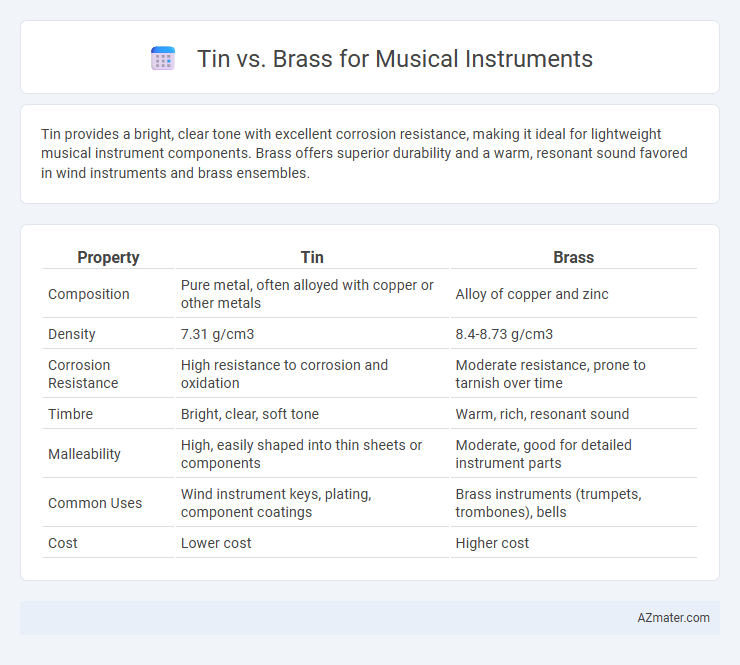
Tin provides a bright, clear tone with excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for lightweight musical instrument components. Brass offers superior durability and a warm, resonant sound favored in wind instruments and brass ensembles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tin | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure metal, often alloyed with copper or other metals | Alloy of copper and zinc |
| Density | 7.31 g/cm3 | 8.4-8.73 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to corrosion and oxidation | Moderate resistance, prone to tarnish over time |
| Timbre | Bright, clear, soft tone | Warm, rich, resonant sound |
| Malleability | High, easily shaped into thin sheets or components | Moderate, good for detailed instrument parts |
| Common Uses | Wind instrument keys, plating, component coatings | Brass instruments (trumpets, trombones), bells |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Tin and Brass in Musical Instruments
Tin is a lightweight metal often used as a coating or alloy component in musical instruments to enhance corrosion resistance and add brightness to the sound. Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is widely favored in wind instruments for its excellent durability, workability, and warm tonal qualities. Both materials contribute distinct acoustic properties, with tin primarily influencing surface characteristics and brass shaping the instrument's core sound and structural integrity.
Composition and Properties of Tin
Tin, primarily composed of the element Sn, is a soft, malleable metal with excellent corrosion resistance and low toxicity, making it ideal for use in musical instruments. Its acoustic properties include a bright, clear tone that enhances resonance when alloyed with copper to form bronze or combined with other metals. Unlike brass, which contains copper and zinc, tin's unique composition contributes to a distinct sound quality and improved durability in specific instrument components such as bells and cymbals.
Composition and Properties of Brass
Brass, an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, offers excellent acoustic properties due to its high malleability and corrosion resistance, making it a preferred material for musical instruments like trumpets and trombones. Its density and tensile strength contribute to a bright, resonant sound, while the specific copper-to-zinc ratio can be adjusted to optimize durability and tonal quality. In contrast, tin, often used as a coating or in bronze alloys, lacks the mechanical strength and acoustic clarity that brass provides, resulting in less favorable performance for wind instruments.
Historical Use of Tin and Brass in Instrument Making
Tin has been historically used as a component in alloys like bronze, crucial for early percussion instruments such as cymbals and bells due to its malleability and resonant properties. Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, became prominent in wind instrument manufacturing from the Renaissance onward, prized for its durability and bright tonal quality in trumpets, trombones, and tubas. The evolution from tin-based alloys to brass marked a significant advancement in musical instrument craftsmanship, enhancing sound projection and tonal clarity across various musical genres.
Sound Quality: Tin vs Brass
Tin produces a softer, more mellow sound in musical instruments, often favored for its warm tonal characteristics in percussion and wind instruments. Brass, composed primarily of copper and zinc, delivers a bright, powerful, and resonant sound, making it the preferred material for trumpets, trombones, and other brass instruments. The distinct acoustic properties of tin and brass significantly influence timbre, projection, and dynamic range, crucial for professional sound quality in orchestras and bands.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Tin offers moderate durability but is prone to denting and corrosion, requiring frequent cleaning to maintain sound quality. Brass exhibits superior durability with excellent resistance to wear and environmental damage, making it less susceptible to tarnish and easier to maintain over time. Brass instruments typically retain their tonal integrity longer with minimal upkeep compared to tin counterparts.
Cost and Availability of Tin and Brass
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is generally more cost-effective and widely available than tin, making it the preferred choice for many musical instruments like trumpets and trombones. Tin, though crucial as a component in some alloys like bronze, is rarer and more expensive, which can increase the overall cost and limit availability for instrument manufacturing. The abundant supply and lower price of brass contribute to its dominance in musical instrument production, allowing for easier sourcing and budget-friendly options.
Popular Instruments Made from Tin
Tin is commonly used in the construction of handbells and certain types of cymbals, valued for its bright, clear tone and resonance. Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, dominates the manufacture of trumpets, trombones, and saxophones due to its durability and warm, rich sound qualities. Instruments made from tin are often favored in folk and historical music settings, where their lightweight and tonal clarity enhance performance authenticity.
Popular Instruments Made from Brass
Brass, an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, is widely favored for making popular musical instruments such as trumpets, trombones, and tubas due to its superior acoustic properties and durability. Unlike tin, which is often used for plating or in combination with other metals, brass provides a bright, resonant tone essential for brass and wind instruments. Its malleability and corrosion resistance make brass ideal for crafting intricate shapes and enduring frequent handling in performance settings.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Musical Instrument
Choosing between tin and brass for a musical instrument involves considering sound quality, durability, and weight. Brass is favored for its bright, resonant tones and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for wind instruments like trumpets and trombones. Tin, though less common, offers a softer, mellower sound but may lack the structural strength and longevity needed for frequently played instruments.
Infographic: Tin vs Brass for Musical Instrument
 azmater.com
azmater.com