintain structural integrity and remain in circulation significantly longer under rigorous use conditions.
Security Features and Print Quality
Hemp paper used in currency notes offers superior durability and enhanced resistance to tearing compared to cotton paper, which contributes to extended circulation life. Security features such as embedded watermarks, security threads, and micro-printing are more effectively integrated into hemp fibers due to their coarse texture, improving counterfeit deterrence. Cotton paper, while softer and better suited for high-resolution print quality, may lack the robustness that hemp provides for embedding advanced security elements in banknotes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp paper for currency notes offers superior environmental benefits due to its rapid growth cycle, requiring fewer pesticides and less water compared to cotton paper, which relies heavily on intensive agricultural inputs. The higher fiber yield per acre of hemp reduces deforestation and soil degradation, making it a more sustainable option for long-term currency production. Moreover, hemp paper's durability extends the lifespan of currency notes, decreasing the frequency of replacements and subsequent resource consumption.
Cost of Production and Efficiency
Hemp paper offers lower cost of production compared to cotton paper due to faster growth cycles and higher yield per acre, reducing raw material expenses for currency note manufacturing. The strong fibers in hemp enhance durability and wear resistance, increasing the lifespan of currency notes and improving efficiency in circulation. Cotton paper remains slightly more expensive due to limited supply and processing costs, but hemp's sustainability and cost benefits position it as a more efficient alternative in currency production.
Availability and Sourcing of Raw Materials
Hemp paper used for currency notes benefits from the rapid growth cycle of hemp plants, allowing for a more sustainable and renewable supply compared to cotton, which requires longer cultivation periods and extensive water resources. Cotton fibers, traditionally favored in currency production, face challenges in availability due to fluctuating agricultural yields and competition with the textile industry. Sourcing hemp is increasingly viable as regulations relax globally, offering a consistent raw material that supports environmentally friendly production practices in currency paper manufacturing.
Public Perception and Government Preferences
Hemp paper is often perceived by the public as more durable and environmentally sustainable compared to cotton paper, which is traditionally favored for its softness and familiarity in currency production. Governments prefer cotton paper due to its proven resistance to wear, ease of printing high-security features, and established supply chains, despite increasing interest in hemp for its ecological benefits and cost-effectiveness. Public trust in currency authenticity is closely tied to tactile experience and durability, factors that currently give cotton paper an edge in official preferences.
Future Trends in Currency Note Manufacturing
Hemp paper offers enhanced durability and anti-counterfeiting properties compared to cotton paper, making it a promising material for future currency note manufacturing. Innovations in hybrid blends combining hemp fibers with traditional cotton aim to improve sustainability while maintaining security features. Advances in biodegradable inks and smart embedded technologies further support the trend towards eco-friendly and highly secure banknotes.
Infographic: Hemp paper vs Cotton paper for Currency note
 azmater.com
azmater.com