Hemp paper offers superior durability and biodegradability compared to recycled paper, making it an eco-friendly choice for sustainable packaging. Recycled paper reduces waste and lowers carbon emissions but often lacks the strength and longevity of hemp-based packaging materials.
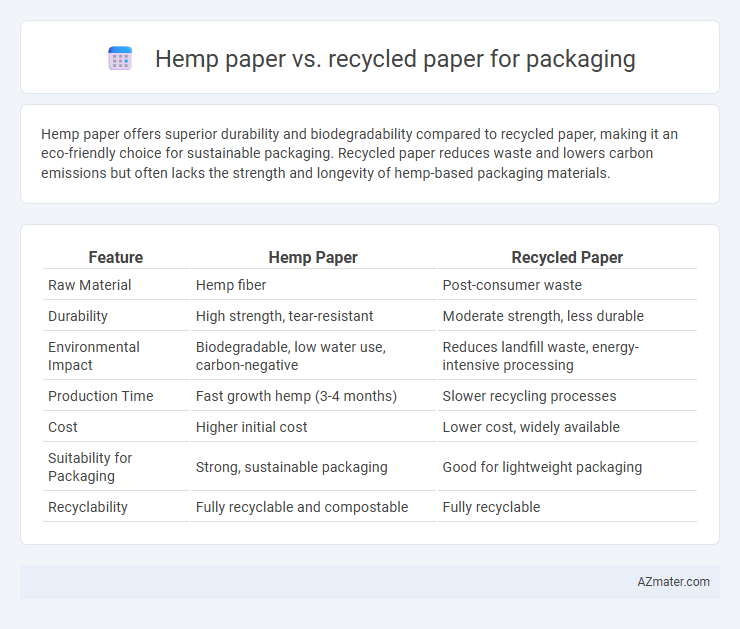
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Paper | Recycled Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Hemp fiber | Post-consumer waste |
| Durability | High strength, tear-resistant | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low water use, carbon-negative | Reduces landfill waste, energy-intensive processing |
| Production Time | Fast growth hemp (3-4 months) | Slower recycling processes |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Suitability for Packaging | Strong, sustainable packaging | Good for lightweight packaging |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable and compostable | Fully recyclable |
Introduction to Sustainable Packaging Materials
Hemp paper offers superior durability and biodegradability compared to recycled paper, making it an increasingly popular choice for sustainable packaging materials. Derived from fast-growing hemp fibers, hemp paper requires fewer chemicals and less water during production, reducing environmental impact. Recycled paper, while effective in reducing waste, often involves lower fiber quality and increased energy consumption, positioning hemp paper as a more eco-friendly alternative in packaging applications.
Overview of Hemp Paper
Hemp paper offers superior durability and biodegradability compared to recycled paper, making it an eco-friendly choice for sustainable packaging solutions. Its fibers are longer and stronger, resulting in packaging that resists tearing and absorbs less moisture, which is advantageous for protecting goods. Hemp cultivation also requires fewer pesticides and less water than traditional paper sources, reducing environmental impact throughout the production process.
Overview of Recycled Paper
Recycled paper for packaging is produced by processing used paper materials to reduce waste and conserve natural resources, offering an eco-friendly alternative to virgin fiber paper. It typically contains varying percentages of post-consumer waste and post-industrial waste, contributing to lower energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions during production. Despite sometimes having lower strength and brightness compared to virgin or hemp paper, advances in recycling technology have significantly improved the quality and durability of recycled packaging paper.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Hemp paper production consumes 50% less water and emits 60% fewer greenhouse gases compared to recycled paper, making it a more sustainable choice for packaging. Hemp's rapid growth cycle allows for up to 4 harvests per year, significantly reducing deforestation associated with recycled paper derived from wood pulp. Biodegradability rates of hemp paper exceed those of recycled paper by 20%, enhancing its environmental compatibility in packaging waste management.
Resource Efficiency and Renewability
Hemp paper offers superior resource efficiency compared to recycled paper due to its faster growth rate and higher cellulose content, requiring less water and fewer chemicals during production. Its renewability is enhanced by hemp plants maturing within 3-4 months, whereas tree-based recycled paper depends on slower-growing forests, often taking decades to replenish. Using hemp paper for packaging reduces environmental impact by minimizing deforestation and supporting sustainable agriculture practices.
Durability and Performance in Packaging
Hemp paper offers superior durability compared to recycled paper due to its longer fibers, which enhance tear resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging applications. Recycled paper, while eco-friendly, often has shorter fibers and reduced structural integrity, potentially compromising performance in protecting fragile items during transit. Hemp's natural resistance to moisture and microbial degradation further improves packaging longevity, outperforming recycled paper in demanding storage conditions.
Production Costs and Scalability
Hemp paper production incurs higher initial costs due to specialized processing equipment and longer fiber preparation times, while recycled paper benefits from established industrial systems that reduce expenses by repurposing post-consumer waste. Scalability for recycled paper is more advanced, supported by extensive global recycling infrastructure and steady material supply, whereas hemp paper faces limitations in large-scale growth due to restricted hemp cultivation and processing facilities. Despite these challenges, hemp paper offers superior durability and biodegradability, factors that may justify investment as production technologies evolve.
Challenges and Limitations
Hemp paper for packaging faces challenges such as higher production costs and limited industrial-scale availability compared to recycled paper. Recycled paper often contains contaminants and reduced fiber strength, which can compromise packaging durability and print quality. Both materials encounter limitations in sourcing consistency and require advancements in processing technology to fully meet commercial packaging standards.
Industry Adoption and Consumer Acceptance
Hemp paper is gaining traction in the packaging industry due to its durability, biodegradability, and faster renewability compared to traditional wood-based recycled paper. Companies investing in sustainable materials show increasing adoption of hemp paper, driven by its lower environmental impact and superior strength for packaging applications. Consumer acceptance is growing alongside heightened eco-consciousness, with many preferring hemp packaging for its eco-friendly reputation and superior performance compared to recycled paper products.
Future Trends in Sustainable Packaging
Hemp paper offers superior durability, biodegradability, and faster growth cycles compared to recycled paper, making it a promising material for future sustainable packaging solutions. Innovations in hemp processing technology are reducing production costs, enabling scalable adoption across industries aiming to minimize environmental impact. As consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging rises, hemp paper is positioned to complement and potentially surpass recycled paper in circular economy models and zero-waste initiatives.
Infographic: Hemp paper vs Recycled paper for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com