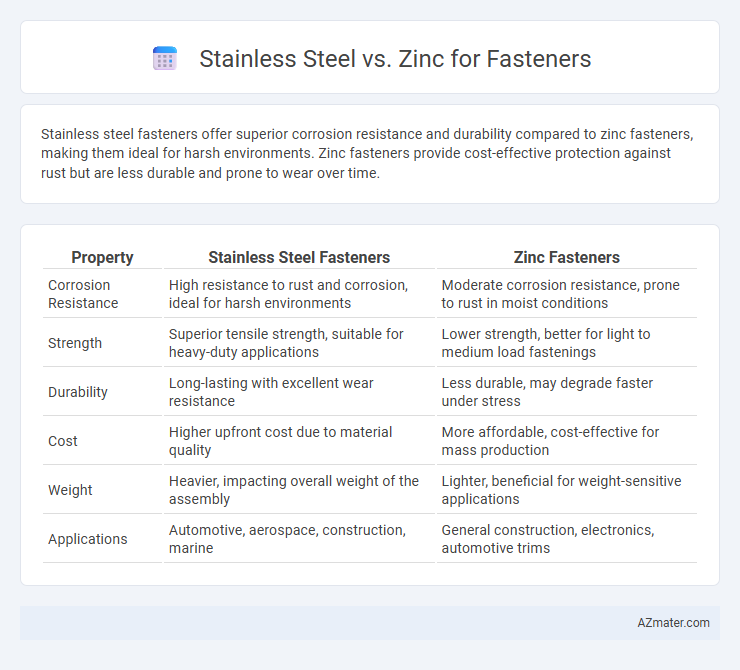
Stainless steel fasteners offer superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to zinc fasteners, making them ideal for harsh environments. Zinc fasteners provide cost-effective protection against rust but are less durable and prone to wear over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stainless Steel Fasteners | Zinc Fasteners |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to rust and corrosion, ideal for harsh environments | Moderate corrosion resistance, prone to rust in moist conditions |
| Strength | Superior tensile strength, suitable for heavy-duty applications | Lower strength, better for light to medium load fastenings |
| Durability | Long-lasting with excellent wear resistance | Less durable, may degrade faster under stress |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to material quality | More affordable, cost-effective for mass production |
| Weight | Heavier, impacting overall weight of the assembly | Lighter, beneficial for weight-sensitive applications |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, construction, marine | General construction, electronics, automotive trims |
Introduction to Fastener Materials
Stainless steel fasteners offer superior corrosion resistance and strength, making them ideal for harsh environments and long-term applications. Zinc fasteners provide cost-effective protection against rust through galvanization but may corrode faster under extreme conditions. Material selection depends on factors like exposure, mechanical stress, and budget, with stainless steel favored for durability and zinc for economical, moderate-use scenarios.
Overview of Stainless Steel Fasteners
Stainless steel fasteners are renowned for their exceptional corrosion resistance, strength, and durability, making them ideal for harsh environments and long-term applications. These fasteners typically contain chromium, which forms a passive oxide layer preventing rust and degradation, thus enhancing their lifespan in marine, chemical, and outdoor settings. Compared to zinc fasteners, stainless steel offers superior mechanical properties and maintenance-free performance, justifying a higher initial cost in critical structural and industrial uses.
Key Properties of Zinc Fasteners
Zinc fasteners offer excellent corrosion resistance due to their sacrificial coating, making them ideal for outdoor and marine applications where protection against rust is critical. They provide strong adhesion to substrates and are cost-effective compared to stainless steel, offering durability in less aggressive environments. Zinc fasteners also exhibit good mechanical strength and ease of installation, making them suitable for a wide range of construction and industrial uses.
Corrosion Resistance: Stainless Steel vs Zinc
Stainless steel fasteners offer superior corrosion resistance due to their chromium content, which forms a passive oxide layer that protects against rust and oxidation even in harsh environments. Zinc fasteners rely on galvanization, providing a sacrificial coating that corrodes first to shield the base metal but tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to moisture and chemicals. In marine or industrial applications where long-term durability is critical, stainless steel fasteners significantly outperform zinc-coated options in resisting corrosion and maintaining structural integrity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Stainless steel fasteners exhibit superior strength and corrosion resistance, maintaining structural integrity in harsh environments. Zinc fasteners provide moderate strength but excel in cost-effectiveness and corrosion protection through galvanization. Choosing stainless steel offers enhanced durability for high-stress applications, while zinc suits less demanding settings with budget constraints.
Cost Analysis: Stainless Steel vs Zinc Fasteners
Stainless steel fasteners typically exhibit higher upfront costs compared to zinc fasteners due to their alloy composition and corrosion resistance properties. Zinc fasteners offer a more economical option, especially in applications requiring lower corrosion resistance, reducing initial material expenses. Long-term cost analysis also favors stainless steel fasteners in harsh environments as their durability minimizes replacement and maintenance costs, offsetting the higher purchase price.
Applications and Industry Preferences
Stainless steel fasteners are preferred in marine, chemical, and food processing industries due to their superior corrosion resistance and strength under extreme conditions. Zinc-coated fasteners are commonly used in construction, automotive, and electrical applications where cost-effectiveness and moderate corrosion protection are required. Industry preferences lean towards stainless steel for long-term durability and zinc for economies in less demanding environments.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Stainless steel fasteners offer superior corrosion resistance, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and ensuring a smoother installation process without the risk of rust-related seizing. Zinc-coated fasteners provide a cost-effective solution with moderate corrosion protection but may require more regular maintenance to prevent degradation in harsh environments. Ease of installation is enhanced with stainless steel due to its strength and durability, minimizing issues like stripping or breaking during fastening.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Stainless steel fasteners exhibit superior corrosion resistance and a longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements and thus minimizing waste. Zinc fasteners often require coatings that can leach harmful substances into the environment, whereas stainless steel is more recyclable and has a lower overall environmental footprint. The sustainable choice heavily depends on application durability and end-of-life recycling potential, with stainless steel generally favored for eco-friendly construction projects.
Choosing the Right Fastener Material
Choosing the right fastener material depends on environmental conditions and mechanical needs, where stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and strength for harsh or marine environments. Zinc-coated fasteners provide a cost-effective solution with adequate corrosion protection in less demanding applications, thanks to their sacrificial zinc layer preventing rust. Assessing factors like load requirements, exposure to moisture, and budget constraints ensures optimal performance and longevity for the fastener application.
Infographic: Stainless steel vs Zinc for Fastener
 azmater.com
azmater.com