Silver batteries offer higher conductivity and longer lifespan compared to zinc batteries, which are more cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Zinc batteries excel in lightweight applications with stable discharge rates, while silver batteries deliver superior performance in high-drain devices.
Table of Comparison
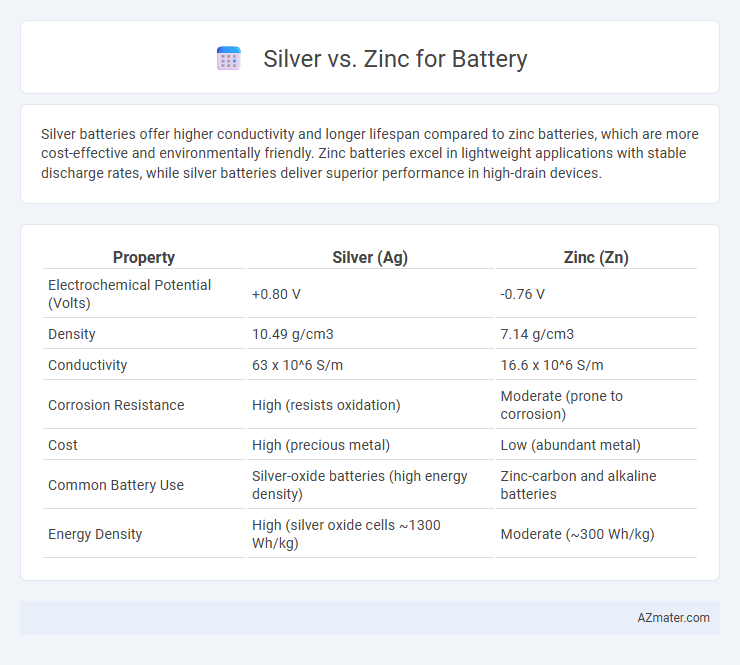
| Property | Silver (Ag) | Zinc (Zn) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical Potential (Volts) | +0.80 V | -0.76 V |
| Density | 10.49 g/cm3 | 7.14 g/cm3 |
| Conductivity | 63 x 10^6 S/m | 16.6 x 10^6 S/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (resists oxidation) | Moderate (prone to corrosion) |
| Cost | High (precious metal) | Low (abundant metal) |
| Common Battery Use | Silver-oxide batteries (high energy density) | Zinc-carbon and alkaline batteries |
| Energy Density | High (silver oxide cells ~1300 Wh/kg) | Moderate (~300 Wh/kg) |
Introduction to Silver and Zinc in Batteries
Silver and zinc serve distinct roles in battery technology due to their unique electrochemical properties. Silver, known for its high electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, is often used in silver-zinc batteries that deliver high energy density and long cycle life, making them ideal for aerospace and military applications. Zinc, prized for its abundance, low cost, and safety, is commonly employed in alkaline and zinc-air batteries, offering reliable performance for everyday portable electronics and renewable energy storage.
Key Chemical Properties: Silver vs Zinc
Silver exhibits higher electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to zinc, making it ideal for applications requiring stable and efficient electron flow. Zinc offers a lower electrochemical potential and greater abundance, leading to cost-effective and environmentally friendly battery components. The distinct redox potentials of silver (+0.80 V) and zinc (-0.76 V) significantly influence their voltage output and energy density in battery technologies.
Common Battery Types Using Silver and Zinc
Silver oxide batteries utilize silver oxide as the cathode and zinc as the anode, offering high energy density and stable voltage, commonly used in hearing aids and watches. Alkaline zinc-carbon batteries employ zinc as the anode and a manganese dioxide cathode, favored for low-cost, general-purpose applications such as remote controls and flashlights. Silver-zinc batteries combine silver oxide cathodes and zinc anodes, prized in aerospace and military devices for their superior energy-to-weight ratio and rechargeability.
Performance Comparison: Energy Density and Capacity
Silver batteries exhibit higher energy density than zinc batteries, offering superior capacity for long-lasting power applications. Zinc batteries provide a cost-effective alternative but typically have lower energy density, resulting in shorter battery life and less efficient storage. The silver's high conductivity enhances performance in high-drain devices, whereas zinc batteries are favored for disposable and low-drain uses.
Longevity and Cycle Life Differences
Silver batteries exhibit superior longevity and cycle life compared to zinc batteries due to silver's higher electrochemical stability and resistance to corrosion. Silver-based cells can sustain thousands of charge-discharge cycles with minimal capacity loss, whereas zinc batteries typically suffer from dendrite formation and faster degradation, reducing their effective lifespan. The enhanced cycle life of silver batteries makes them ideal for applications requiring reliable, long-term energy storage.
Cost Analysis: Silver vs Zinc Batteries
Silver batteries generally have higher upfront costs due to the premium price of silver, which significantly increases material expenses compared to zinc batteries. Zinc batteries offer a more cost-effective solution with lower raw material costs and simpler manufacturing processes, making them more attractive for large-scale or budget-sensitive applications. Despite the higher price, silver batteries provide superior conductivity and longevity, potentially balancing lifetime costs in high-performance or specialized uses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Silver batteries offer moderate environmental impact due to silver's limited abundance and energy-intensive mining processes, raising concerns about long-term sustainability. Zinc batteries are more environmentally sustainable, utilizing abundant, non-toxic zinc that is easier to recycle and poses lower ecological risks during extraction and disposal. The overall sustainability of zinc-based batteries makes them preferable for green energy applications and reducing carbon footprints.
Safety Considerations for Silver and Zinc Batteries
Silver batteries offer enhanced thermal stability and reduced risk of leakage due to their robust chemical composition, making them safer for high-performance applications. Zinc batteries exhibit excellent safety profiles with low toxicity and resistance to overcharging, minimizing hazards such as overheating and explosion. Both battery types provide reliable safety features, but zinc's environmental friendliness and abundance make it a preferred choice in consumer electronics.
Real-World Applications and Industry Use
Silver batteries offer superior conductivity and energy density, making them ideal for high-performance applications such as military equipment and aerospace technology. Zinc batteries are favored in large-scale energy storage and consumer electronics due to their cost-effectiveness and environmental friendliness. Industries increasingly adopt zinc-based batteries for grid storage solutions, while silver-based batteries remain niche in specialized, high-demand environments.
Choosing the Right Battery: Silver or Zinc?
Choosing the right battery between silver and zinc depends on application requirements such as energy density and cost. Silver batteries offer higher energy density, longer life cycles, and better stability, making them ideal for high-performance electronics and medical devices. Zinc batteries are more economical and environmentally friendly, suitable for low-drain devices and disposable applications where budget and sustainability are priorities.
Infographic: Silver vs Zinc for Battery
 azmater.com
azmater.com